The Fallen Angel 150 years later inspires a character from the Star Wars
Inferno inspires Rodin in 1900’s to make Thinking Man gazing into the center of hell.


49200 BC -43,500 BC
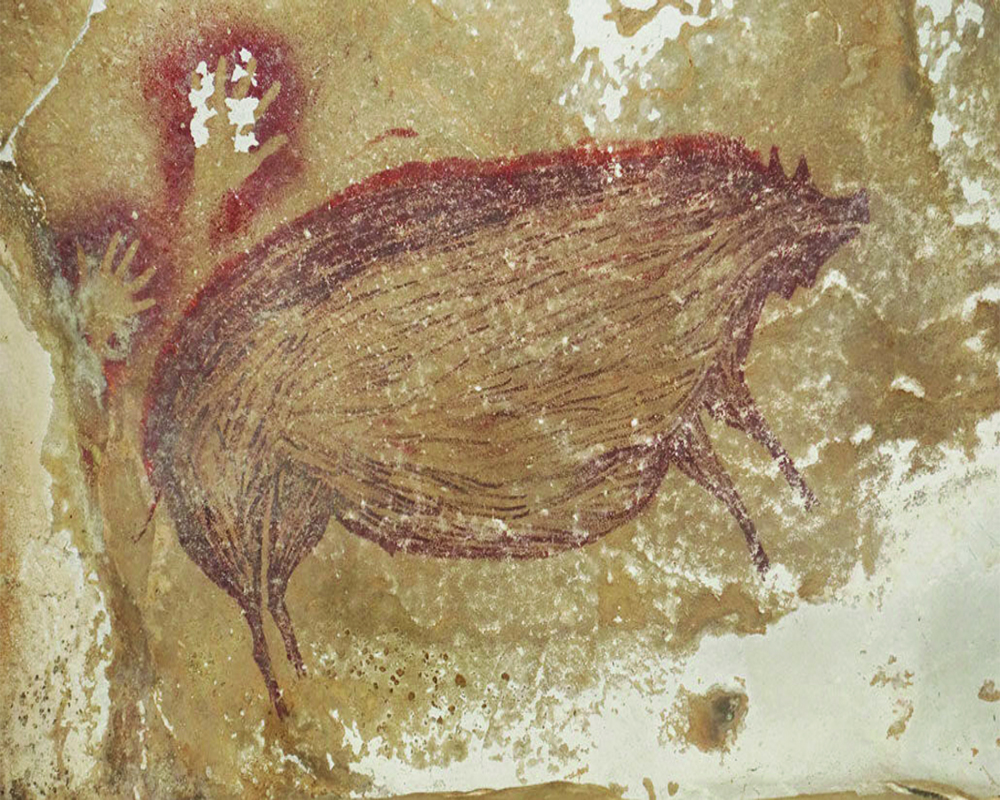
The oldest known
figurative painting
The oldest known figurative painting is a depiction of a wild pig found in a cave on the Indonesian island of Sulawesi, dating back at least 45,500 years, according to a 2019 report in Nature.


Castoroides (Giant Beaver)

Neanderthals went extinct around 40,000 years ago
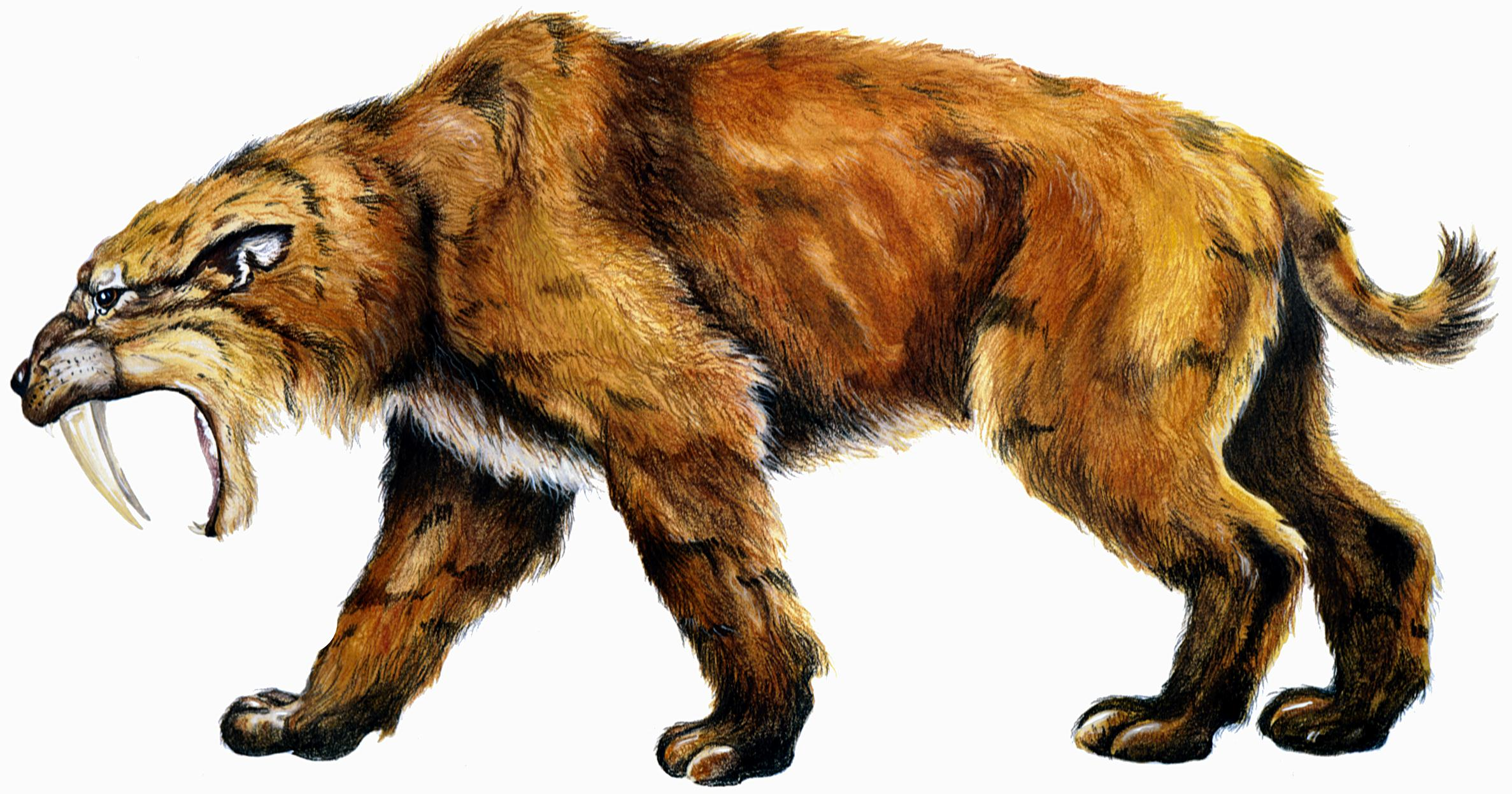

saber toothed cat
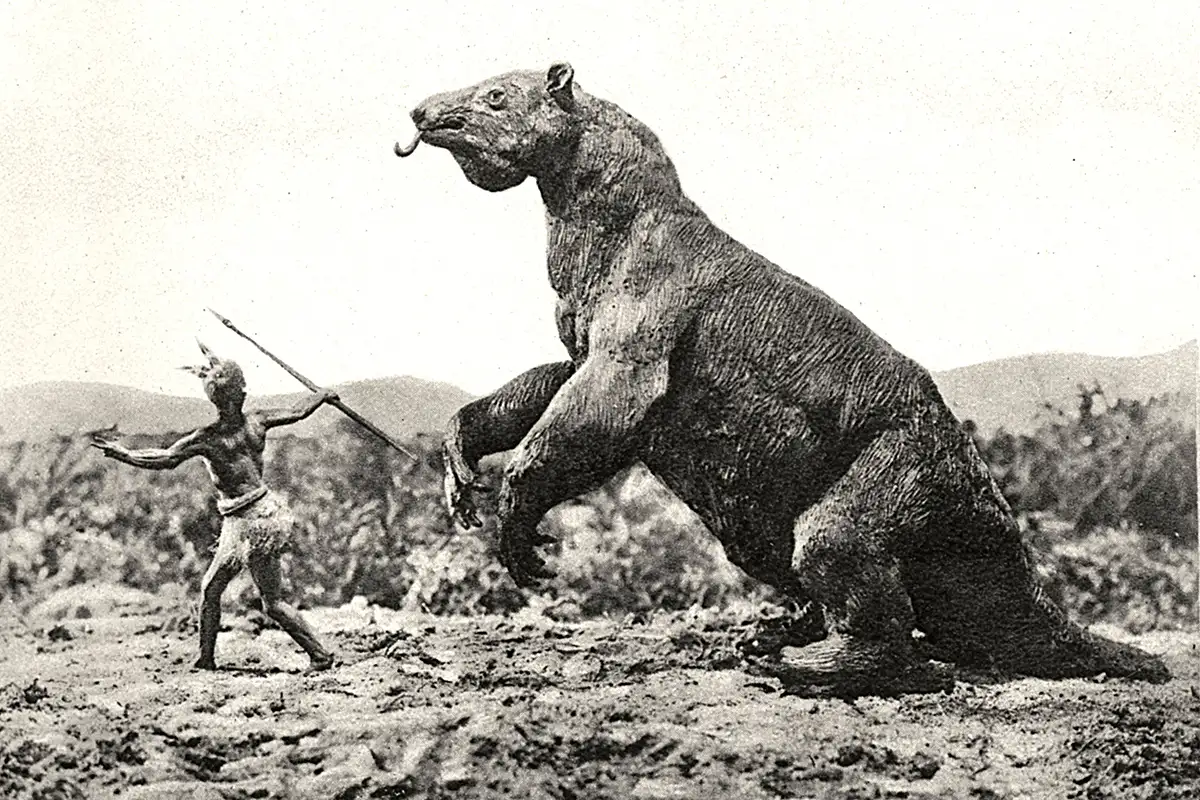

Giant Ground Sloth

33,000 - 38000 BC
The Lion Man
The Lion Man, also known as Löwenmensch, is a prehistoric ivory sculpture found in Germany, considered one of the oldest known examples of figurative art and the oldest confirmed statue. Dating back 35,000 to 40,000 years, it combines human and lion features, suggesting a hybrid creature and possibly a shamanistic figure used in rituals.
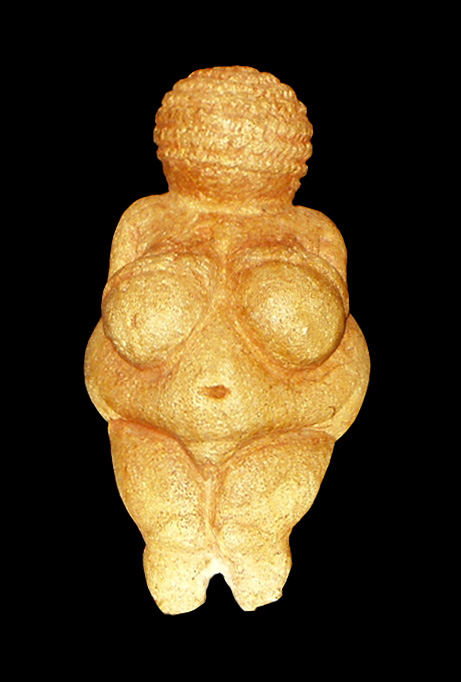
33,000 BC
the Venus of Hohle Fels
This figurine was later called the Venus of Hohle Fels and can be dated to at least 35,000 years ago. It represents the earliest known sculpture of this type and the earliest known work of figurative art.

woolly mammoth
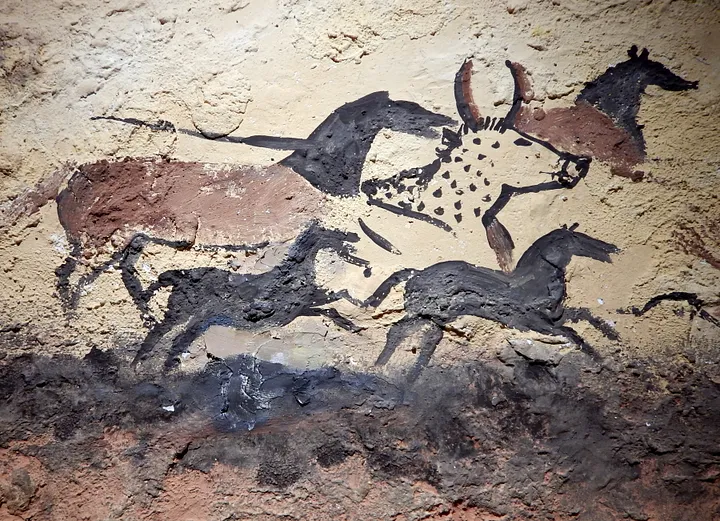

17,000 BC
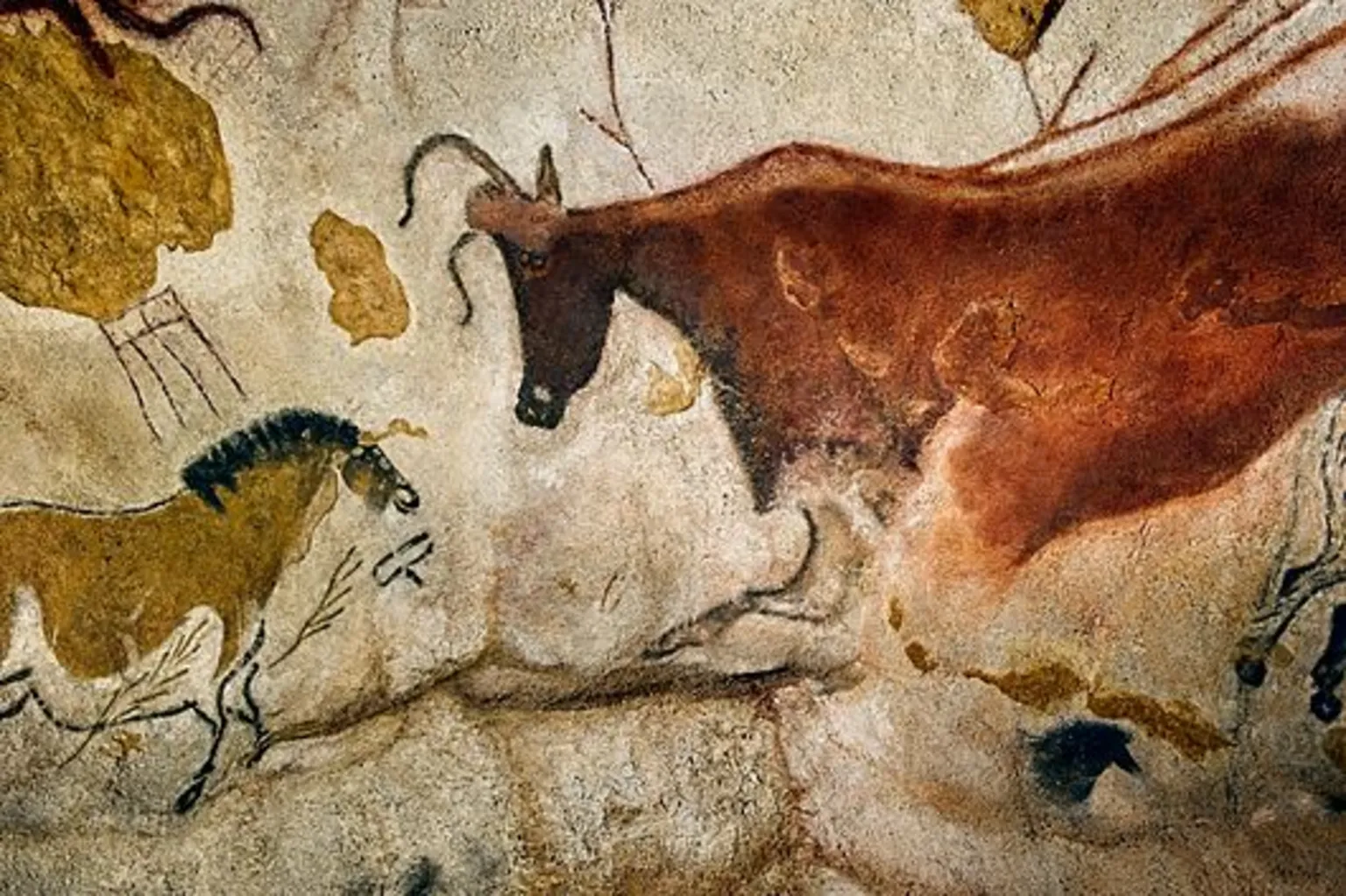
The Lascaux cave paintings
The Lascaux cave paintings are a renowned series of prehistoric artworks found in southwestern France, estimated to be around 17,000 years old. These paintings, primarily featuring animals like horses, bison, and deer, are considered among the finest examples of Upper Paleolithic art. Discovered in 1940, the cave contains over 600 paintings and nearly 1,500 engravings, showcasing the artistic skill of early humans.

1,3000 BC
청주 소로리볍씨
세계적인 고고학 개론서 ‘현대 고고학의 이해(Archaeology)’에 한국이 쌀의 기원지로 명시돼 있어 눈길을 끌고 있다.
4년마다 개정판을 발간되는 이 책은 2004년 이전에는 BC 9000년쯤 중국 후난성에서 출토된 볍씨를 쌀의 기원으로 기술했지만 최신 개정판에서는 쌀의 기원지를 한국으로, 연대는 BC 1만3000년 전으로 바꿨다.
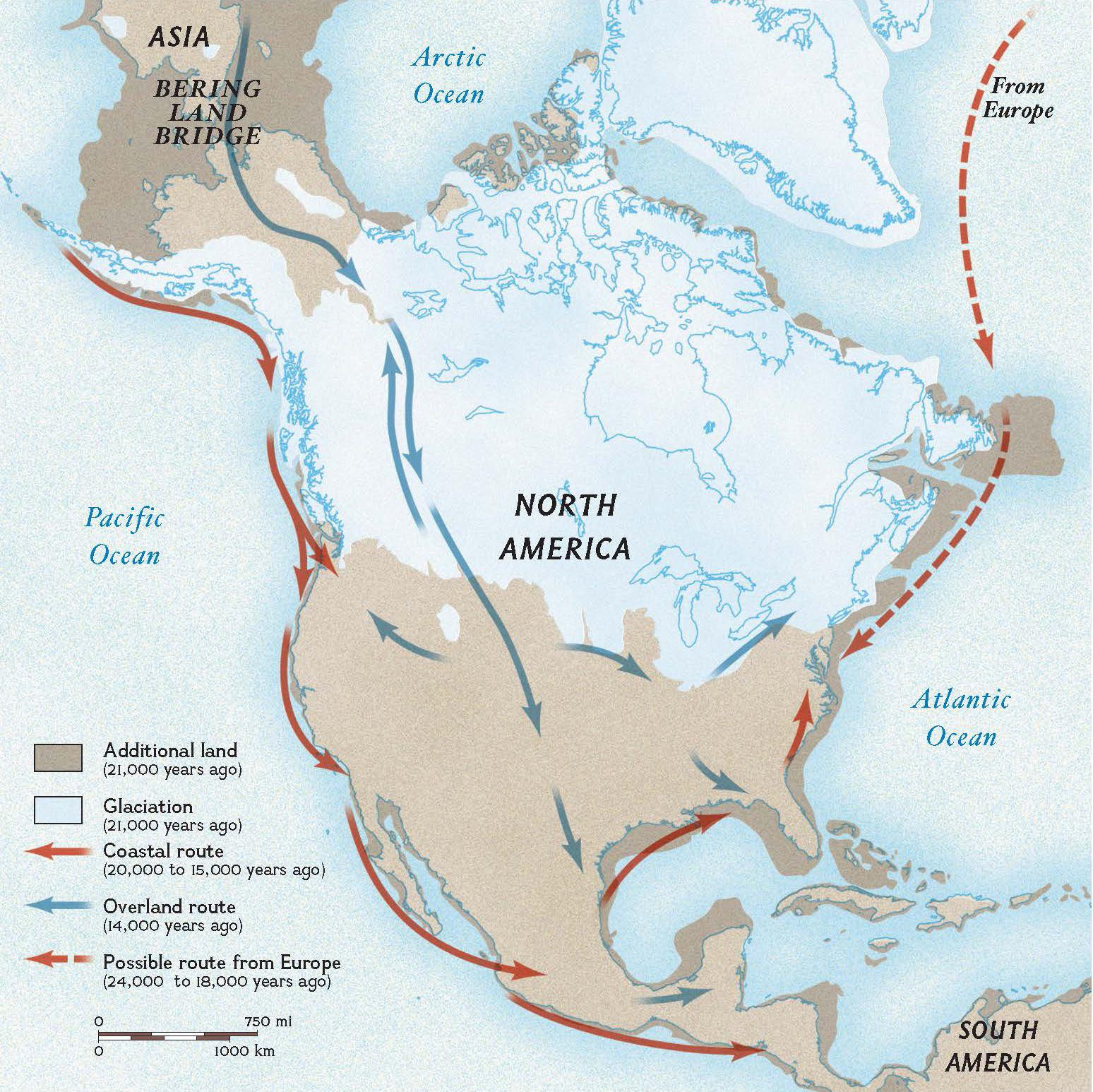
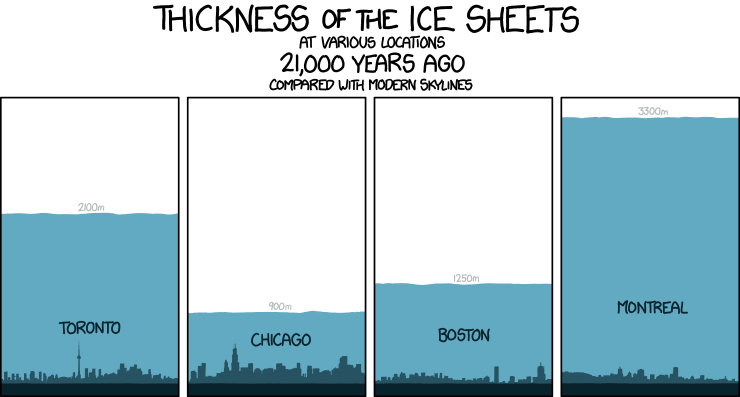
15,000 - 20,000 years ago
Into the Americas
Homo sapiens are believed to have crossed into the Americas during the last glacial period, specifically between 15,000 and 20,000 years ago. This migration likely occurred via the Bering Land Bridge, a now-submerged landmass connecting Siberia and Alaska. While the exact timing is still debated, evidence suggests humans were established in the Americas by at least 14,000 to 15,000 years ago.

11,000 BC
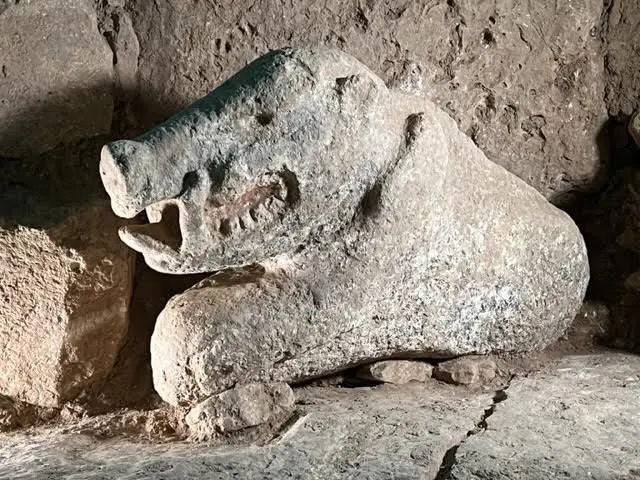
Guebekli Tepe
Göbekli Tepe is a Neolithic archaeological site in Upper Mesopotamia in modern-day Turkey. The settlement was inhabited from around 9500 BCE to at least 8000 BCE, during the Pre-Pottery Neolithic.
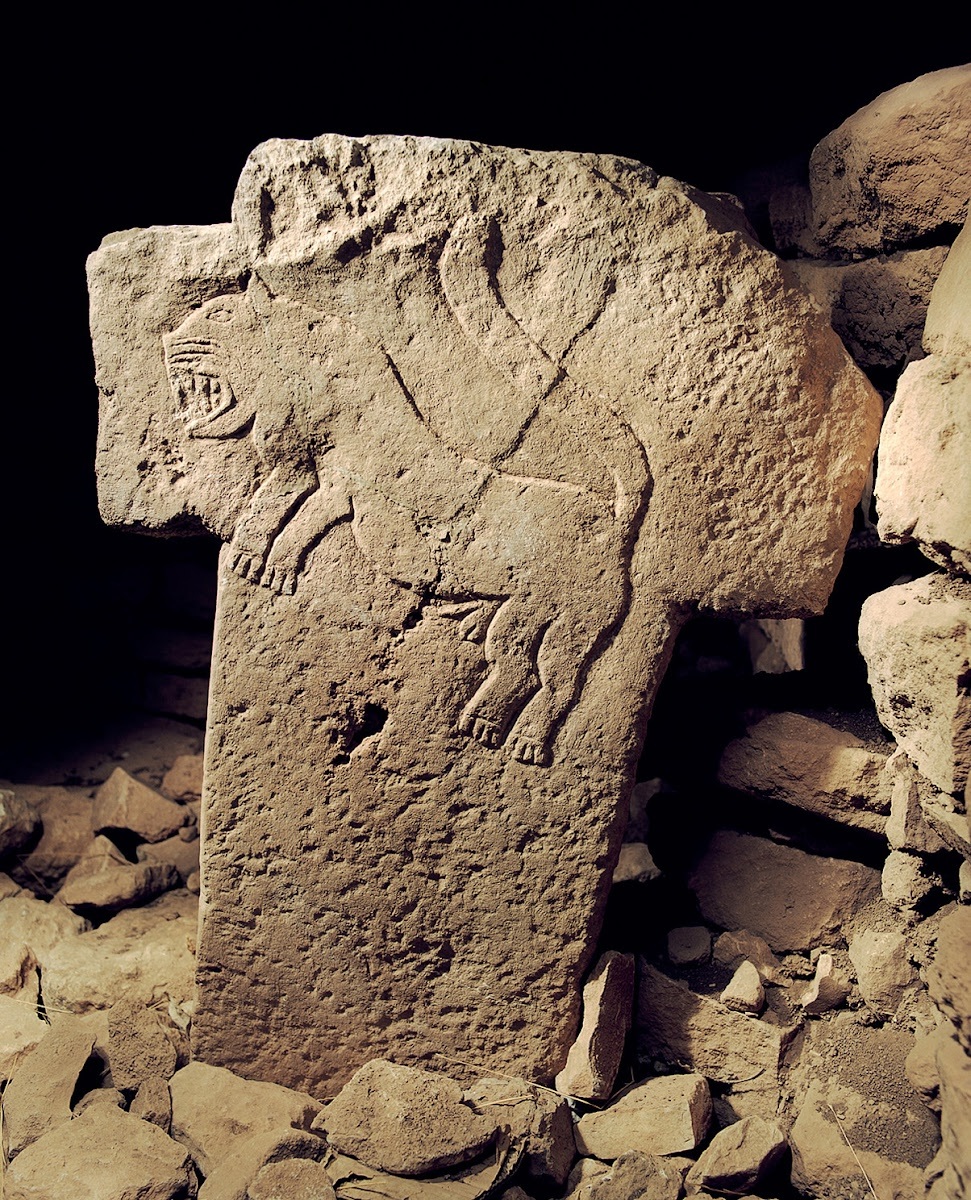
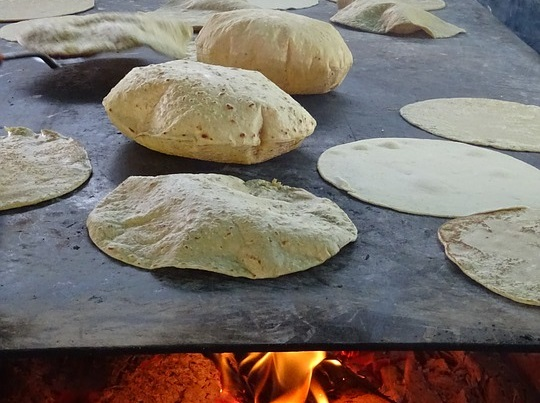




10,000 BC
The earliest tortillas
The earliest tortillas, made from nixtamalized maize, are believed to have originated around 10,000 BC in Mesoamerica, coinciding with the domestication of corn. These flatbreads were a staple in the diets of early Mayan and Aztec civilizations and were used in various ways, including as a base for other foods or as a utensil to eat with.
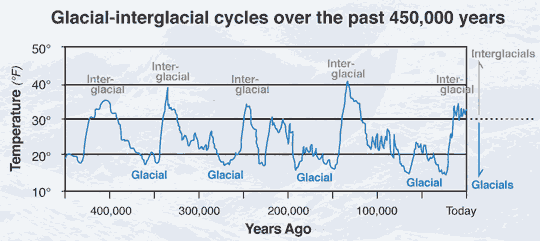
9,700 BC
End of Ice Age
The most recent ice age, also known as the Pleistocene Epoch, began about 2.6 million years ago and ended around 11,700 years ago. We are currently in an interglacial period, which is a warmer phase within the larger ice age. The last glacial period, which corresponds to the peak of the most recent ice age, occurred roughly between 115,000 and 11,700 years ago.
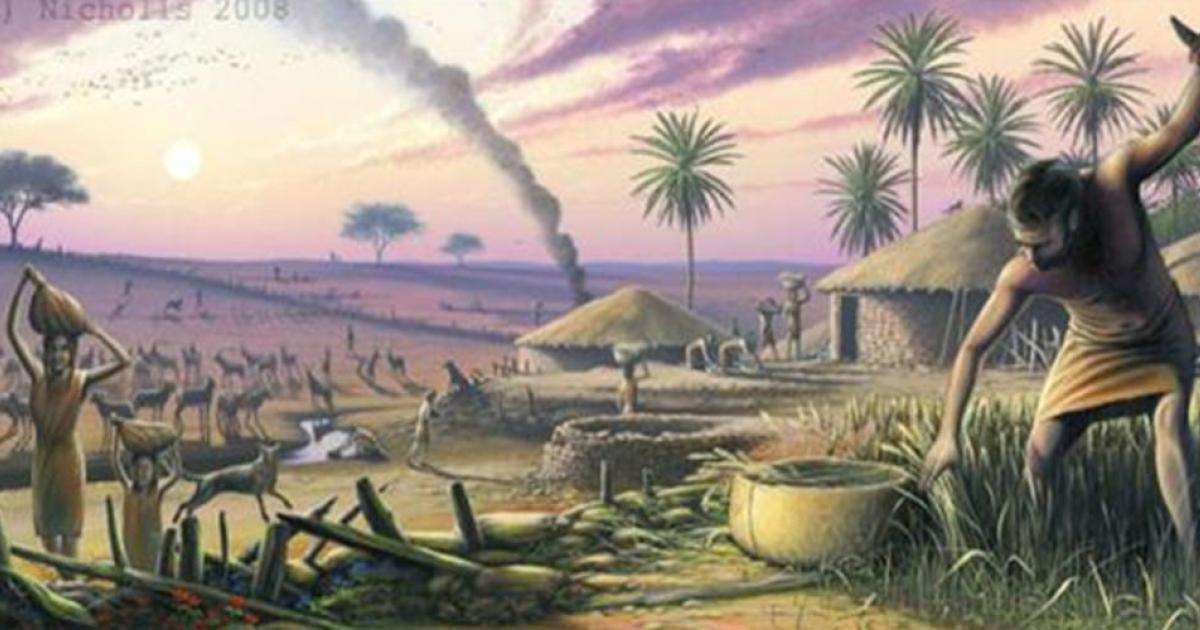

9,700 BC
The earliest evidence of farming
The earliest evidence of farming dates back roughly 11,700 years ago, coinciding with the end of the last Ice Age. While agriculture likely developed independently in various regions, the Fertile Crescent in the Middle East is a key area with significant early archaeological findings.
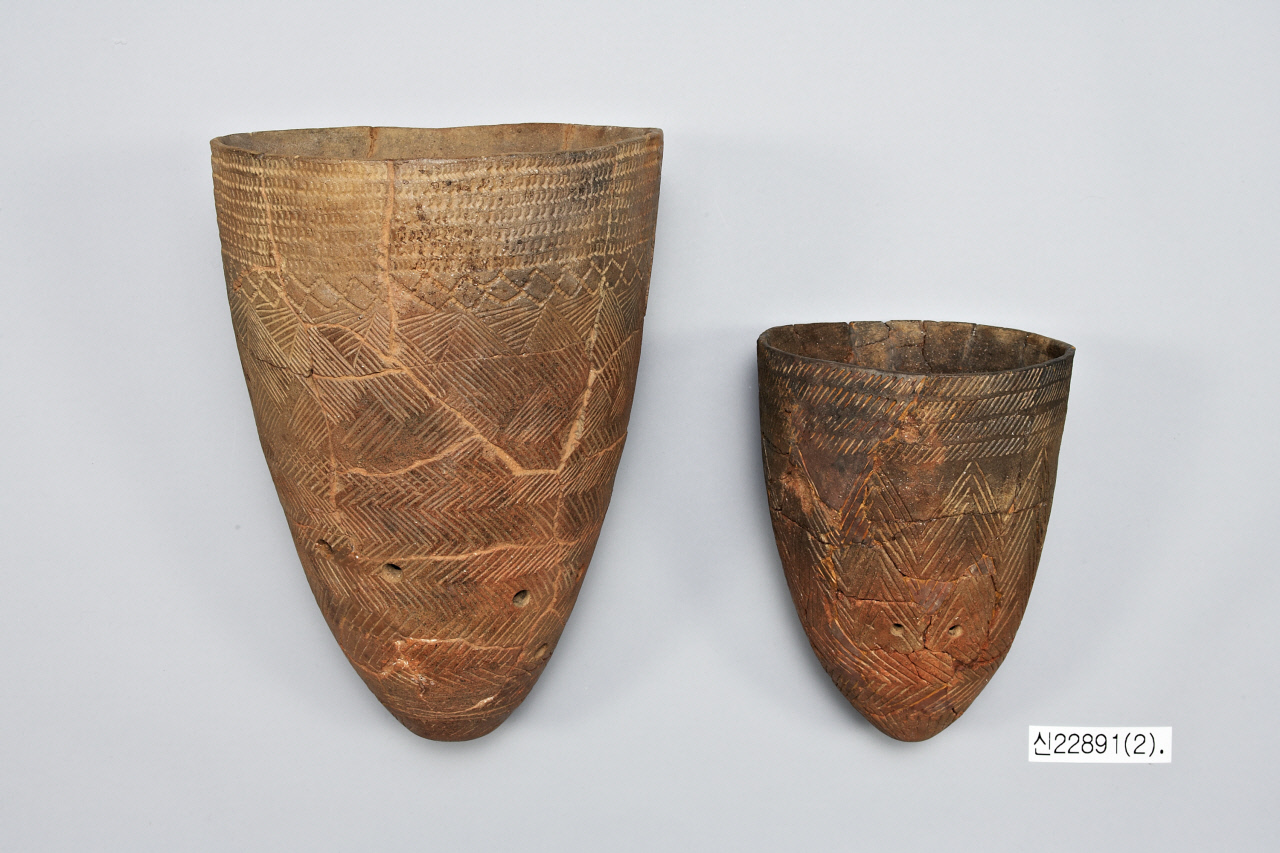

8,200 BC
comb-patterned pottery
The comb-pattern pottery was a type of Neolithic earthenware used from around 8,200 B.C. to 1,500 B.C. In the Korean Peninsula, it first appeared around 4,000 B.C. in the central-western region and spread throughout the entire peninsula by about 3,500 B.C.
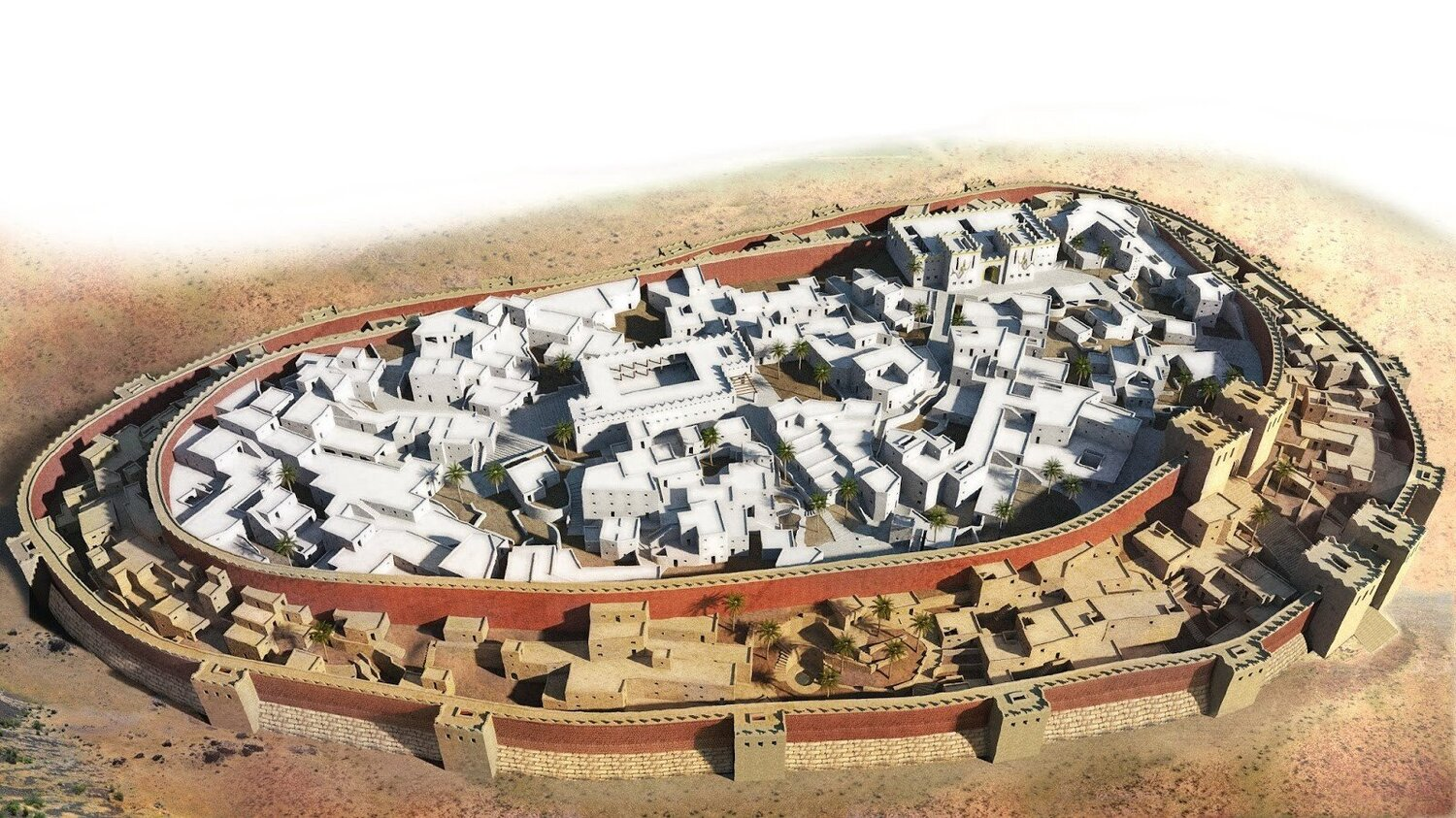

9000-8000 BC
Jericho
Around 8000 BCE, a substantial stone wall and ditch were built around the settlement, along with a significant stone tower, indicating a level of social organization and possibly defense or flood control.
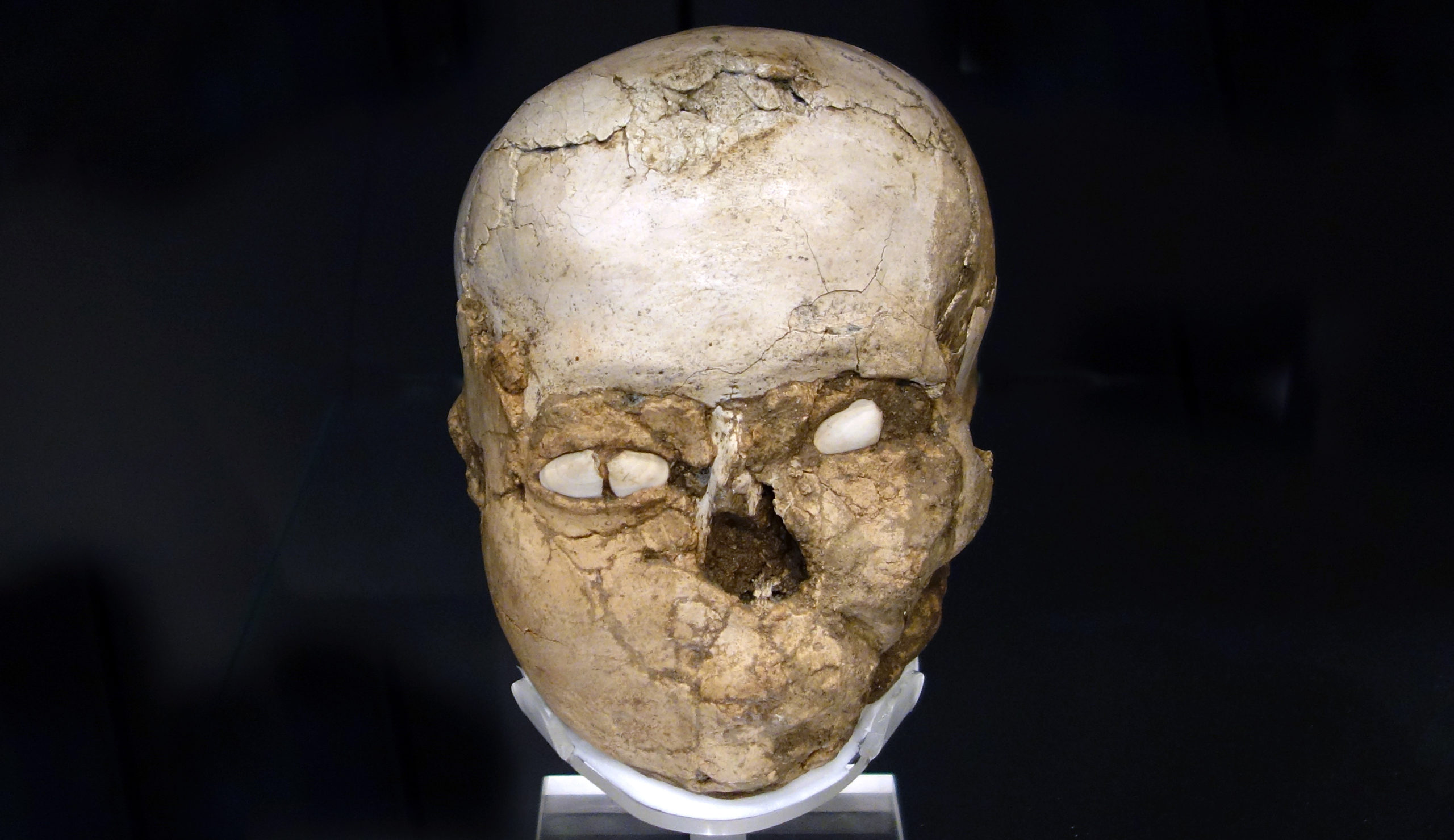
7200 BC
Plastered human skull
Plastered human skull with shell eyes from Jericho, Pre-Pottery Neolithic B, c. 7200 B.C.E. (The British Museum, London; photo: Steven Zucker, CC BY-NC-SA 2.0)
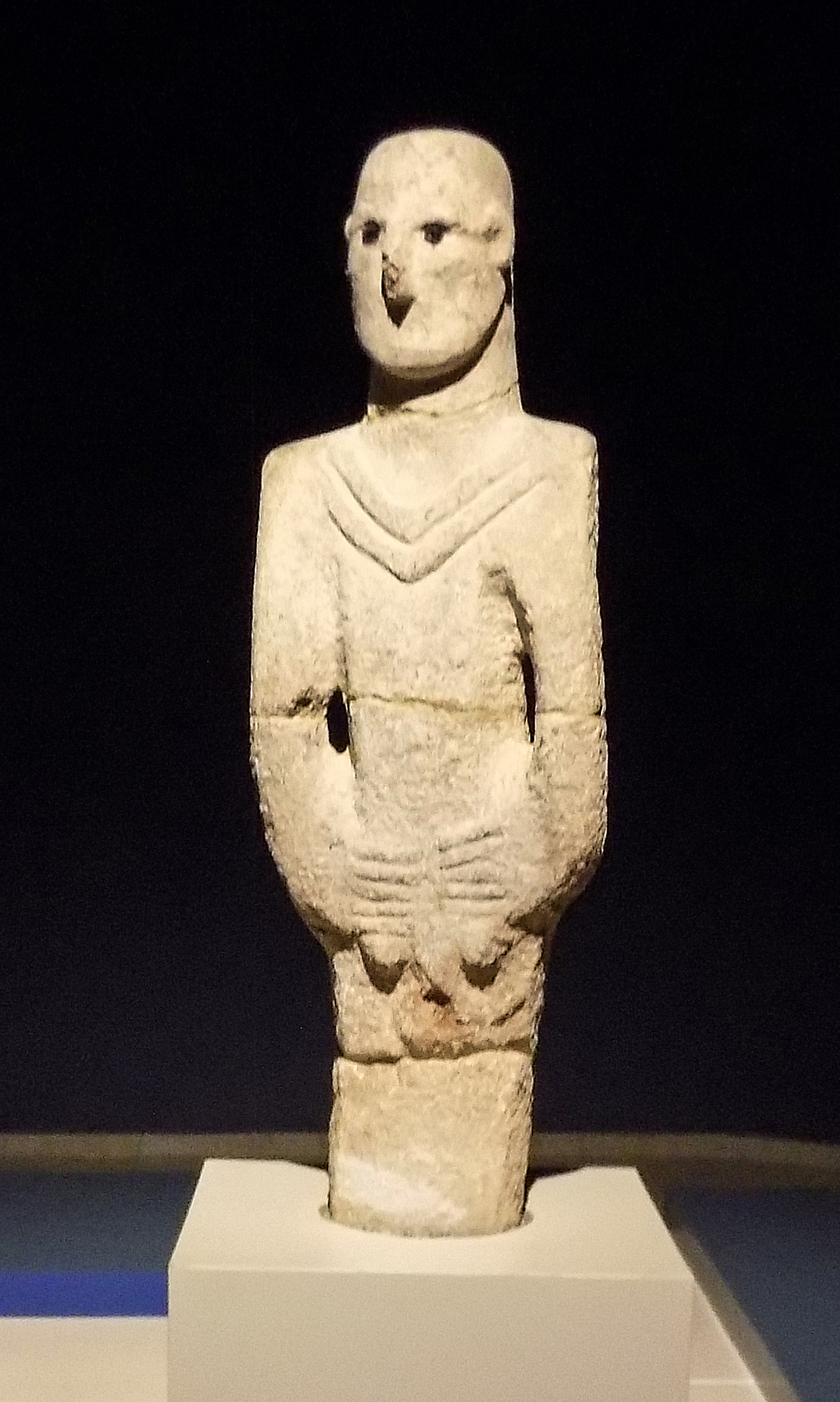

9,000 BC
The Urfa Man
The Urfa Man, from Upper Mesopotamia circa 9000 BC, the "oldest naturalistic life-sized sculpture of a human". Şanlıurfa Museum.
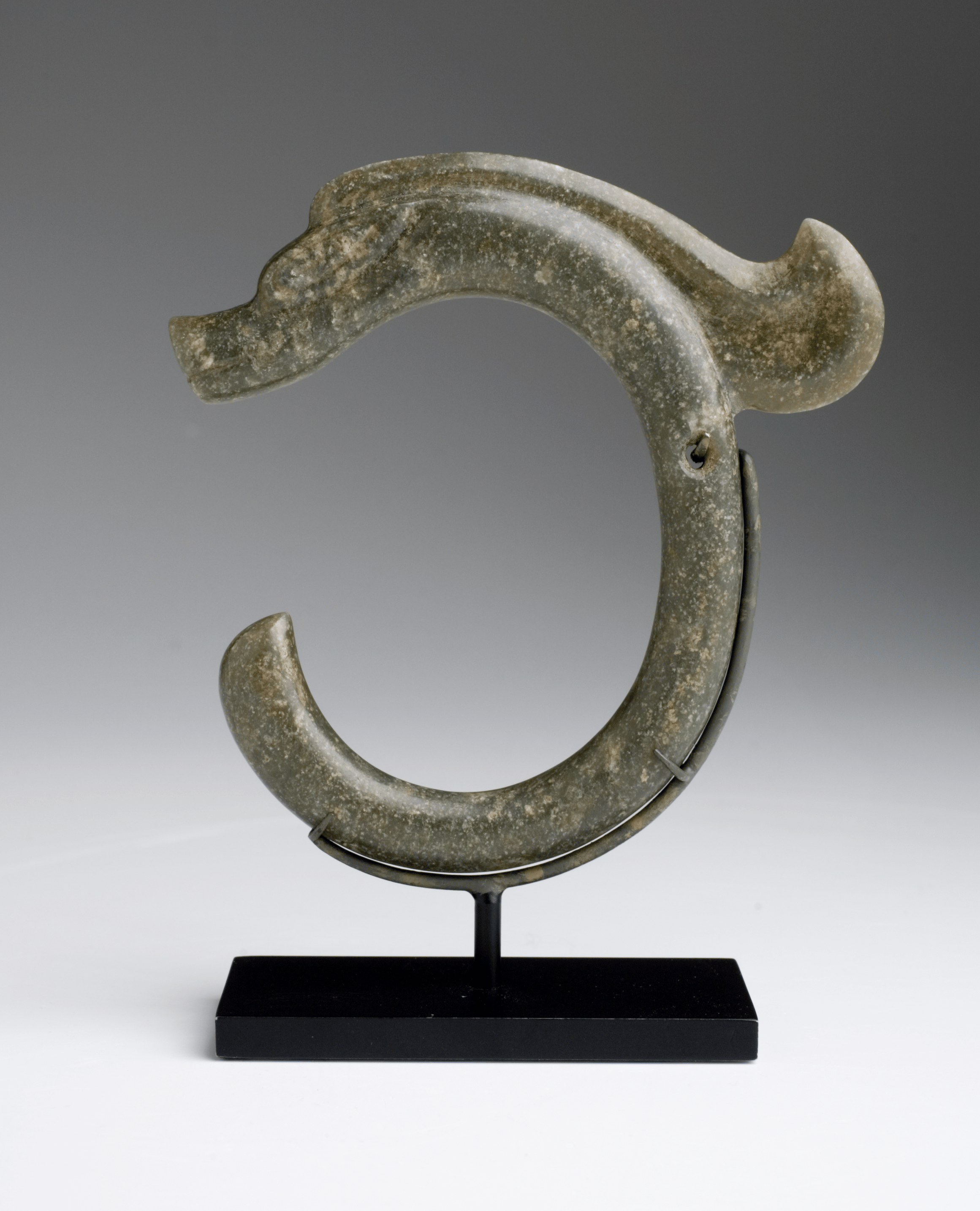

6000-5000 BC
Jade Dragon
A jade dragon pendant from the Neolithic Hongshan culture (6000-5000 BC), a significant example of jade carving from that period.
5000 BC
Jade Road (later becomes Silk Road)
The "Jade Road," referring to early trade routes focused on jade, predates the Silk Road and is believed to have existed as early as the Neolithic Period, potentially 7,000 years ago. These routes saw jade, considered sacred by the Chinese, traded from regions like Khotan (in present-day Xinjiang) to China, and also involved maritime trade in Southeast Asia. The term "Jade Road" is more common in Chinese scholarship than in English literature.
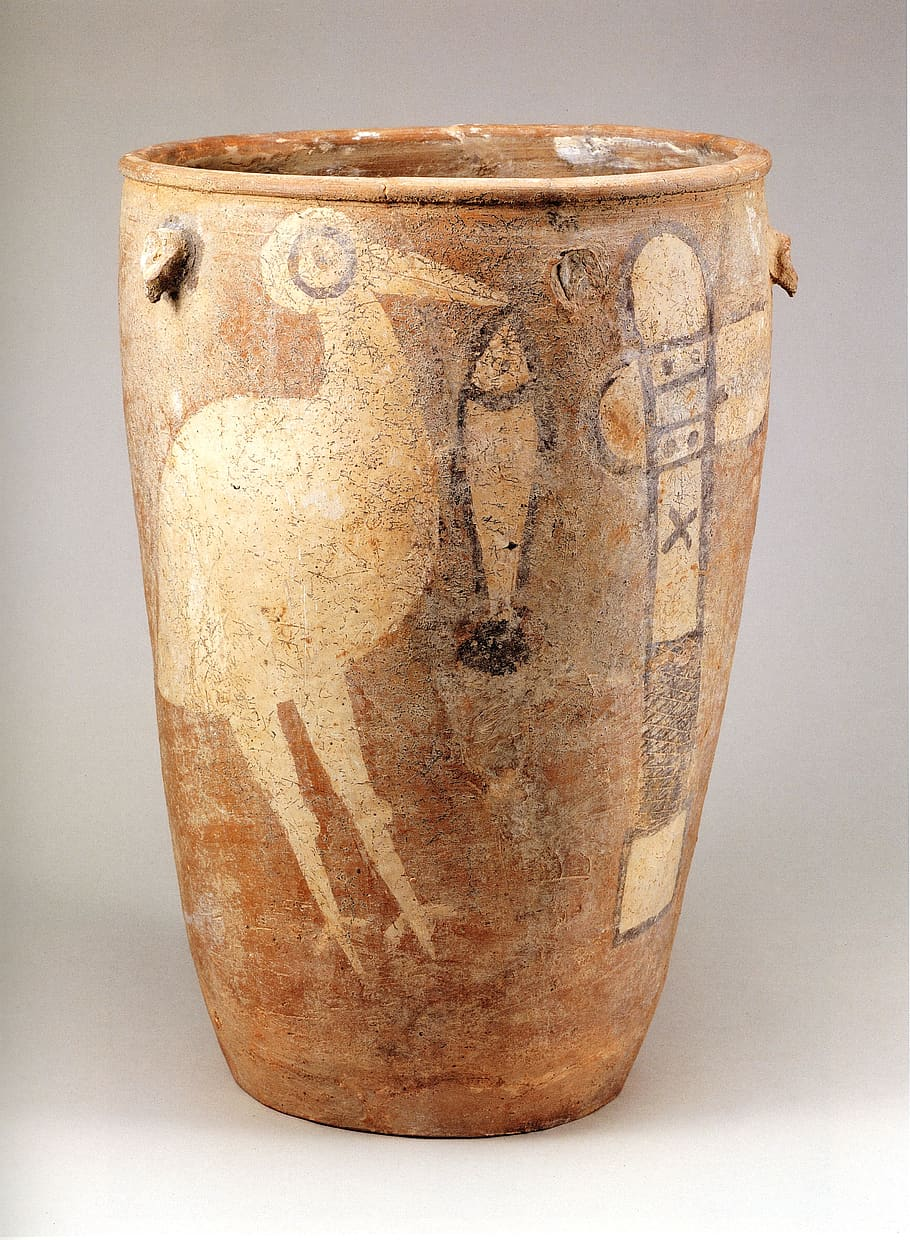

5000-
3000 BC
Jar with Stork, Fish,
and Stone Axe Decoration
A painted pottery jar from the Neolithic Yangshao culture (5000-3000 BC), featuring a stork holding a fish and an axe, possibly a clan totem.

3500 BC
Wheel
The wheel is believed to have been invented around 3500 BCE, during the Bronze Age, with the earliest evidence found in Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq). It's considered one of the most significant inventions in human history, impacting various aspects of life from transportation to pottery.
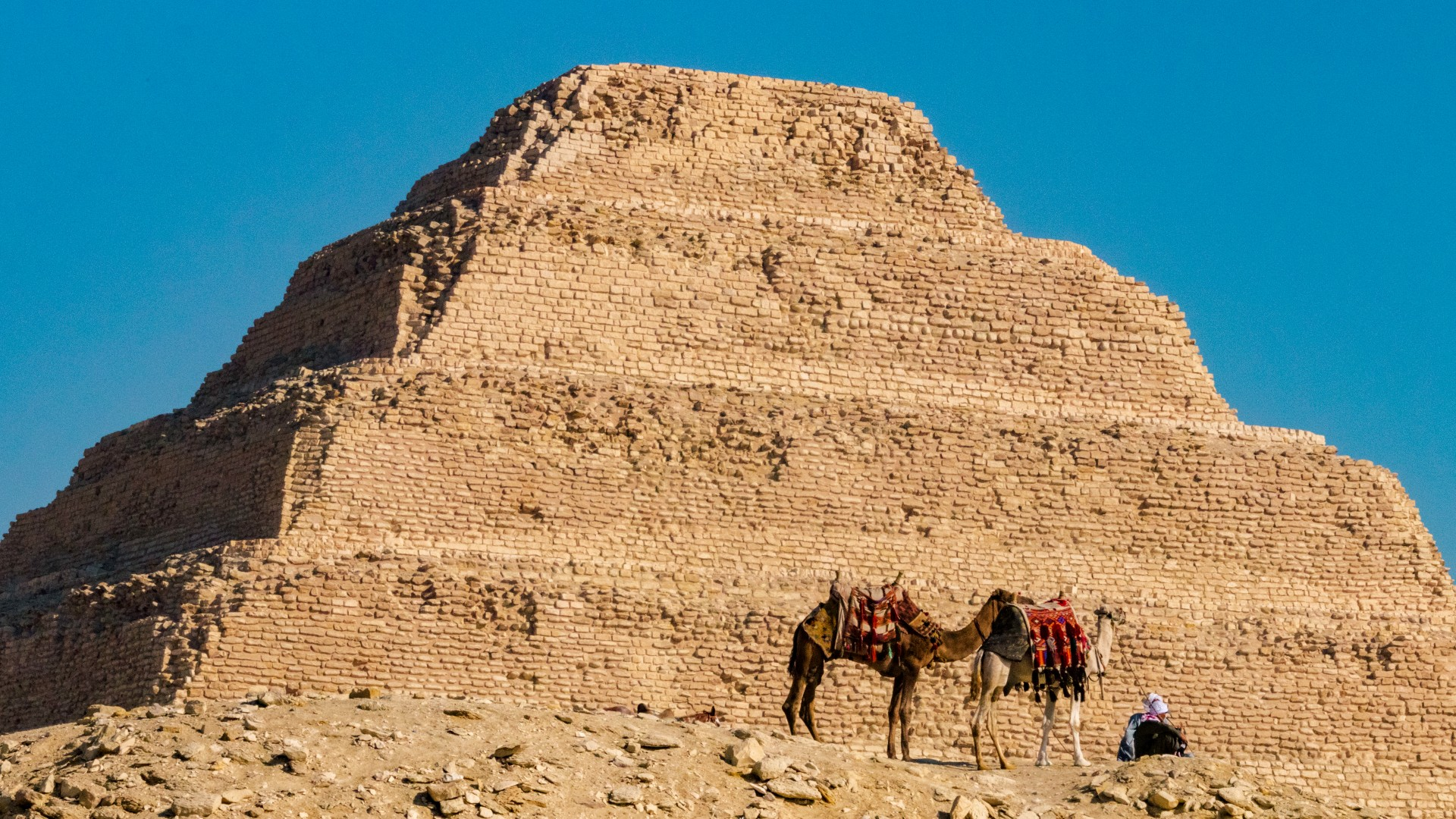

2670-2650 BC
The Pyramid of Djoser
The Pyramid of Djoser, located at Saqqara, Egypt, is widely considered the oldest pyramid in the world. It was built during the Third Dynasty of Egypt, around 2670-2650 BC, by the architect Imhotep for Pharaoh Djoser. While some claim the Gunung Padang site in Indonesia may be older, this theory is not widely accepted within the scientific community.

2600 BC
Great Pyramid of Giza
Great Pyramid of Giza, also known as the Pyramid of Khufu or the Pyramid of Cheops.
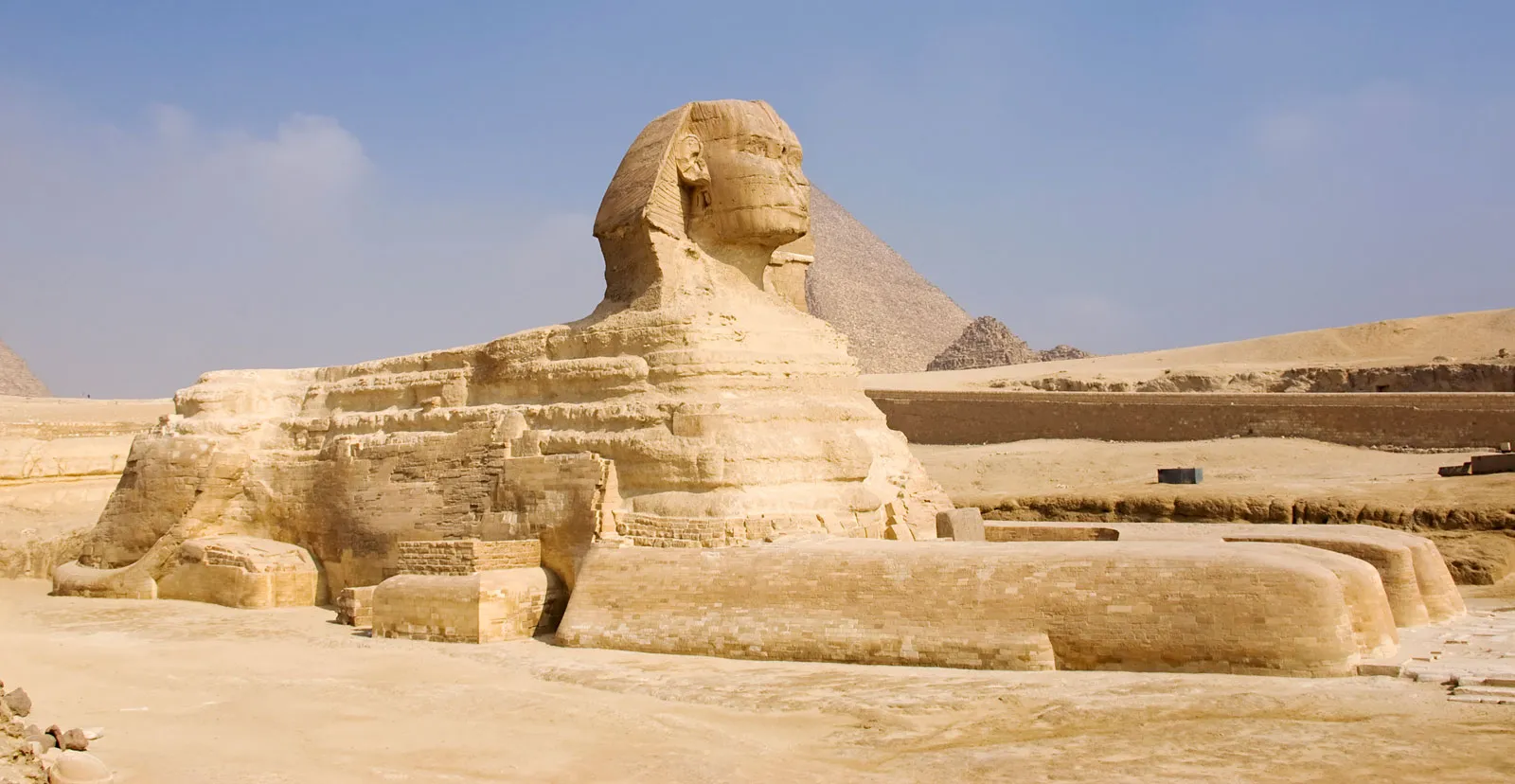

around 2500 BC
Great Sphinx of Giza
--

2100 BC
Ziggurat
Ziggurats, the massive stepped pyramid structures, were primarily built during the Bronze Age, with the earliest examples dating back to around 2100 BCE. These structures, often found in ancient Mesopotamia, served as temples and were dedicated to various deities. The Ziggurat of Ur, for instance, was built during the Ur III Dynasty (around 2100 BCE) and dedicated to the moon god Nanna.

2500 BC
Golden helmet of
Meskalamdug
Golden helmet of Meskalamdug (replica), possible founder of the First Dynasty of Ur, 26th century BC
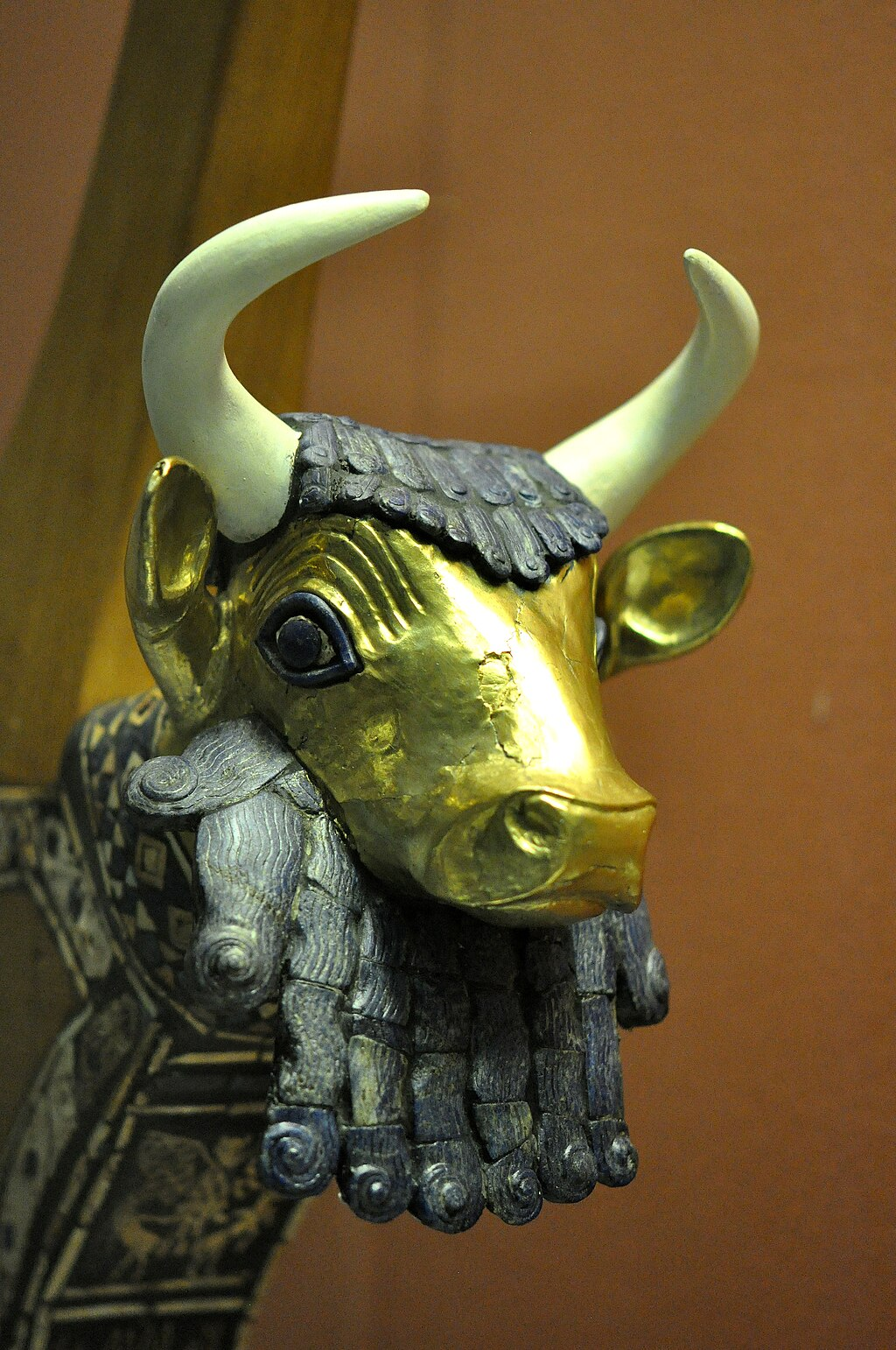

2500 BC
--
This lyre was found in the tomb of queen Pu-Abi. The lapis lazuli, shell, red limestone decoration, and the head of the bull are original. The bull's head is covered with gold. The eyes are lapis lazuli and shell. The beard and hair are lapis lazuli. A lyre of the same type is shown on the Standard of Ur. From grave PG 800 at the Royal Cemetery of Ur, southern Mesopotamia, Iraq. Early dynastic period, circa 2500 BCE. The British Museum, London.
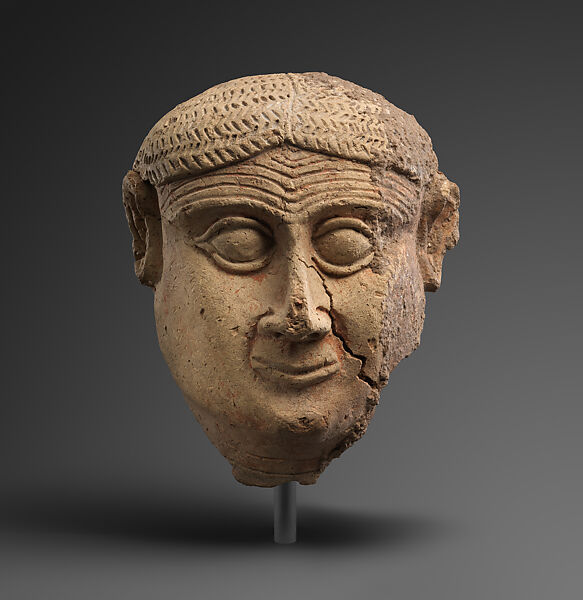

2000–1600 BCE
Head of a male (Babylon)
This head, broken at the neck, depicts a beardless male figure. The male is in an attentive pose: his forehead is furrowed, his eyes are large and heavily rimmed, his nostrils appear to be flared, and his ears are raised and protrude from the sides of his head.

2000 BC
The oldest known noodles
The oldest known noodles were discovered in China, dating back approximately 4,000 years. These ancient noodles were found at an archaeological site in northwestern China, near the Yellow River. The noodles were discovered in an overturned, sealed bowl at the Lajia archaeological site. This discovery predates previous understandings of noodle origins and suggests that noodles were consumed in China much earlier than previously documented.
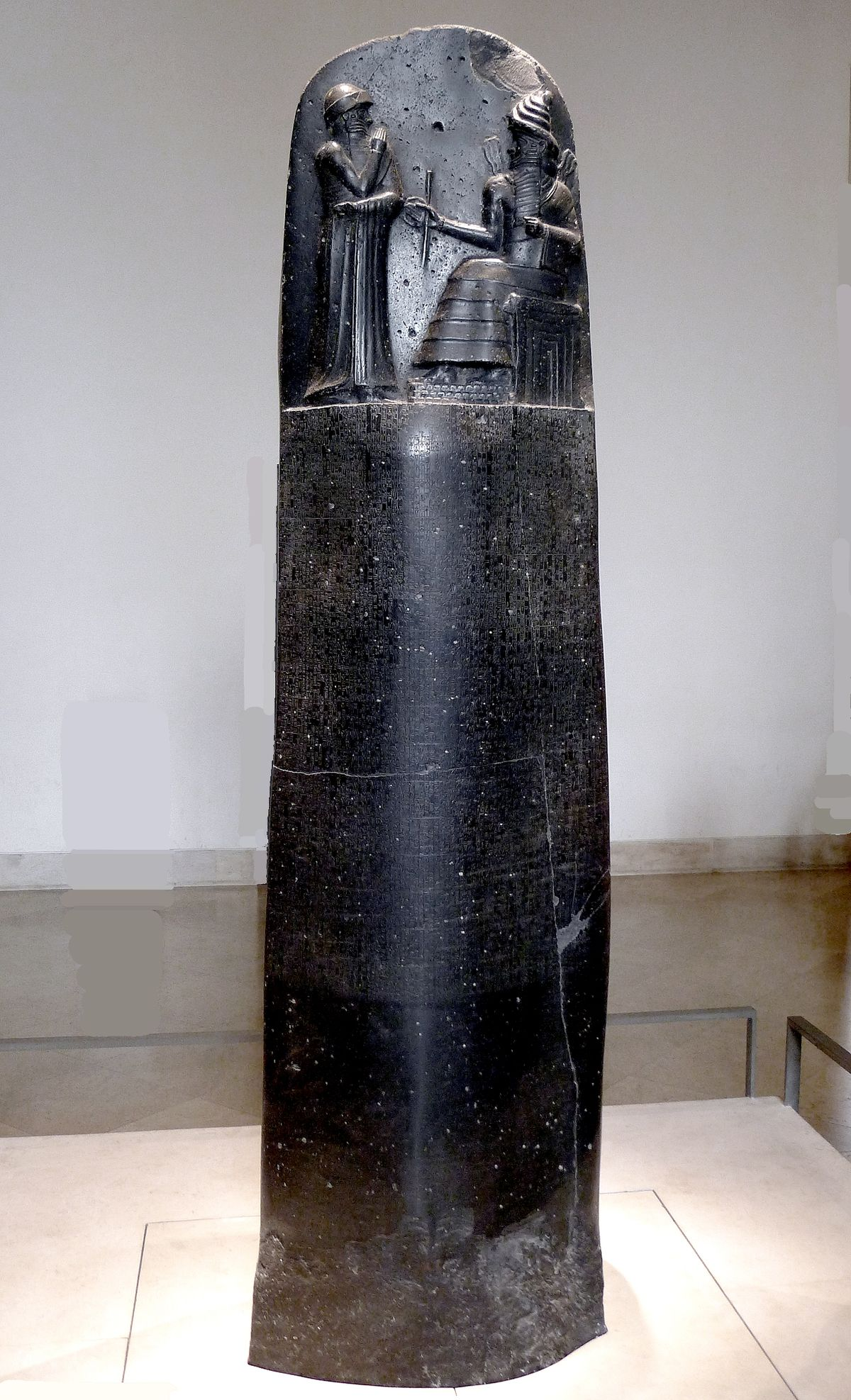

1755–1750 BC
Code of Hammurabi
The Code of Hammurabi is a well-preserved Babylonian law code from around 1754 BC, composed of 282 laws on a stone stele. It's one of the oldest and most complete surviving legal codes, offering insights into Mesopotamian society and legal principles. The code covers various aspects of life, including criminal law, civil law, property rights, and family matters, with punishments often based on social status and the nature of the offense.

1500-1200 BCE
hindu
--

1600 BC-1050 BC
Shang Dynasty artifacts
The Shang Dynasty artifacts primarily date back to the period between roughly 1600 and 1050 BCE. This era represents the first Chinese dynasty supported by both historical records and archaeological evidence.


800 BC
Iliad
Homer
--
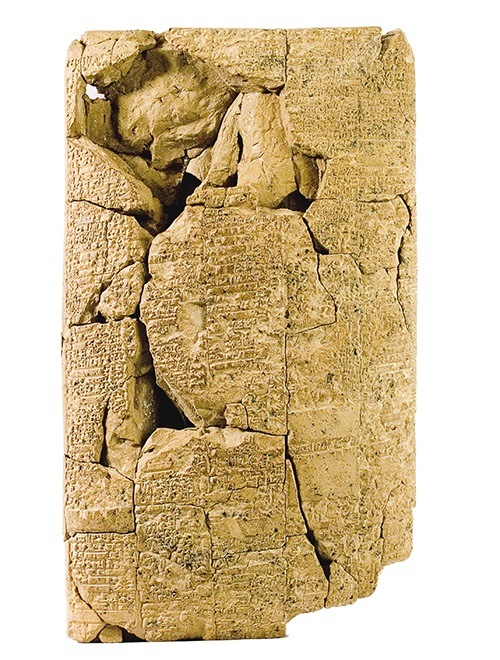

600 BC
The Ketef Hinnom scrolls
The Ketef Hinnom scrolls, two small silver amulets, are considered the oldest surviving texts from the Hebrew Bible. They contain a priestly blessing from the Book of Numbers(민수기) and are dated to around 600 BC. These scrolls predate the Dead Sea Scrolls and are the only surviving biblical writings from the First Temple Period.

600 BC
Zoroaster
--
--

February 15, 399 BC
Death of Socrates
--
--
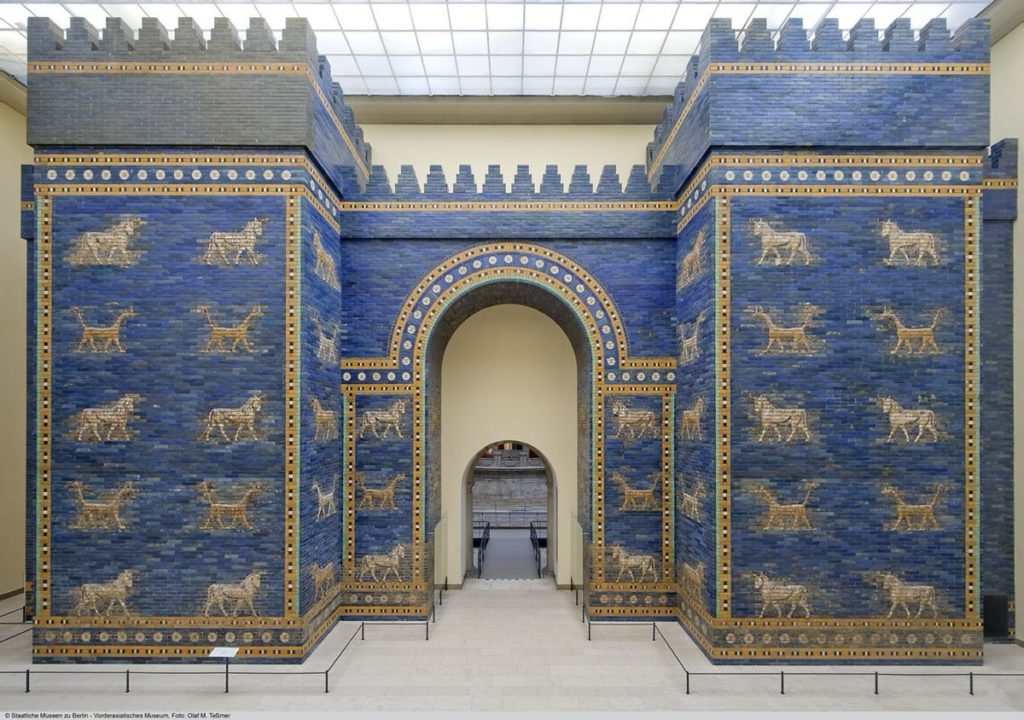

575 BCE
The Ishtar Gate
--
The Ishtar Gate, a grand entrance to the city of Babylon, was built around 575 BCE by King Nebuchadnezzar II. It served as the eighth gate to the inner city and was a part of the processional way leading into the heart of Babylon. The gate is famous for its vibrant blue glazed bricks and relief sculptures of animals, including lions, dragons, and aurochs.

600 BC
Hanging Gardens of Babylon
--
The Hanging Gardens of Babylon are believed to have been constructed around 600 BCE, specifically during the reign of King Nebuchadnezzar II. While historical accounts suggest they existed, archaeological evidence to definitively prove their existence or location has not been found.

380 BC
The Republic
Plato
--
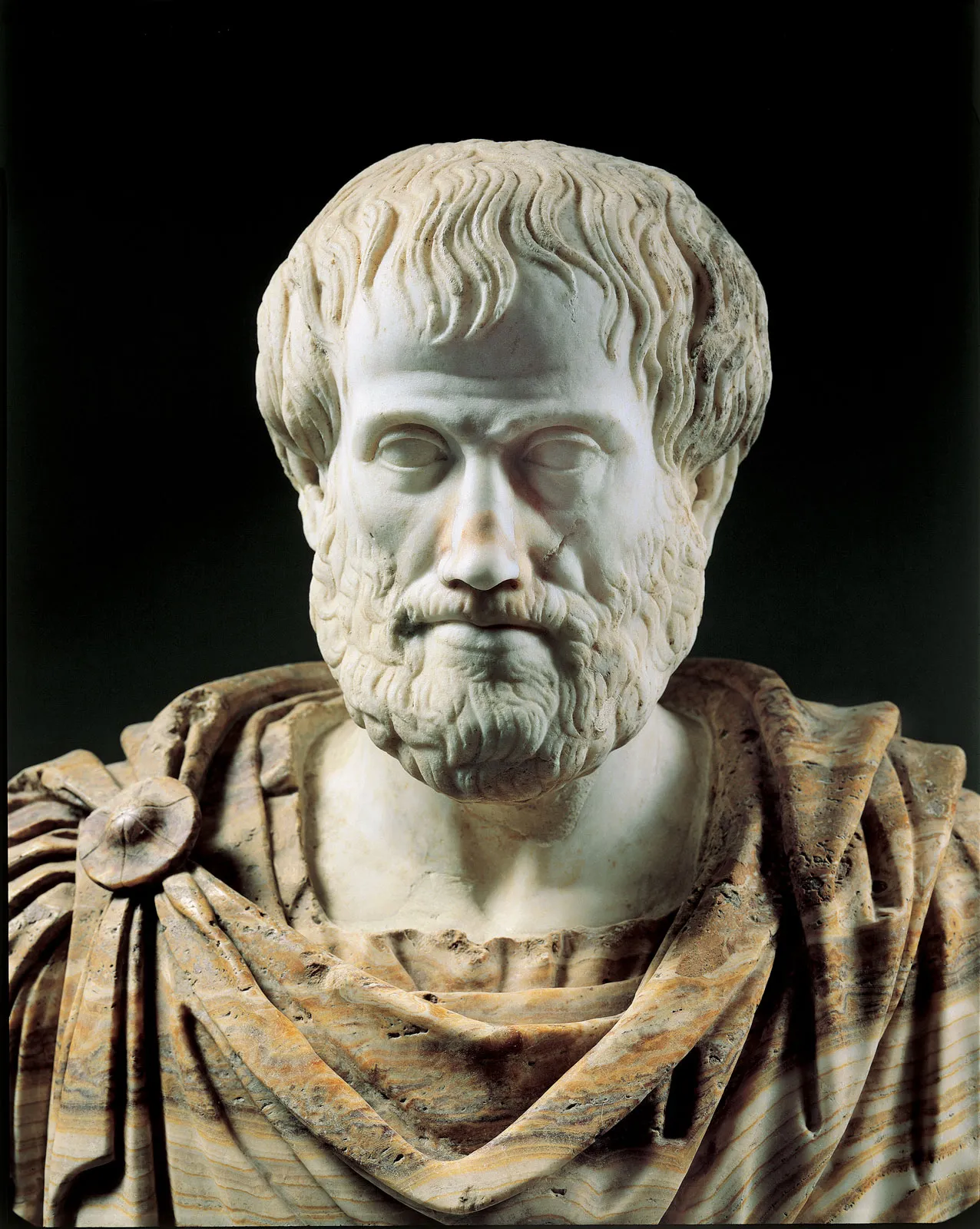

384 BC-322 BC
--
Aristotle
--
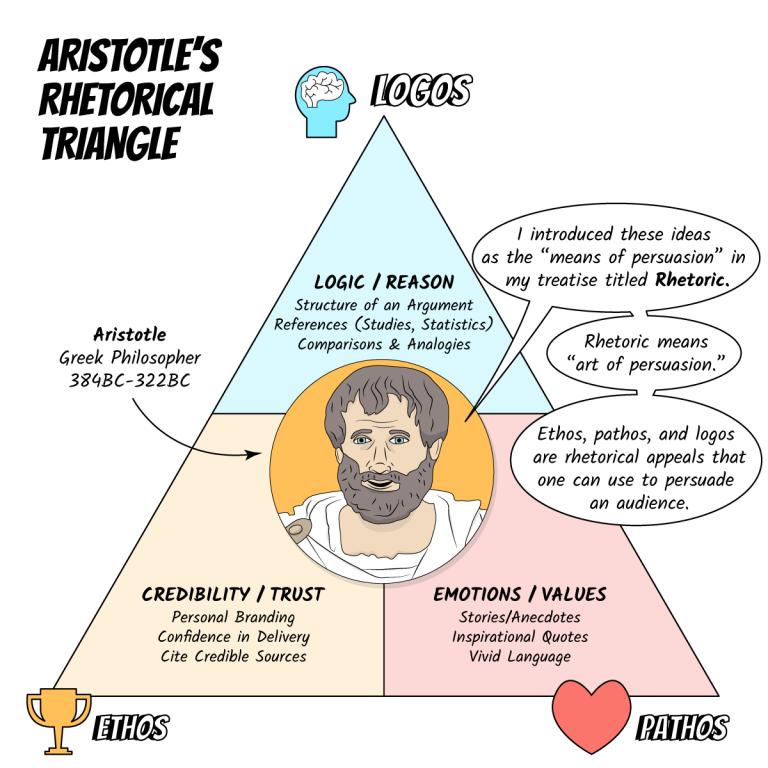
384 BC-322 BC
--
Aristotle
Logos, ethos, and pathos are three persuasive appeals used in rhetoric, aiming to convince an audience. Ethos establishes the speaker's credibility and trustworthiness, logos appeals to logic and reason with evidence and facts, and pathos connects with the audience's emotions to evoke feelings and create a connection.
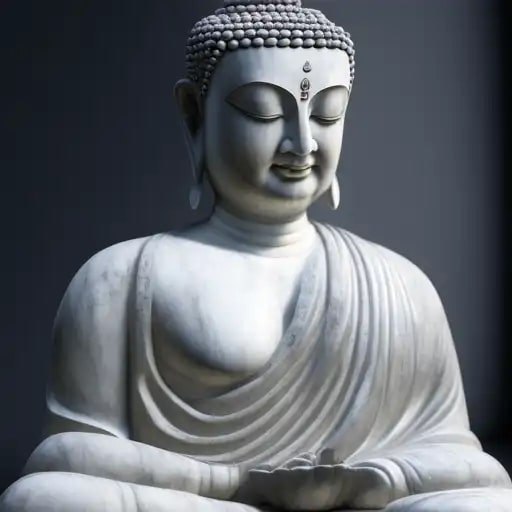

563 or 480 BC
The Buddha
--
The Buddha ; Siddhartha Gautama. c. 563 or 480 BCE

500-450 BC
Capitoline Wolf
--
(c. 500-450 BCE): A bronze sculpture depicting the legendary she-wolf nursing Romulus and Remus, the founders of Rome. This piece is a powerful symbol of the city's origin story.
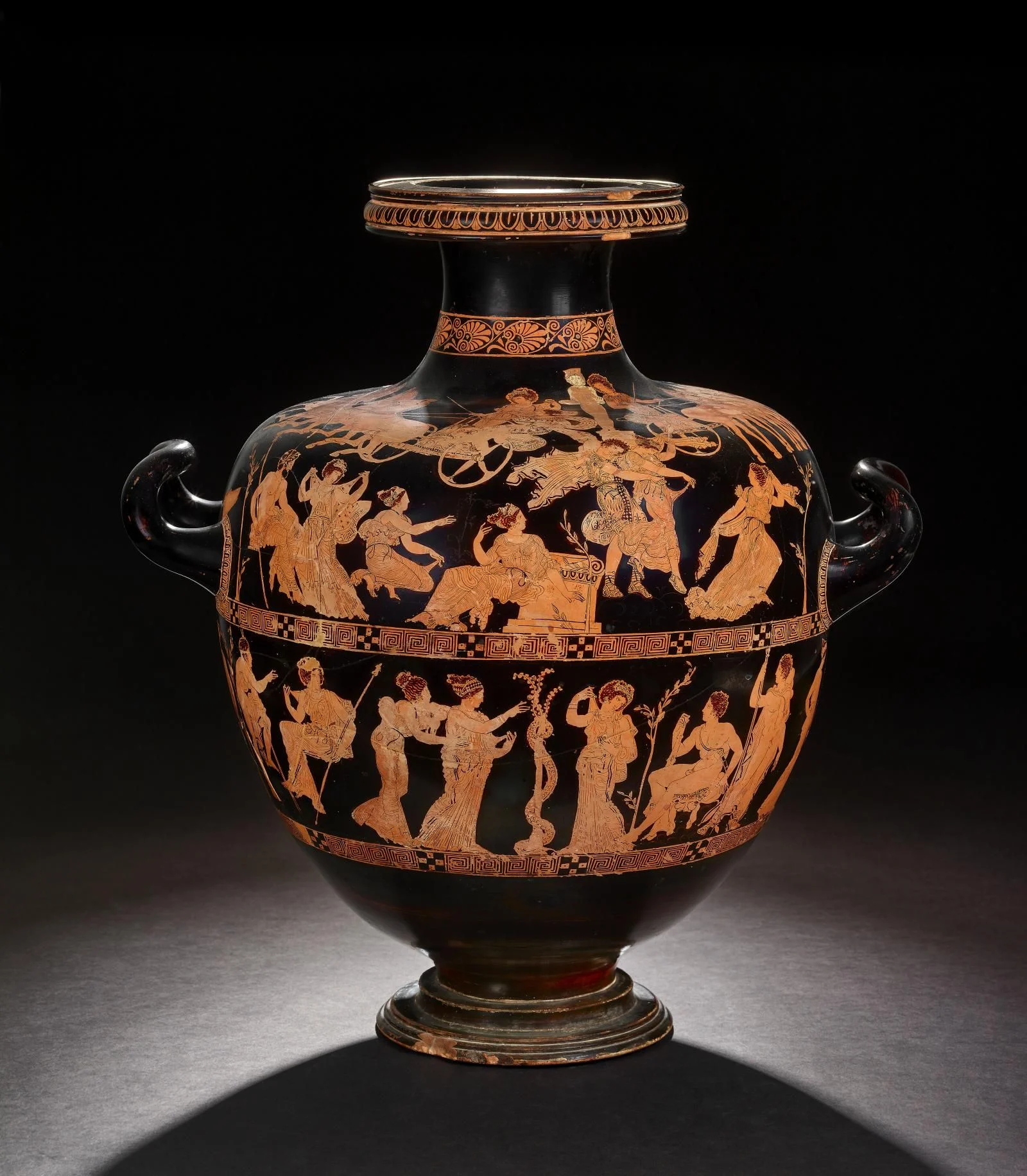

420 BC
The Meidias hydria
Meidias
Athenian red-figure hydria (water jug) signed by Meidias as potter and attributed to the Meidias Painter as painter. Pottery, made in Attica (Greece), about 420 BC, excavated in Italy.
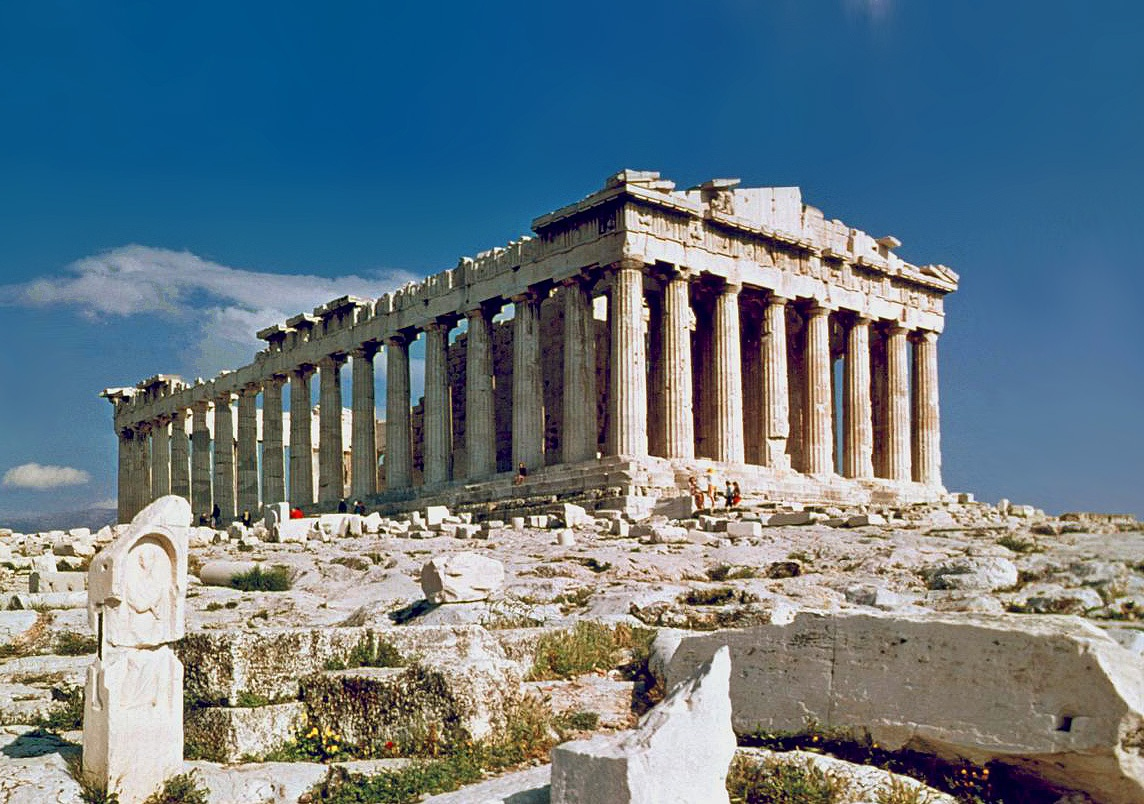

447 BC
Parthenon
--
The Parthenon in Athens was carved out of Pentelic marble and it took the Athenians approximately 10 years to construct the building, 447-438 BCE. Architectural sculpture work continued into approximately 432 BCE.
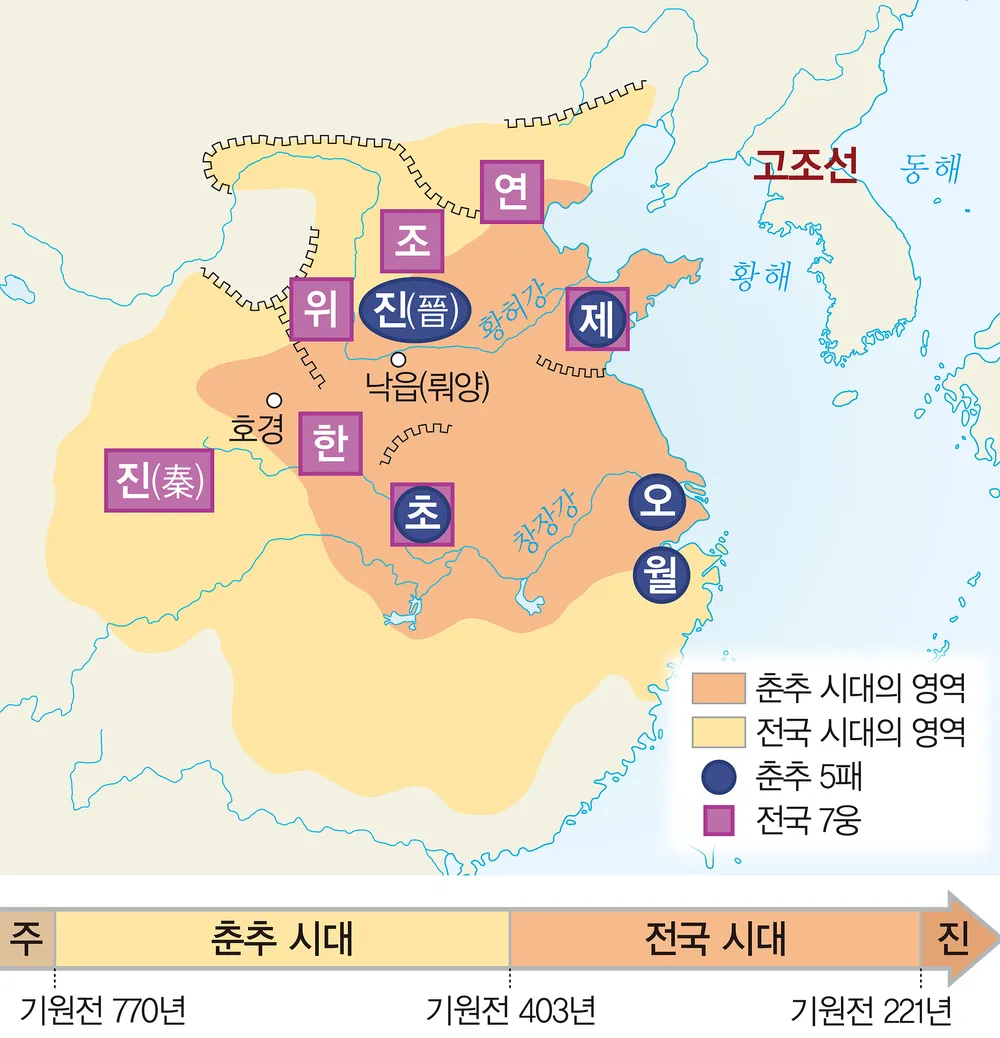
770 BC – 221 BC
춘추전국시대
--
춘추전국시대(春秋戰國時代, 기원전 770년 ~ 기원전 221년)는 춘추 시대와 전국 시대를 아우르는 말이며, 기원전 770년 주(周)왕조의 천도 후부터 기원전 221년 시황제(始皇帝)가 통일한 시기까지며, 선진 시대(先秦時代)라고도 한다.
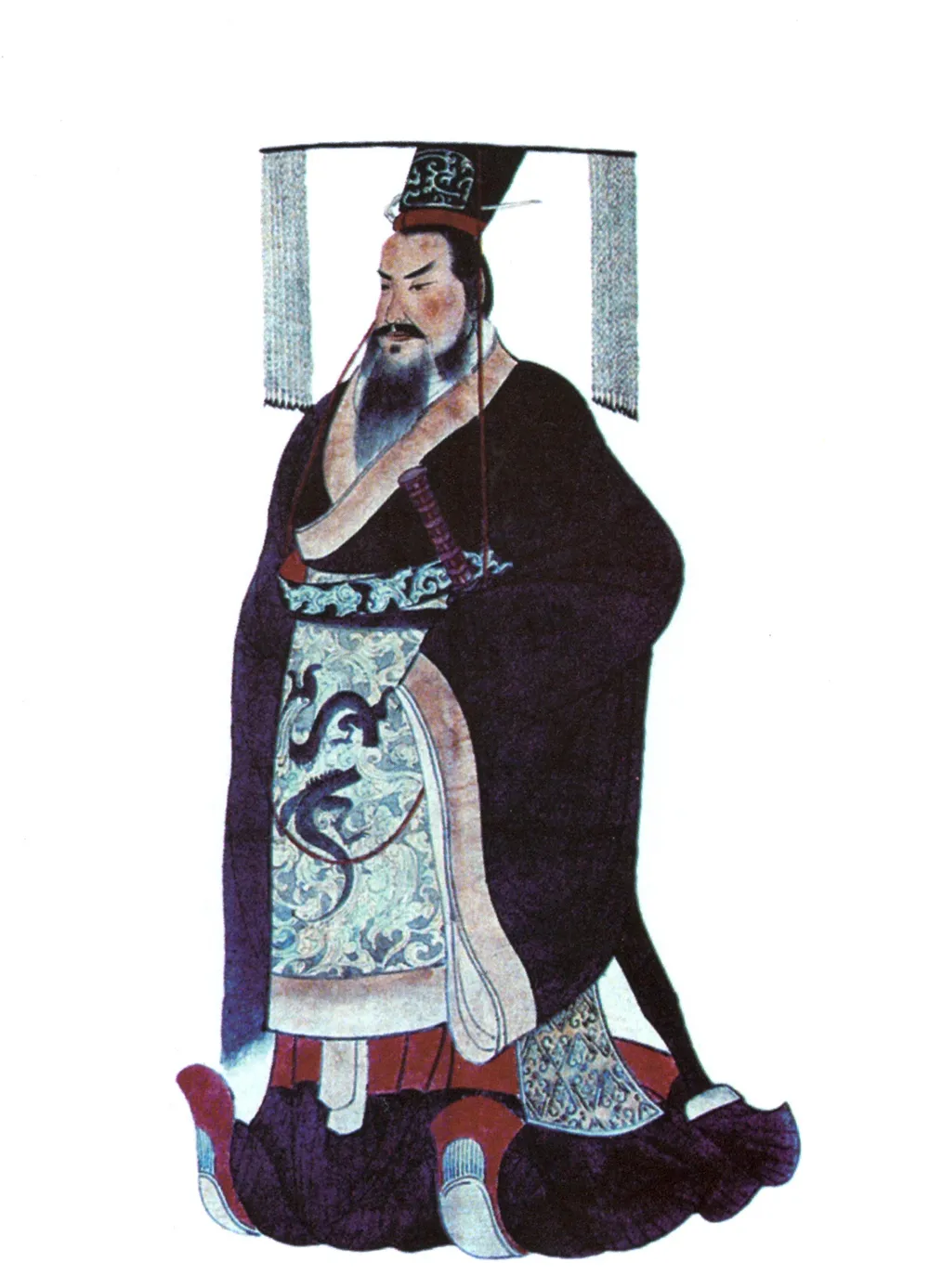

221 BC
진시황의 중국 통일
진시황이 중국을 통일한 해는 기원전 221년입니다. 당시 진시황은 만 40세였으며, 이 해에 전국 시대를 통일하고 황제의 자리에 올랐습니다.
진시황은 기원전 230년에 한나라를 시작으로 기원전 221년까지 약 10년에 걸쳐 위, 조, 연, 제, 초 등 여섯 나라를 멸망시키며 통일을 이루었습니다. 그는 통일 후 진나라의 초대 황제가 되어 시황제라고 불렸습니다.

206 BC - 202 BC
Chu-Han War (초한전쟁)
기원전 206년 진나라의 멸망 이후 유방과 항우가 대립한 끝에 기원전 202년 12월 항우의 패배와 죽음, 그리고 유방의 승리와 천하 통일로 통일 왕조국가 한나라가 건국되는 전쟁. 초한쟁패(楚漢争覇)라고도 하며, 중국에서는 '초한상쟁(楚漢相爭)'이라는 표현도 많이 쓰인다.

104 BC-91 BC
The Grand Scribe's Records (사기)
Sima Qian (사마천)
사마천의 사기(史記)는 기원전 104년에서 기원전 91년 사이에 완성된 것으로 추정됩니다. 사마천은 이 기간 동안 자신의 아버지의 유지를 이어받아 중국 최초의 본격적인 역사서인 사기를 집필했습니다. 사기는 본기, 표, 서, 세가, 열전 등 총 130권으로 구성되어 있습니다.

150-125 BC
Venus de Milo
This famous marble statue, while debated in its precise dating, is celebrated for its graceful pose and idealized features.


197-156 BC
Pergamon Altar
This monumental structure, decorated with a massive frieze depicting the battle between gods and giants, exemplifies the Hellenistic style with its dynamism and heightened emotion.
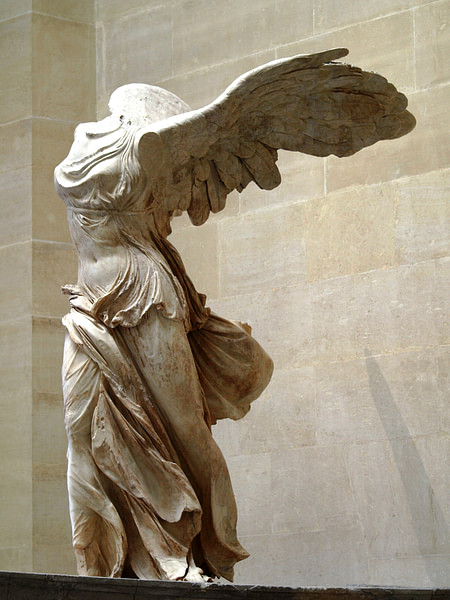

200–190 BC
Winged Victory of
Samothrace “Nike”

196 BC
Rosetta stone
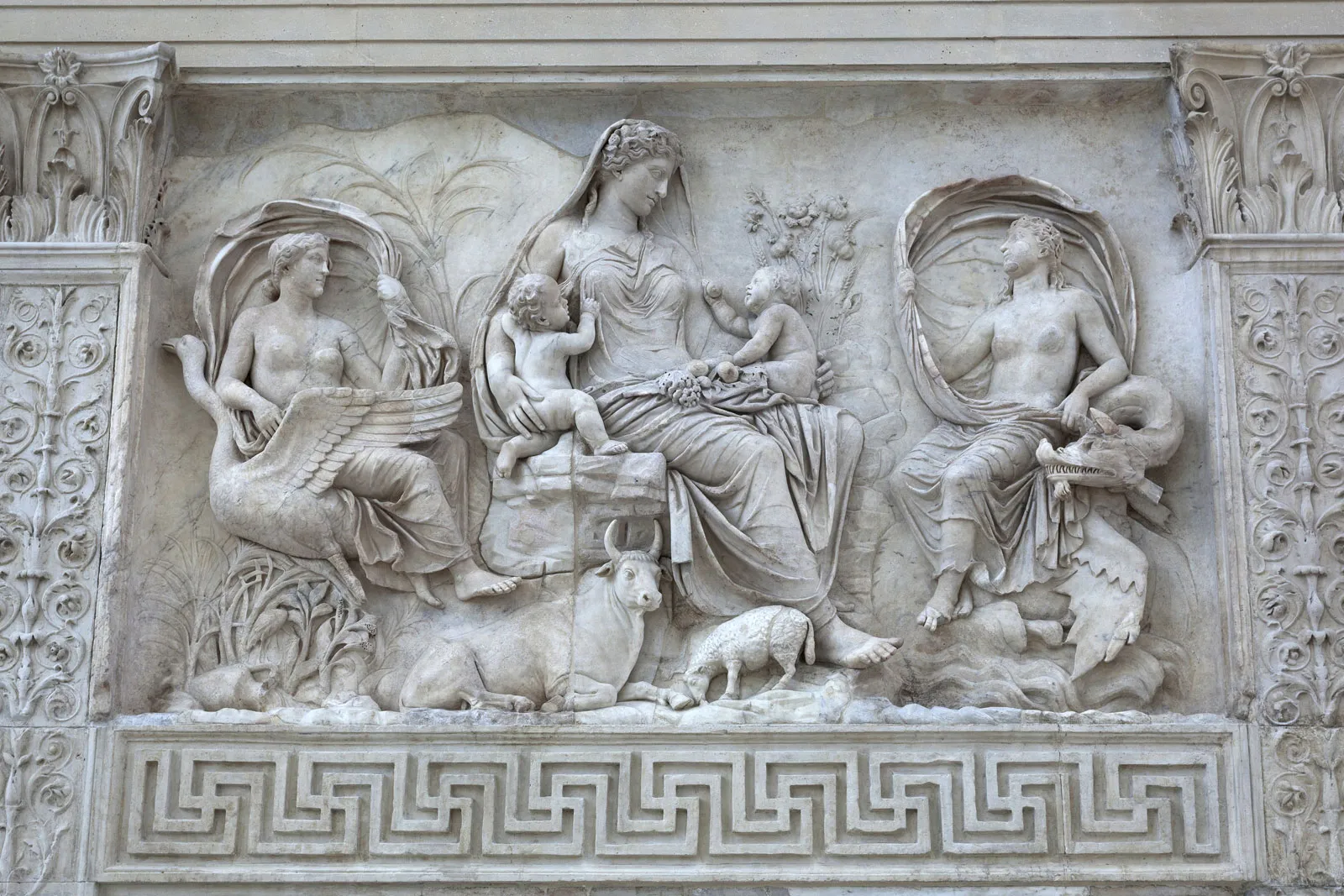

Jul 4, 13 BC
Ara Pacis
The Ara Pacis is, at its simplest, an open-air altar for blood sacrifice associated with the Roman state religion.

2-1 century BC
Compass
The first compass was invented in China during the Han Dynasty, between the 2nd century BC and the 1st century AD, according to the National MagLab. It was initially used for divination and later adapted for navigation, with clear evidence of its use in maritime navigation appearing in the 12th century. The earliest forms of the compass were made from lodestone, a naturally magnetized mineral, and were often shaped like a spoon or a fish.
Greek
Roman art
Art History Timeline
I started making this timeline as a personal learning project. I hope you enjoy it too. New updates will be added every month.
@taco_the.great

70
Glass bowl of fruit and vases
Glass bowl of fruit and vases. Roman wall painting in Pompeii (around 70 AD), Naples National Archaeological Museum, Naples, Italy
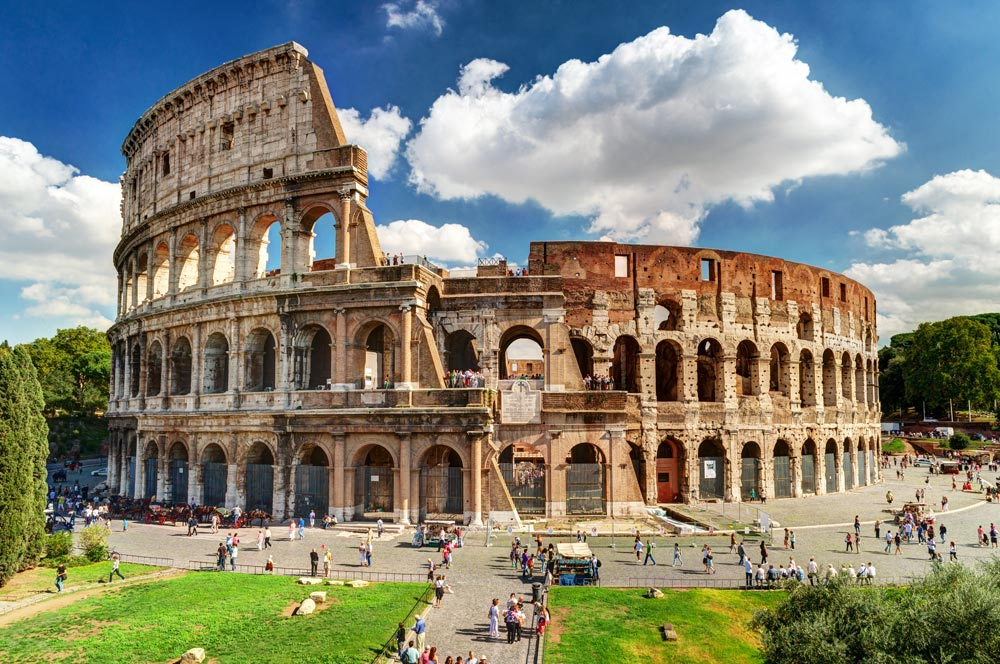

72-80
Colosseum
Construction began under the Emperor Vespasian ( r. 69–79 AD) in 72 and was completed in AD 80 under his successor and heir, Titus ( r. 79–81).
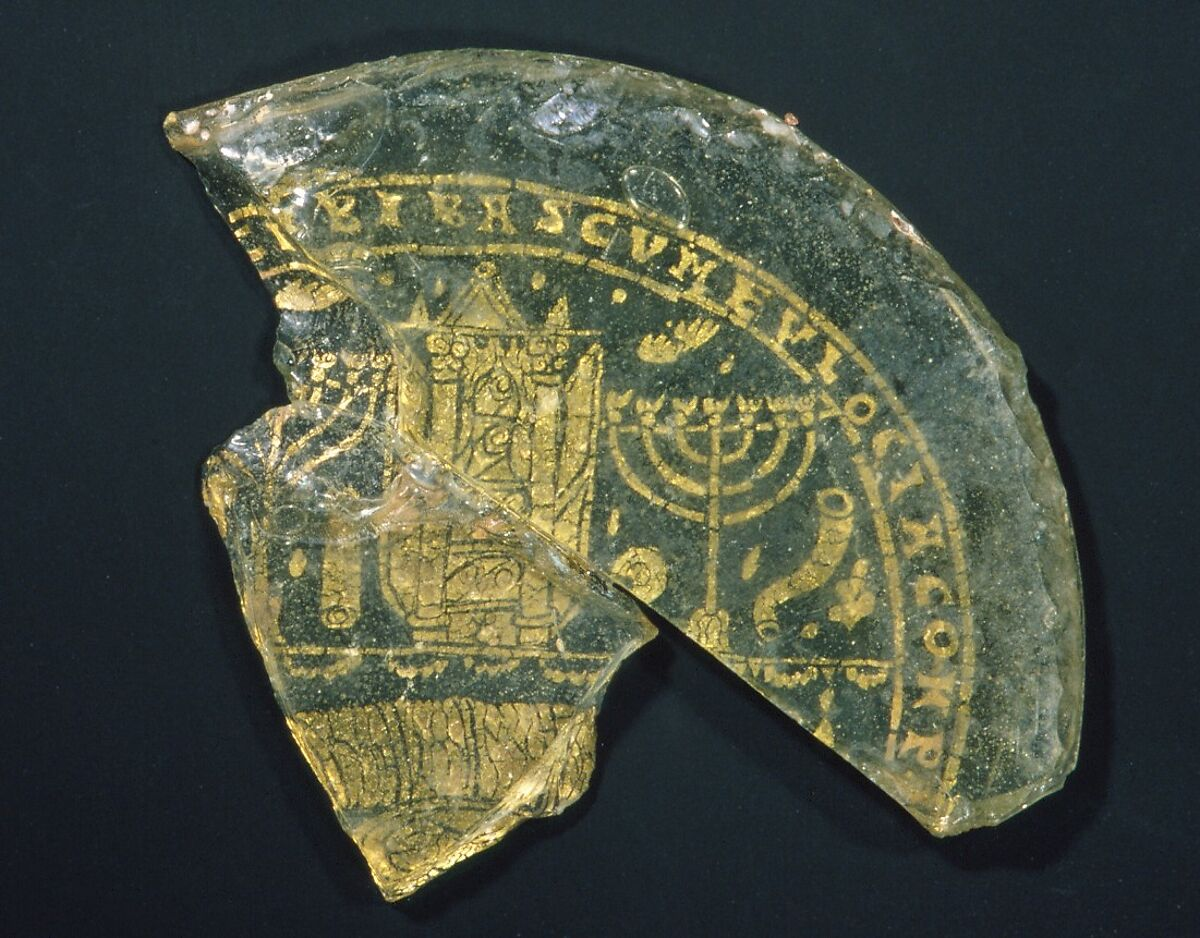

300
–350
Bowl Fragments with
Menorah, Shofar, and Torah Ark
This rare example of Jewish gold glass depicts an open Torah ark, with rolled scrolls on its shelves, and ritual implements of the temple-including two menorot (candelabra), a shofar (ram's horn), and an etrog (citron). Originally, a banqueting scene was shown below, with a fish on the tripod table in front of a cushion.

380
Christianity as the state religion of the Roman Empire
In 380 AD, Emperor Theodosius I officially made Christianity the state religion of the Roman Empire through the Edict of Thessalonica. This edict mandated that all citizens follow Nicene Christianity, which is a specific branch of Christianity.

476
Fall of the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire officially ended in 476 AD when Romulus Augustulus, the last Western Roman Emperor, was deposed by the Germanic chieftain Odoacer. This event is widely recognized as the symbolic end of the Western Roman Empire, although the process of its decline had been ongoing for centuries.
500 AD to 1500 AD
Medieval
Age
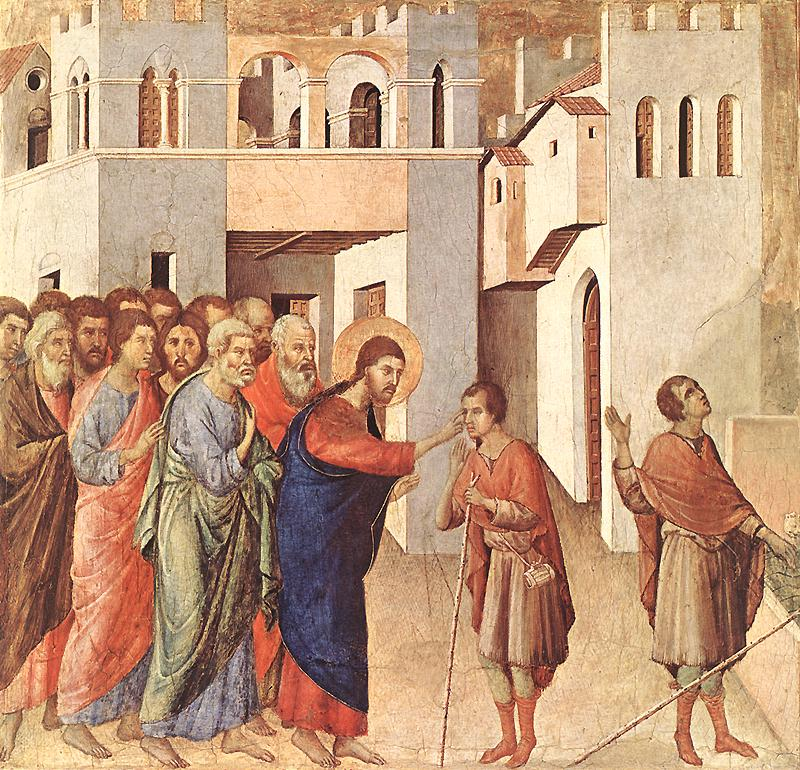
1308-11
Healing of the Man Born Blind
Duccio (1260–1319)
Healing of the Man Born Blind , egg tempera on wood, 45.1 x 46.7 cm, The National Gallery, London.
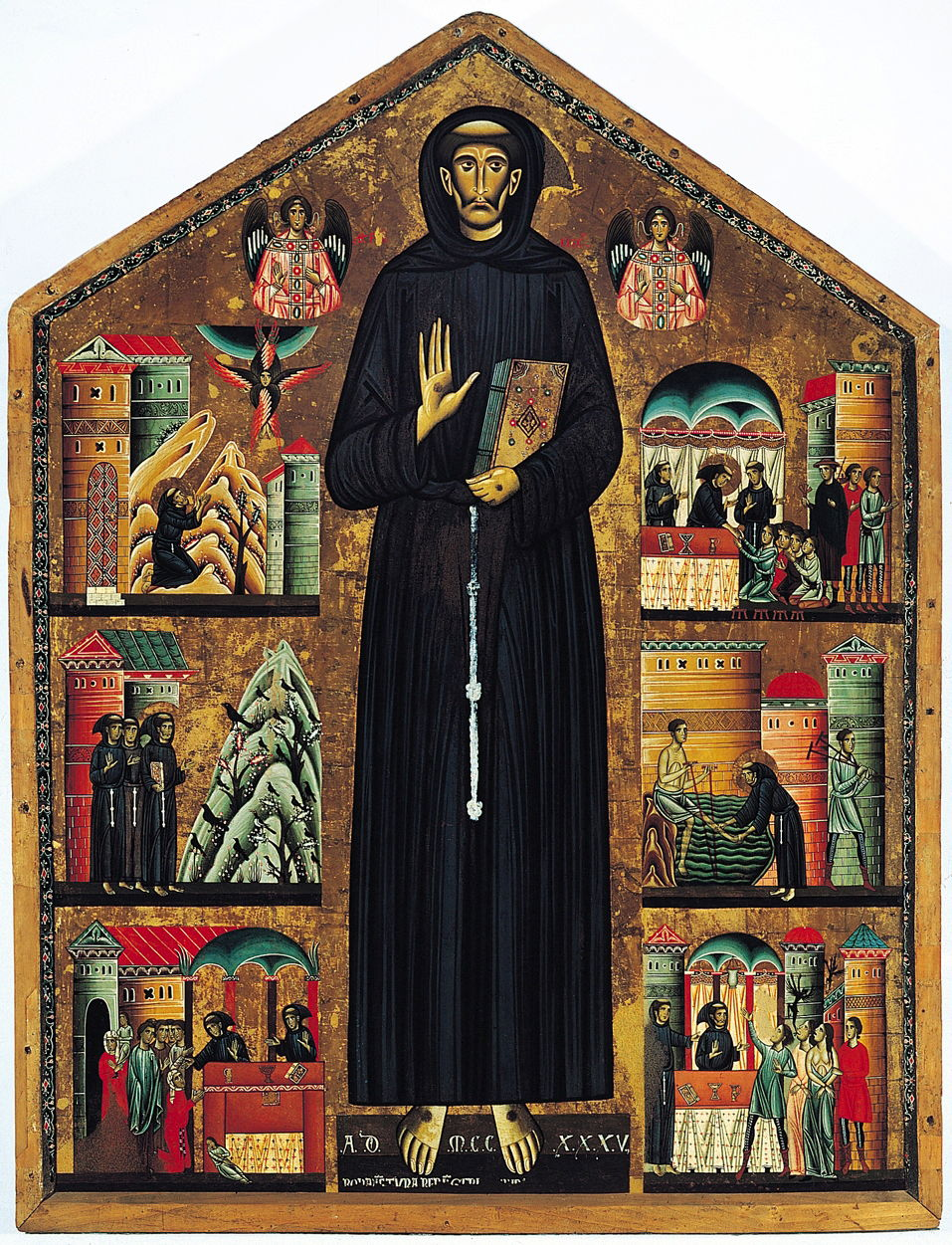

1235
Saint Francis of Assisi and
scenes of his life
Bonaventura Berlinghieri, Saint Francis of Assisi and scenes of his life (1235), tempera on wood, 160 × 123 cm, San Francesco, Pescia, Italy. Wikimedia Commons.

1077
Road to Canossa
The Road to Canossa or Humiliation of Canossa, or, sometimes, the Walk to Canossa was the journey of the Holy Roman Emperor Henry IV to Canossa Castle in 1077, and his subsequent ritual submission there to Pope Gregory VII.
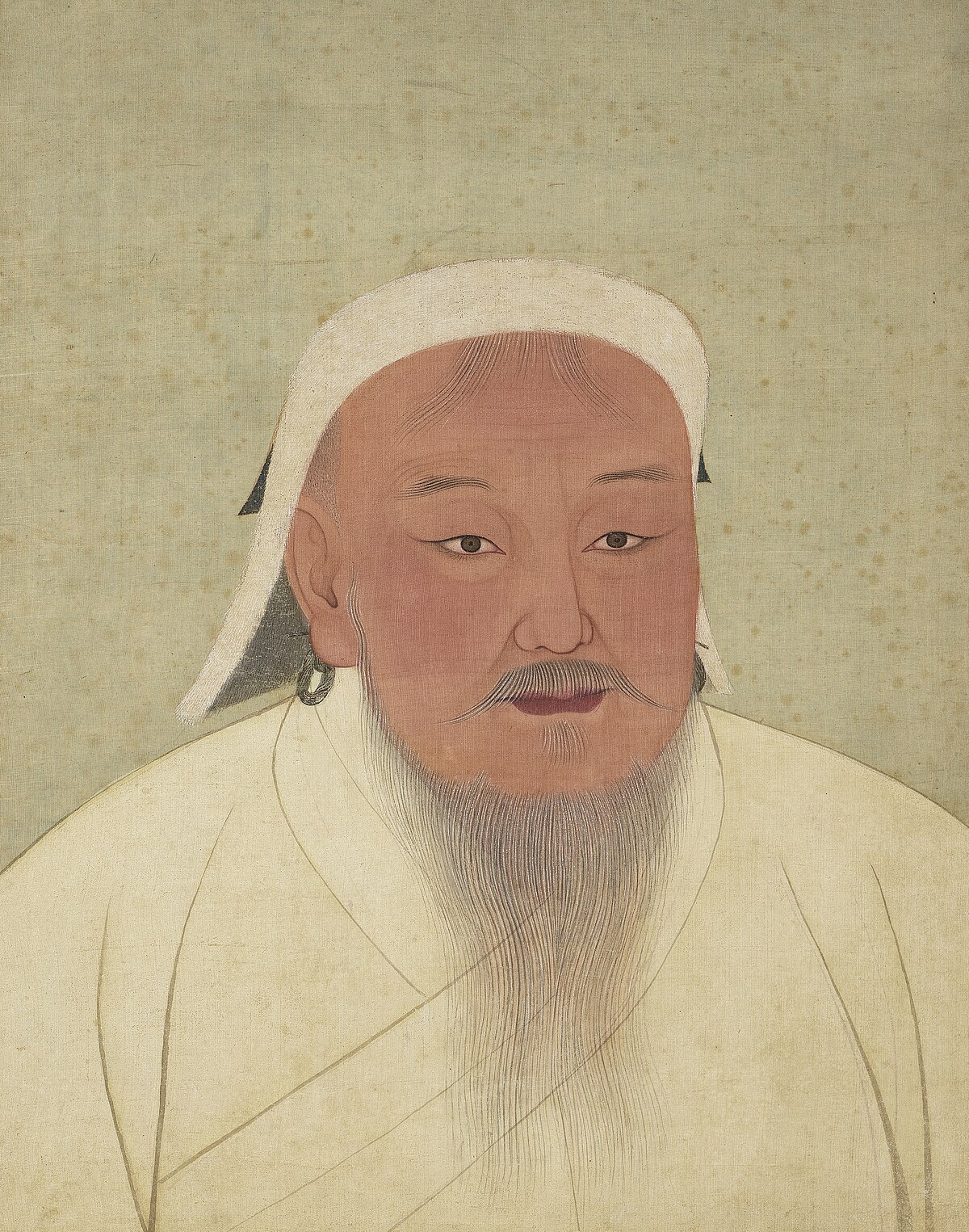

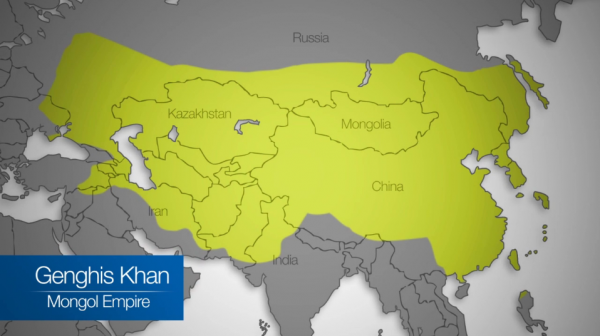
1279-1309
Peak of The Mongol Empire
Genghis Khan
The Mongol Empire, under Genghis Khan and his successors, reached its peak territorial extent around 1279-1309. At this time, it was the largest contiguous land empire in history, encompassing a vast area from Asia to Europe, according to Facebook posts. While Genghis Khan's death in 1227 marked a turning point, his successors continued his expansionist policies, leading to the empire's greatest size.
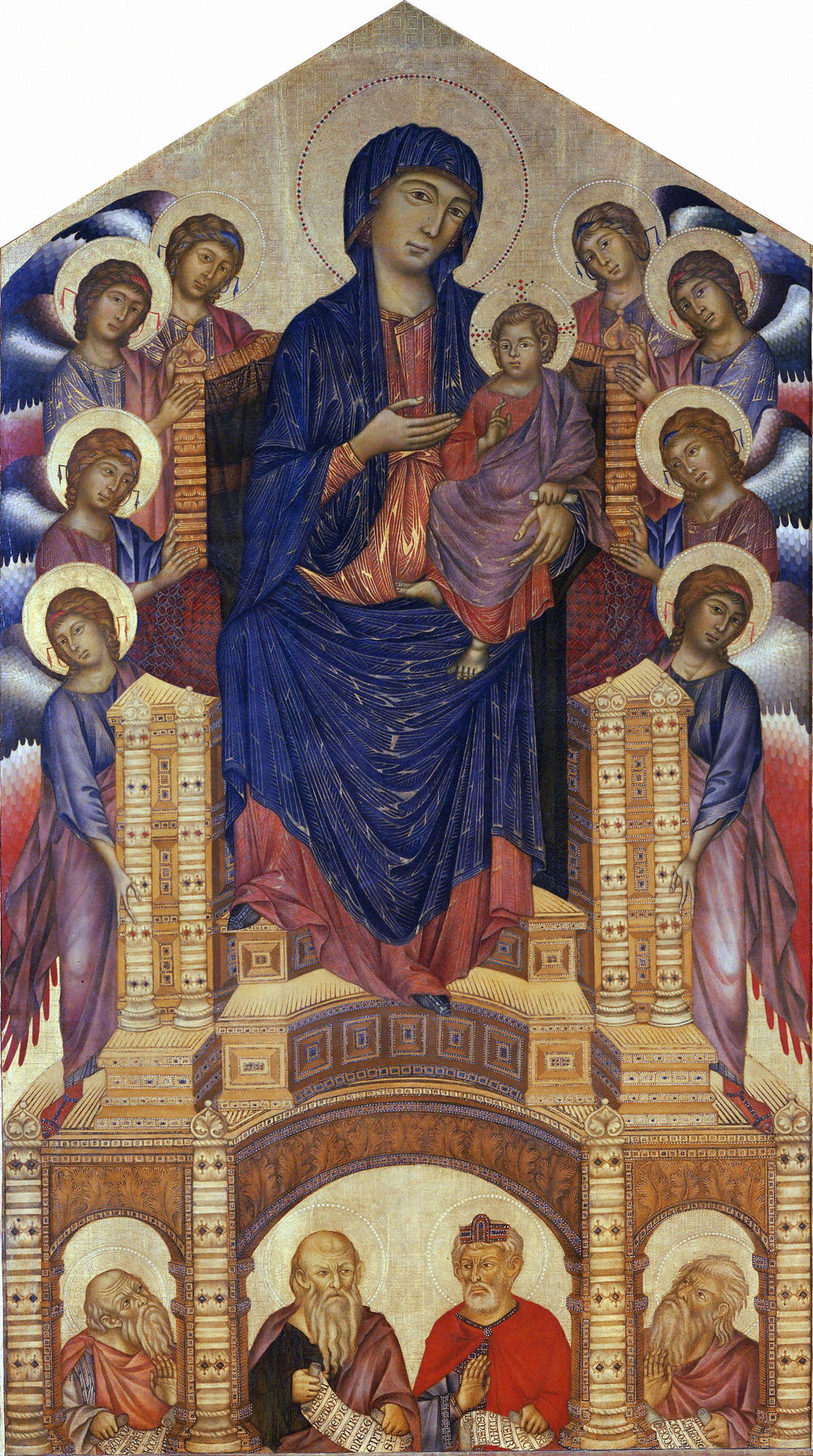

1280-90
Cimabué, Santa Trinita Maestà
Galleria degli Uffizi, Florence, Italy. Wikimedia Commons.
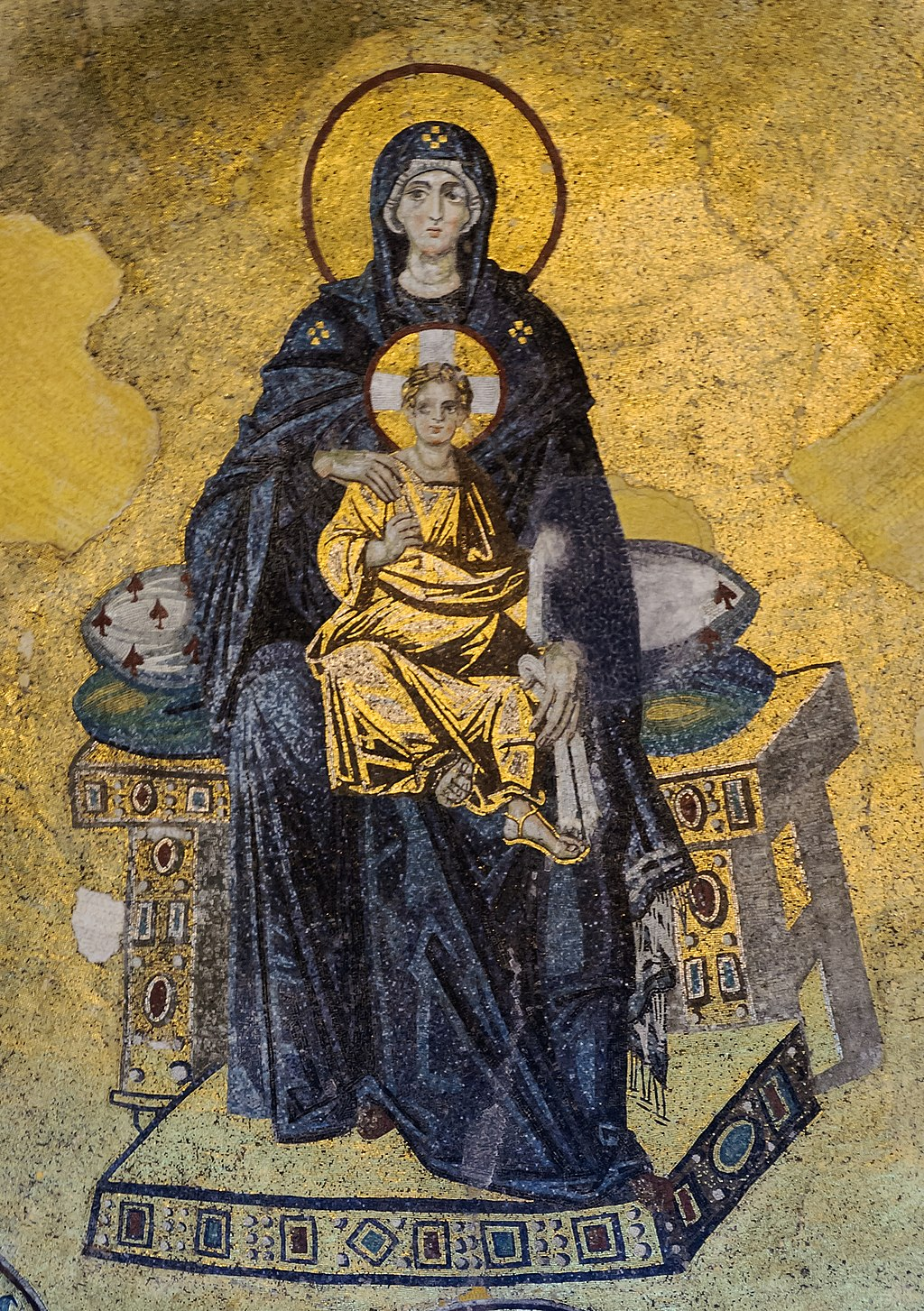

9th century
9th century Byzantine mosaic of the Hagia Sophia showing the image of the Virgin and Child, one of the first post-iconoclastic mosaics. It is set against the original golden background of the 6th century
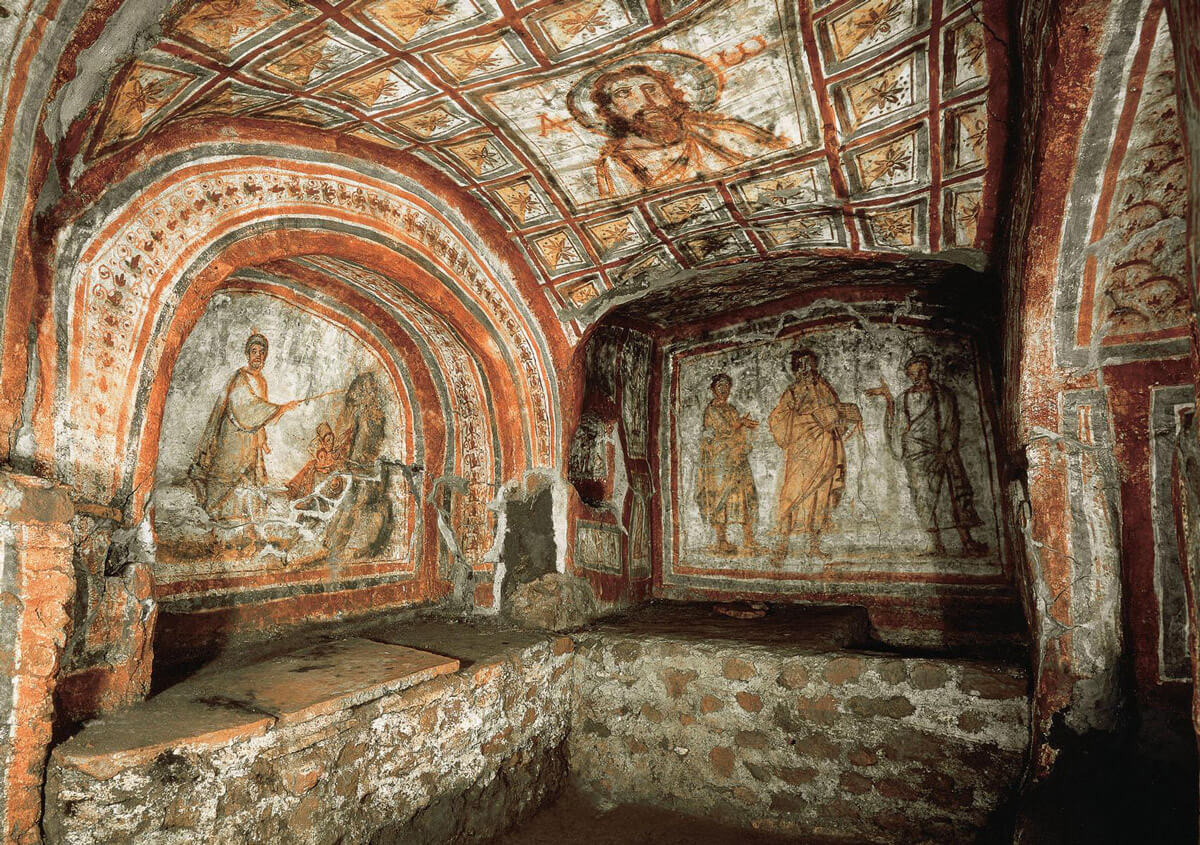

2nd century - 5th century
Roman Catacomb Art
Roman Catacomb Art: The burials of Jewish, pagan and early Christian Roman citizens in the Roman catacombs began in the 2nd century and ended in the 5th century, so ran parallel in time to the Haniwa in Japan. At the end of the 2nd century and starting in the 3rd century, Roman catacombs served as the official cemetery of Rome’s Christian Church. Christians decorated catacombs with frescoes, sculptures, and inscriptions. The earliest identifiably Christian art consists of a few wall and ceiling frescoes, which continued to be decorated in a sketchy style derived from Roman impressionism through the 4th century. The catacombs are extensive, reaching a depth of at least 20 meters beneath the surface, and many of them stretch for 20 kilometers. These catacombs are located just beyond the city center, as it was against the law to bury the dead within the confines of the city walls.

1271 - 1295
The Travels of Marco Polo
Marco Polo (born c. 1254, Venice [Italy]—died January 8, 1324, Venice) was a Venetian merchant and adventurer who traveled from Europe to Asia in 1271–95, remaining in China for 17 of those years. His Il milione (“The Million”), known in English as the Travels of Marco Polo, is a classic of travel literature.
1337–1453
Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (French: Guerre de Cent Ans; 1337–1453) was a conflict between the kingdoms of England and France and a civil war in France during the Late Middle Ages. It emerged from feudal disputes over the Duchy of Aquitaine and was triggered by a claim to the French throne made by Edward III of England. The war grew into a broader military, economic, and political struggle involving factions from across Western Europe, fuelled by emerging nationalism on both sides. The periodisation of the war typically charts it as taking place over 116 years. However, it was an intermittent conflict which was frequently interrupted by external factors, such as the Black Death, and several years of truces.
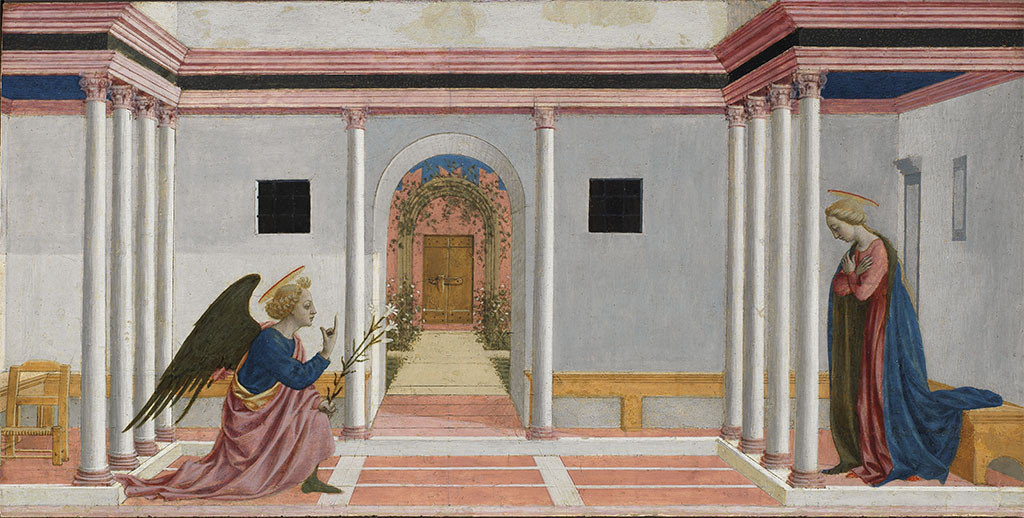

1442–1445
Annunciation
Domenico Veneziano
(predella panel from the St. Lucy Altarpiece)
Tempera on panel, 54 x 27.3 cm.Fitzwilliam Museum, Cambridge
1400’s
Renaissance

1321
Inferno
Dante Alighieri

1306
Lamentation
Giotto

1453
Orban’s Basilic
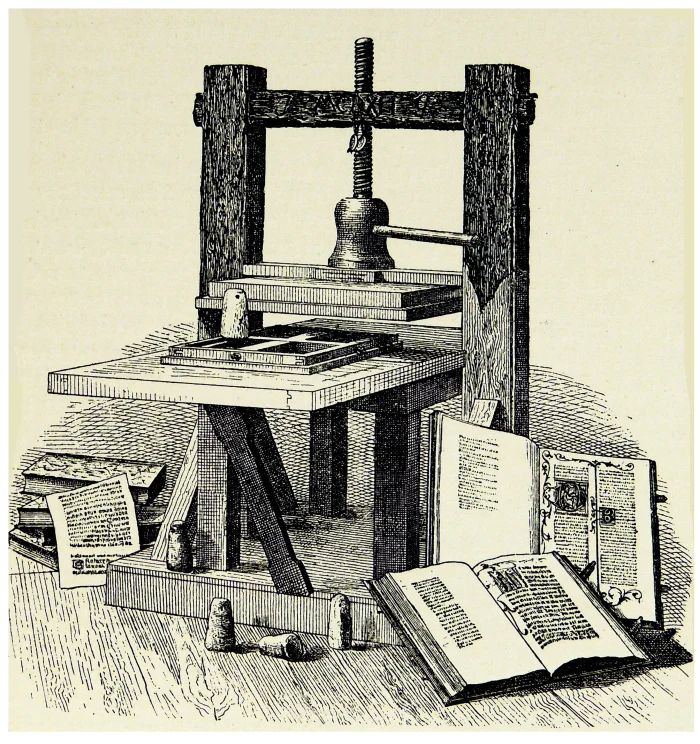
1440
Gutenberg printing press
Johannes Gutenberg
1440 In Germany, around 1440, goldsmith Johannes Gutenberg invented the printing press,
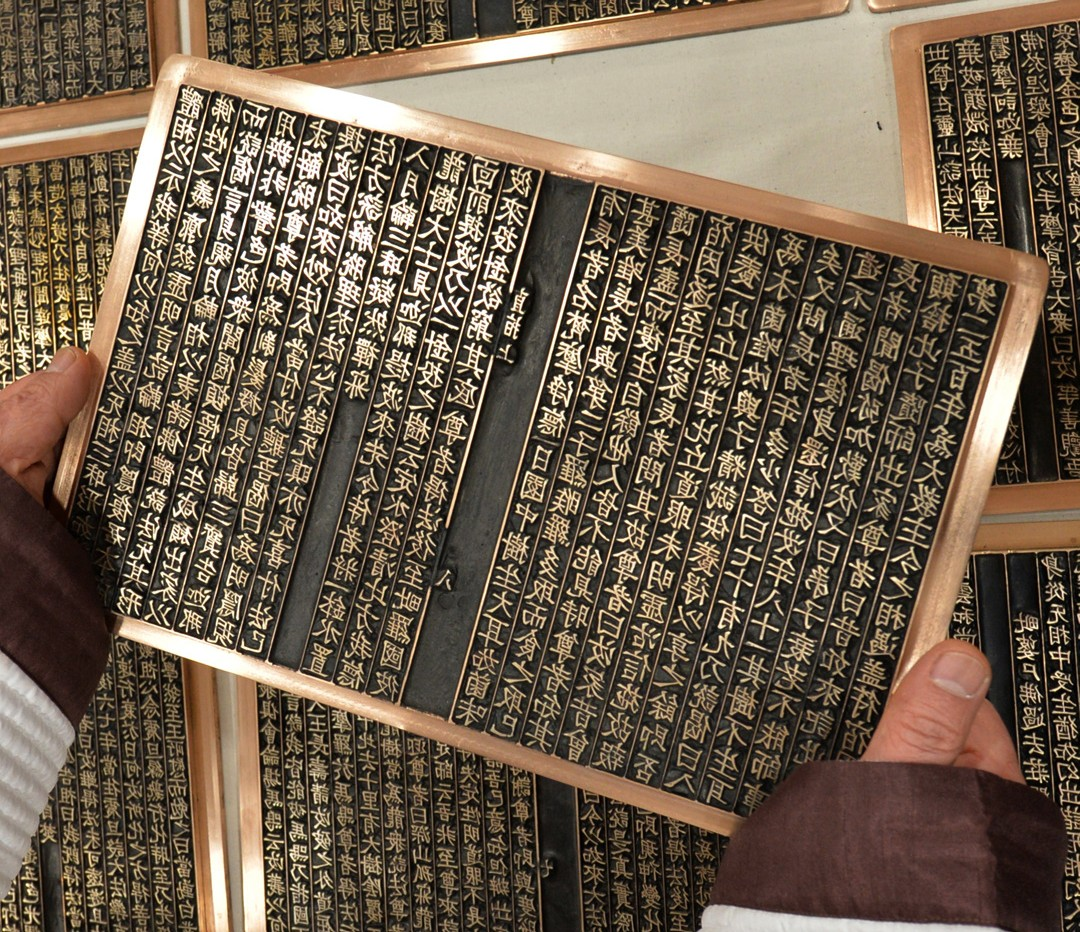

1377
직지심체요절
직지심체요절은 현존하는 가장 오래된 금속활자 인쇄본으로, 1377년 고려 시대 청주 흥덕사에서 금속활자를 사용하여 인쇄되었습니다. 원래 이름은 백운화상초록불조직지심체요절이며, 승려 백운이 고승들의 어록을 모아 편찬한 것입니다. 이 책은 유네스코 세계기록유산으로 등재되어 있으며, 현재 프랑스국립도서관에 소장되어 있습니다.

Gutenberg Bible
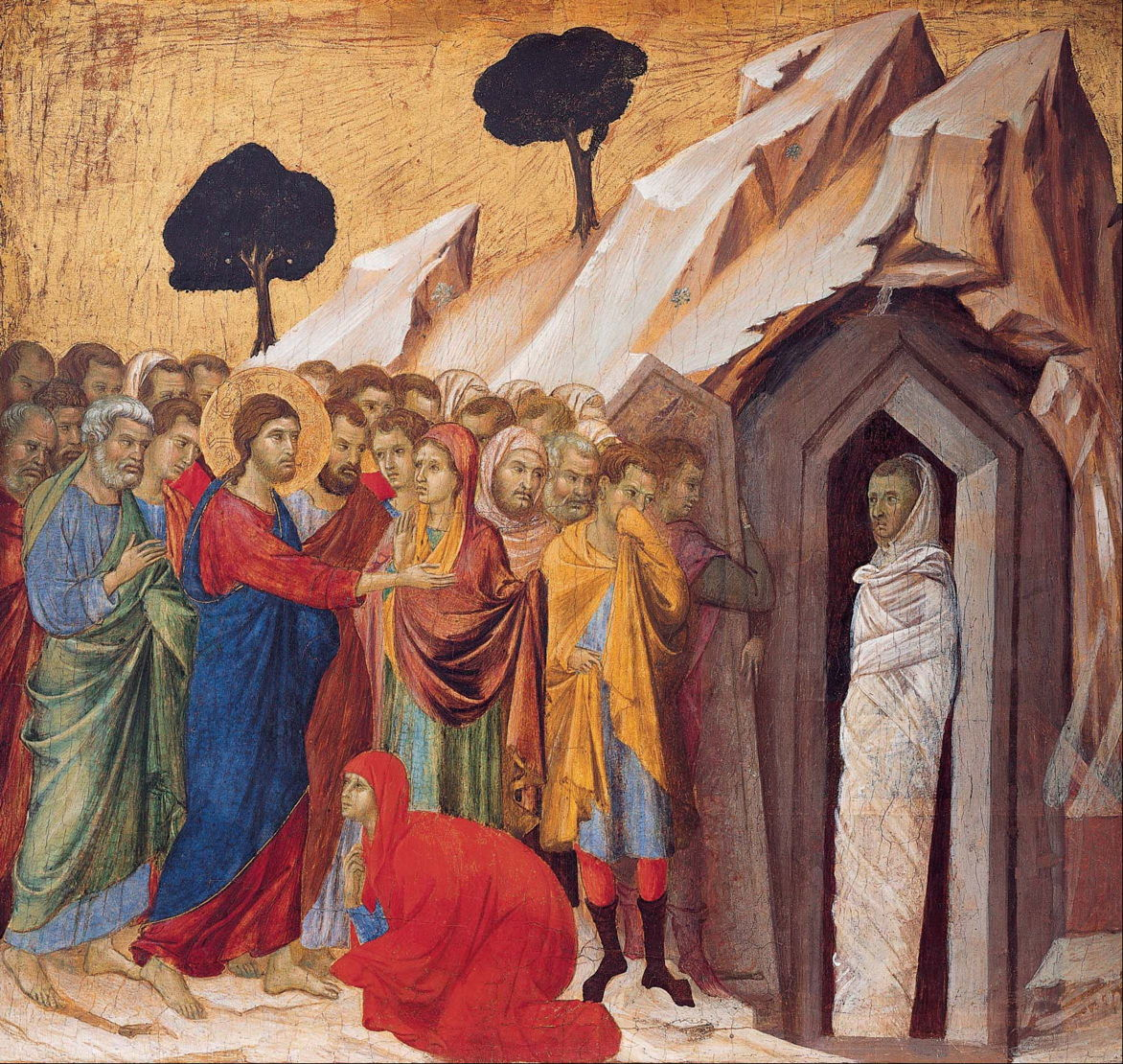

1310–11
The Raising of Lazarus
Duccio di Buoninsegna (c 1255–1318), tempera and gold on panel, 43.5 x 46.4 cm, Kimbell Art Museum, Fort Worth, TX.

1347 - 1351
Black Death
The Black Death was a devastating pandemic of bubonic plague that swept through Europe and Asia in the mid-1300s, killing an estimated 30-60% of Europe's population. It was one of the deadliest pandemics in human history. The plague, caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis, was spread by fleas on rats and other rodents.
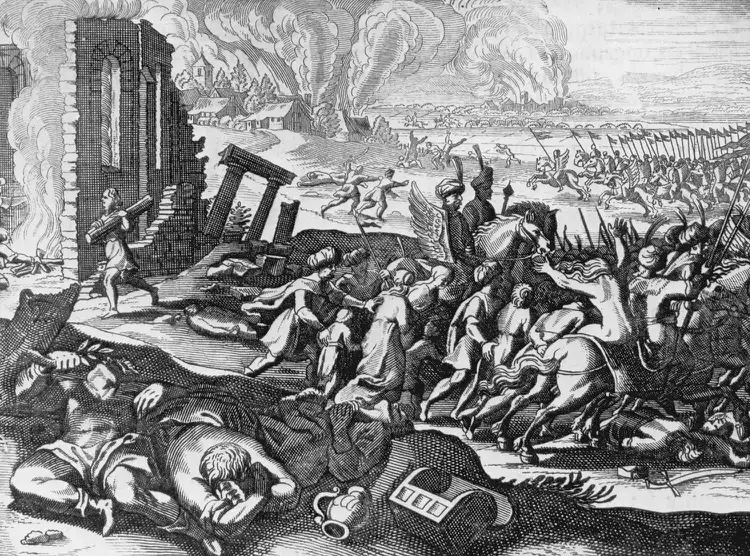

1453
Fall of Constantinople
The capture and sacking of Constantinople by Turkish troops under Mohammed II, 29th May 1453. The Turkish victory marked the end of the Byzantine Empire and the rise of the Ottomans. Hulton Archive/Getty Images
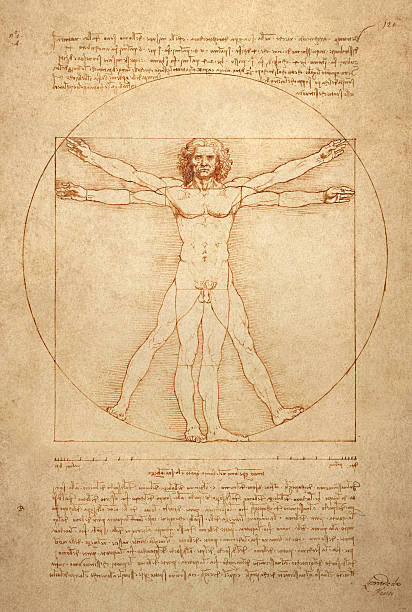
1490
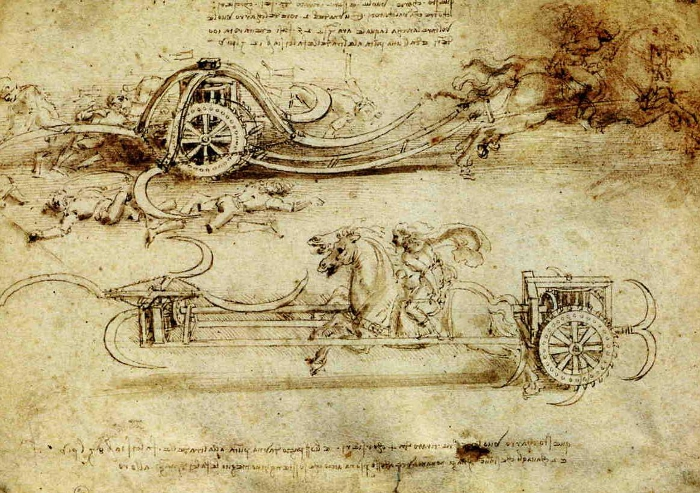
Vitruvian Man
Leonardo da Vinci

1431
Death of Joan of Arc
Acceleration
of
information
delivery
City
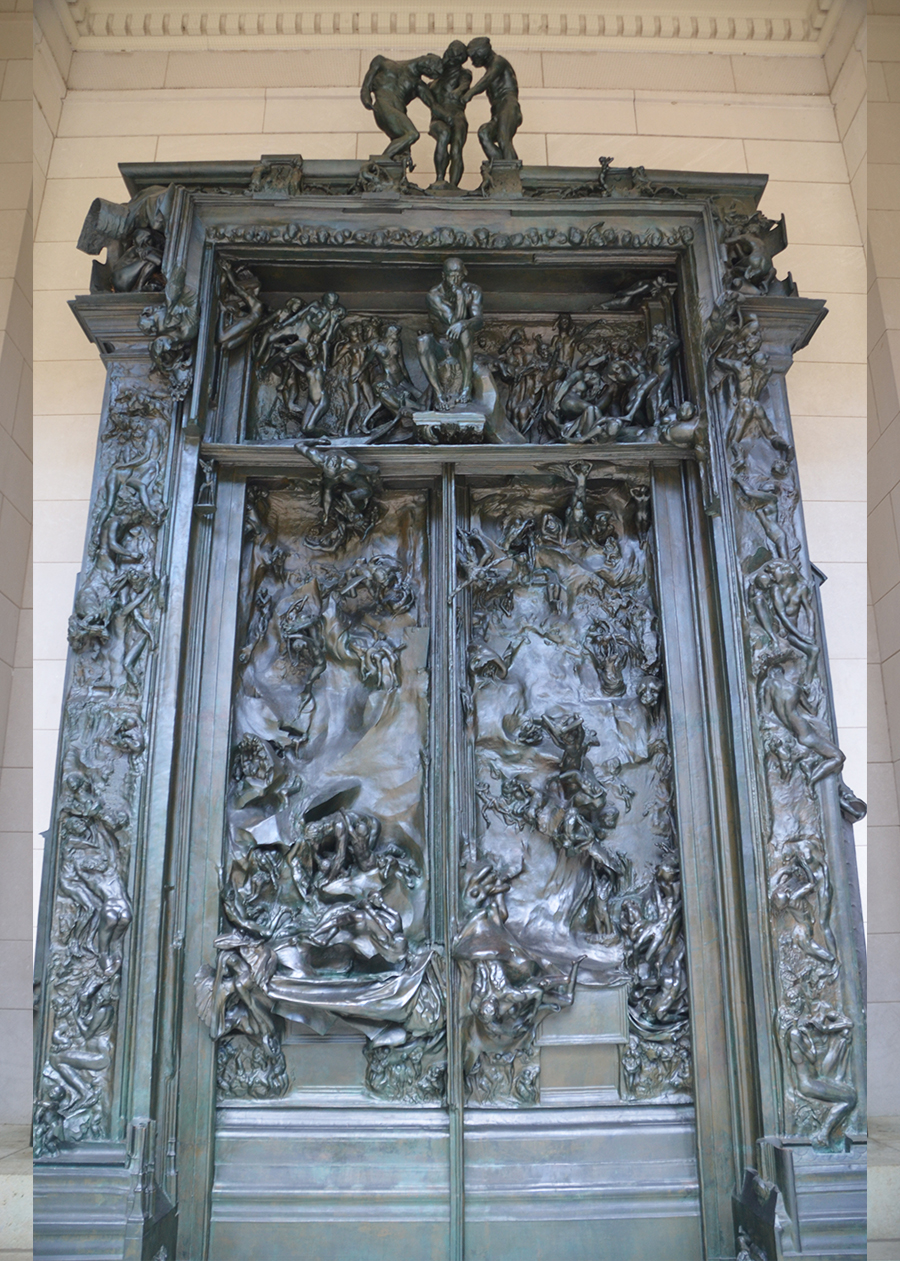

1917
Gates of Hell
Auguste Rodin
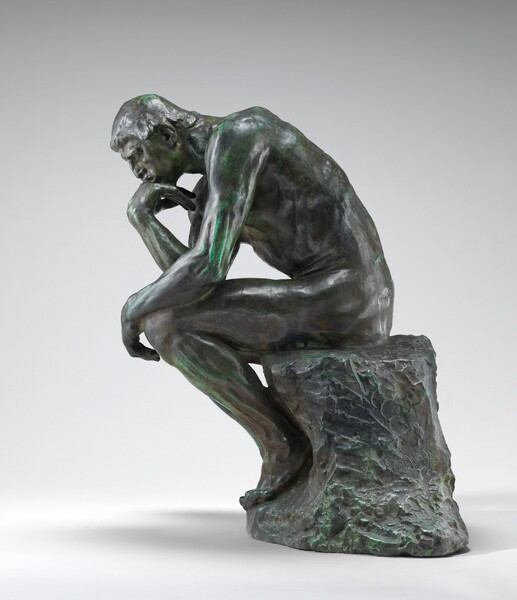

1904
The Thinker
Auguste Rodin
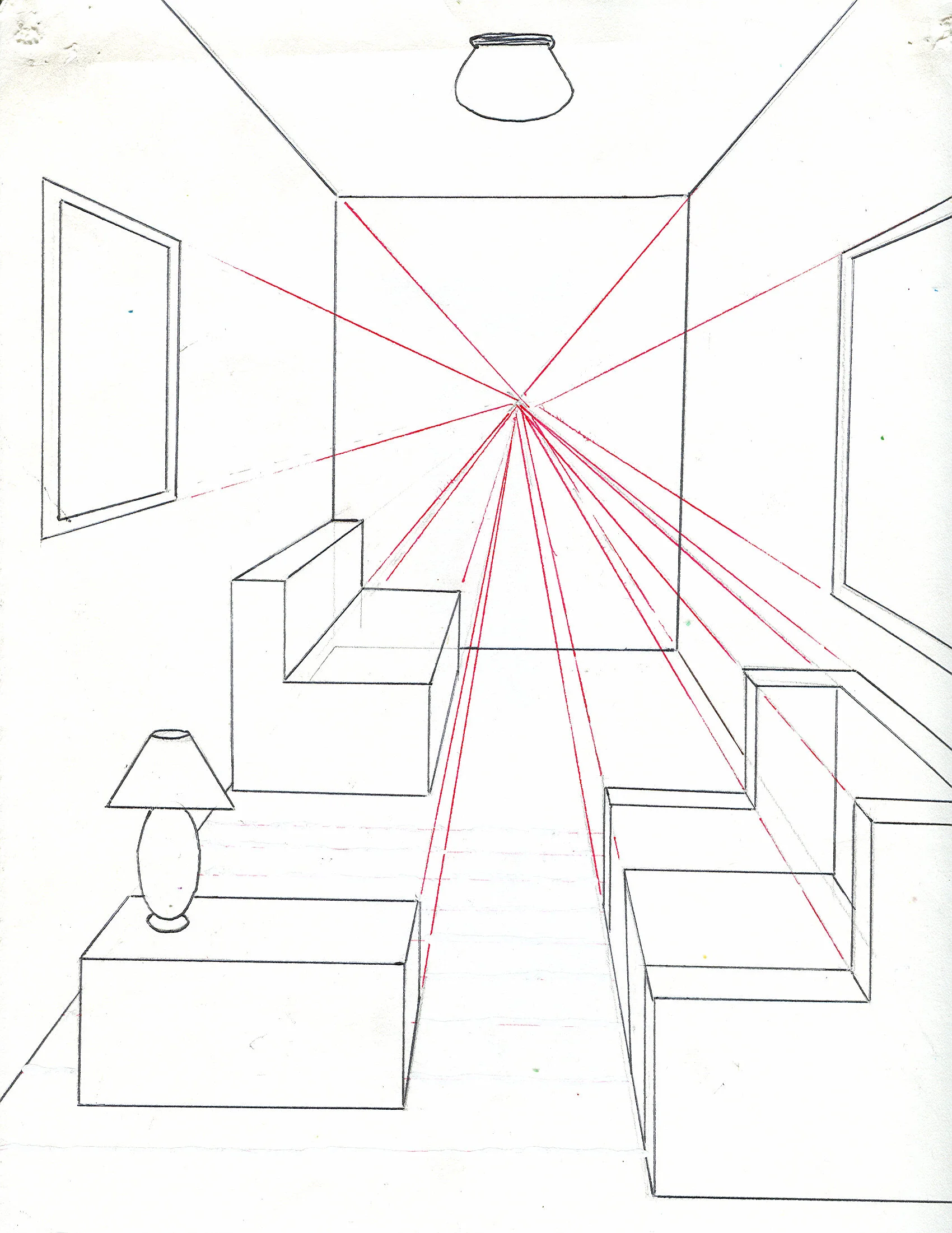
perspective
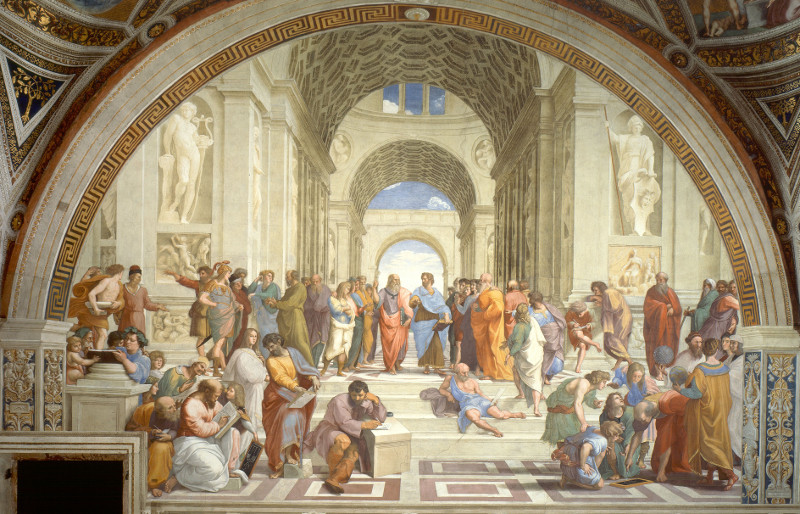

1509–1511
The School of Athens
Raphael
Fresco, 500 x 770 cm.Apostolic Palace, Vatican City
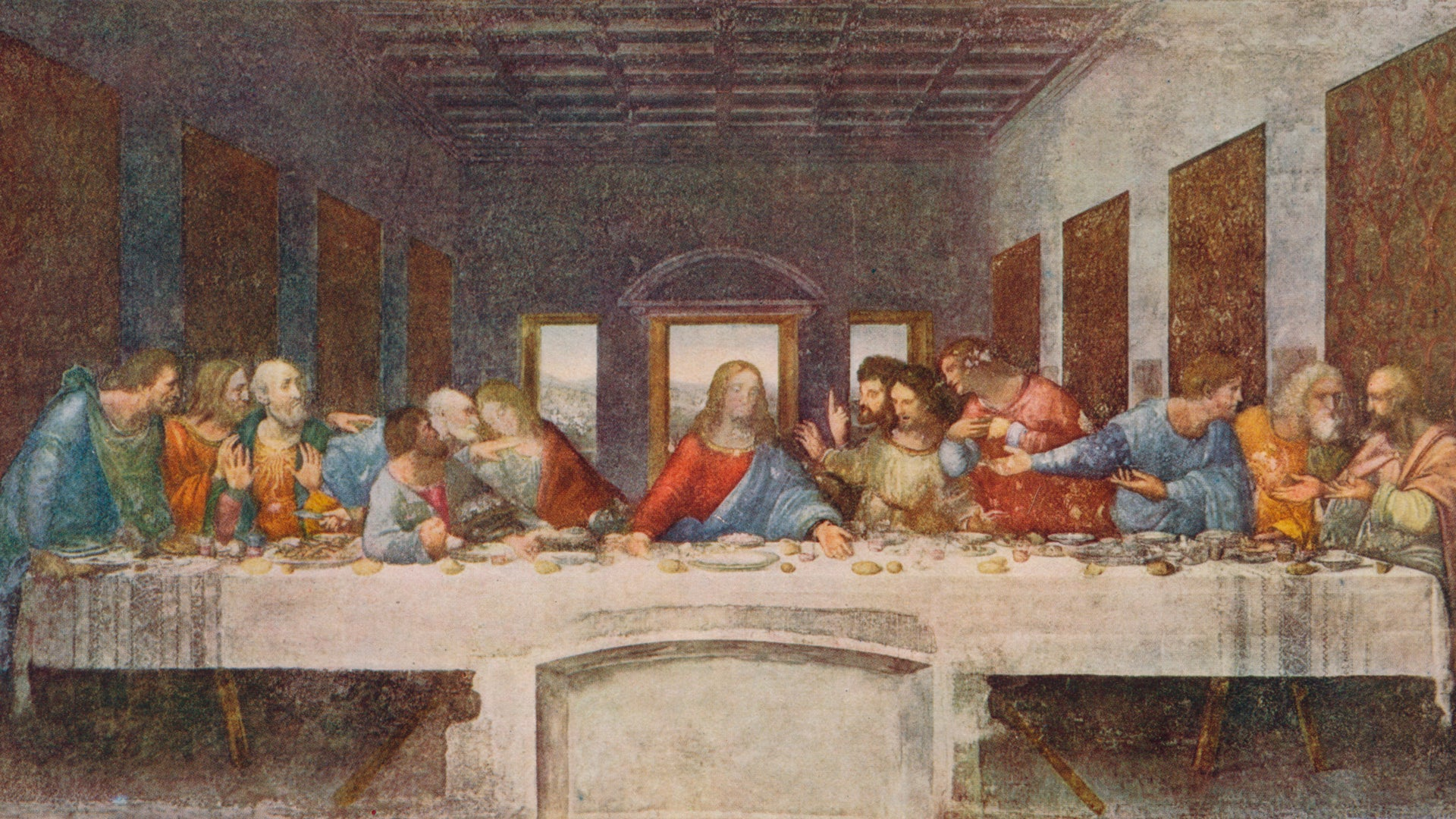
1494-1498
The Last Supper
Leonardo da Vinci
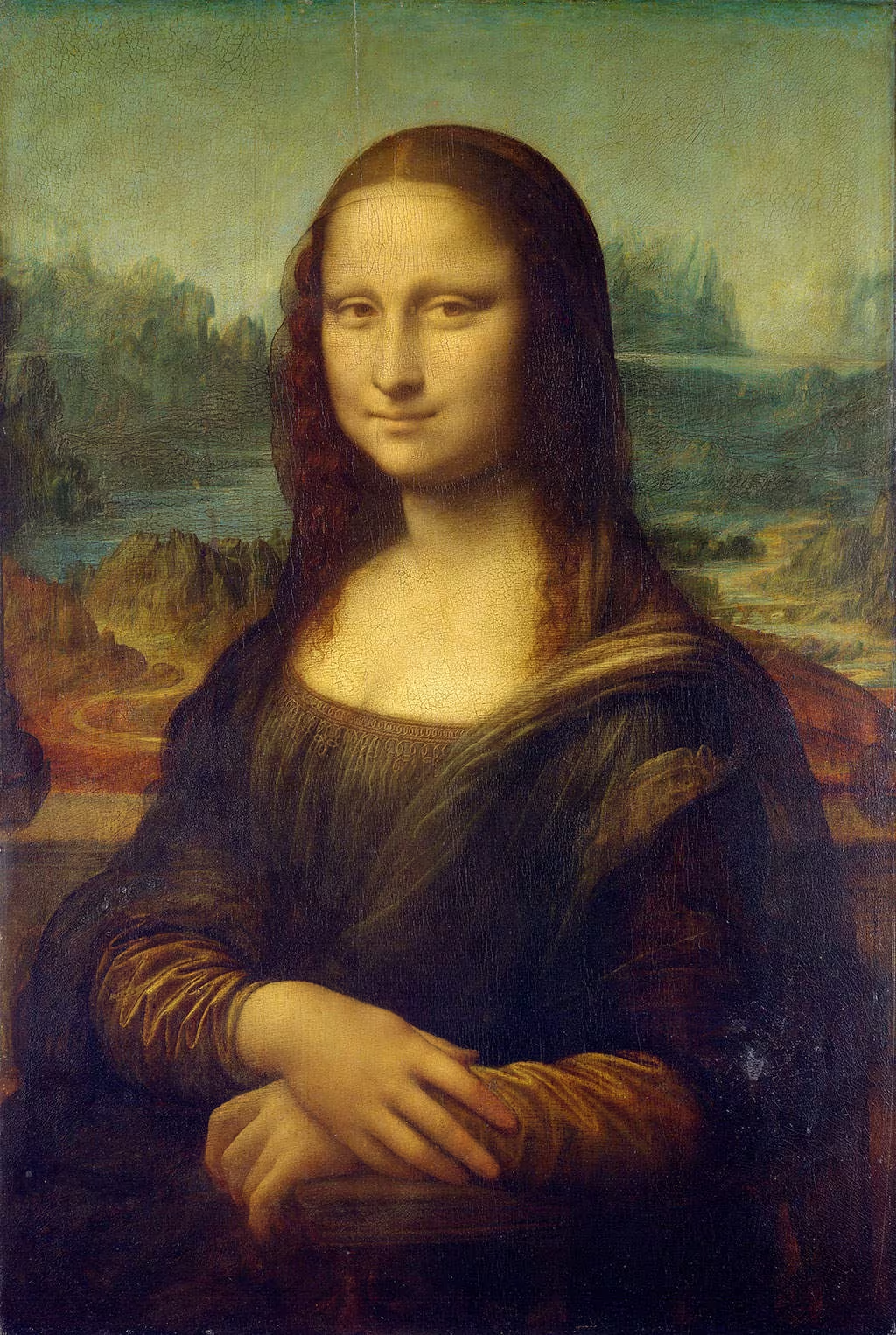

1503-1519
Mona Lisa

1517
Protestant
Reformation
Martin Luther

1532
The Prince 군주론
Niccolo Machiavelli
The Overture to "The Marriage of Figaro" was composed in 1786 by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart. It was written for Mozart's opera, Le nozze di Figaro (The Marriage of Figaro), which premiered on May 1, 1786, at the Burgtheater in Vienna. The overture itself was completed very shortly before the premiere,
Catholic's corruption

1515
Indulgence 면죄부
Pope Leo
On March 31 st 1515 Pope Leo X issued a bull of plenary indulgence to remove sins

1508-1514
Heliocentric Theory
Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus formulated his heliocentric theory, which places the sun at the center of the solar system, between 1508 and 1514, according to the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. He first presented his ideas in a short treatise called Commentariolus, according to History.com and NASA Earth Observatory. He later expanded on these ideas in his major work, De revolutionibus orbium coelestium (On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres), which was published in 1543, the year of his death.

1490 - 1500
The Garden of Earthly
Delights Triptych
Hieronymus Bosch
Hieronymus Bosch's most iconic artwork is undeniably "The Garden of Earthly Delights". This elaborate triptych, dating back to around 1490-1510, is renowned for its fantastical and surreal imagery, depicting a journey from Eden to hell with a central panel filled with bizarre and symbolic figures. It's a masterpiece that continues to captivate art lovers and historians alike due to its unique style and complex symbolism.
1600-1750
Baroque
The Baroque period, spanning roughly from 1600 to 1750, is a significant era in Western art history, encompassing a variety of artistic styles including painting, sculpture, architecture, music, and dance. It's known for its ornate, dramatic, and often theatrical characteristics. The Baroque is a highly ornate and elaborate style of architecture, art and design that flourished in Europe in the 17th and first half of the 18th century.
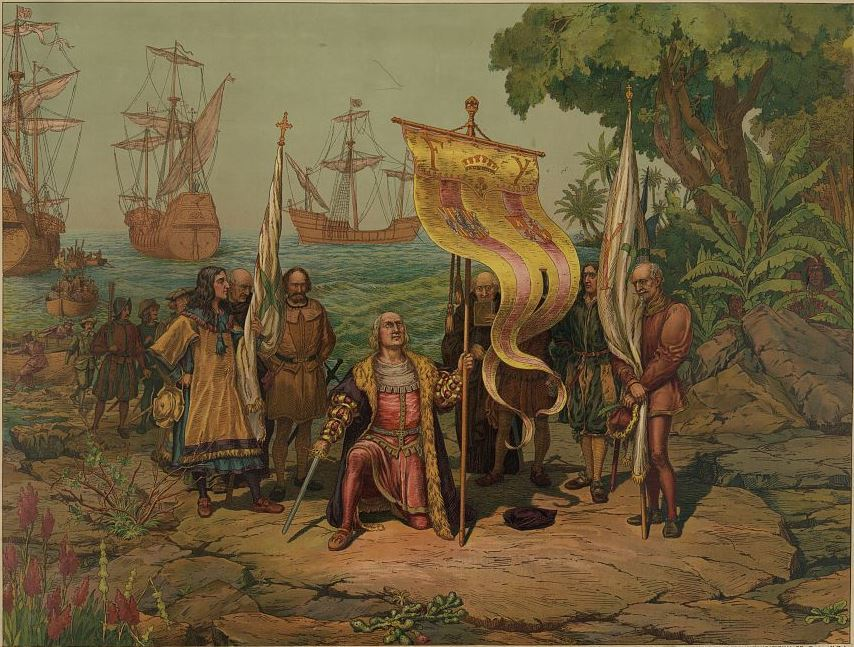
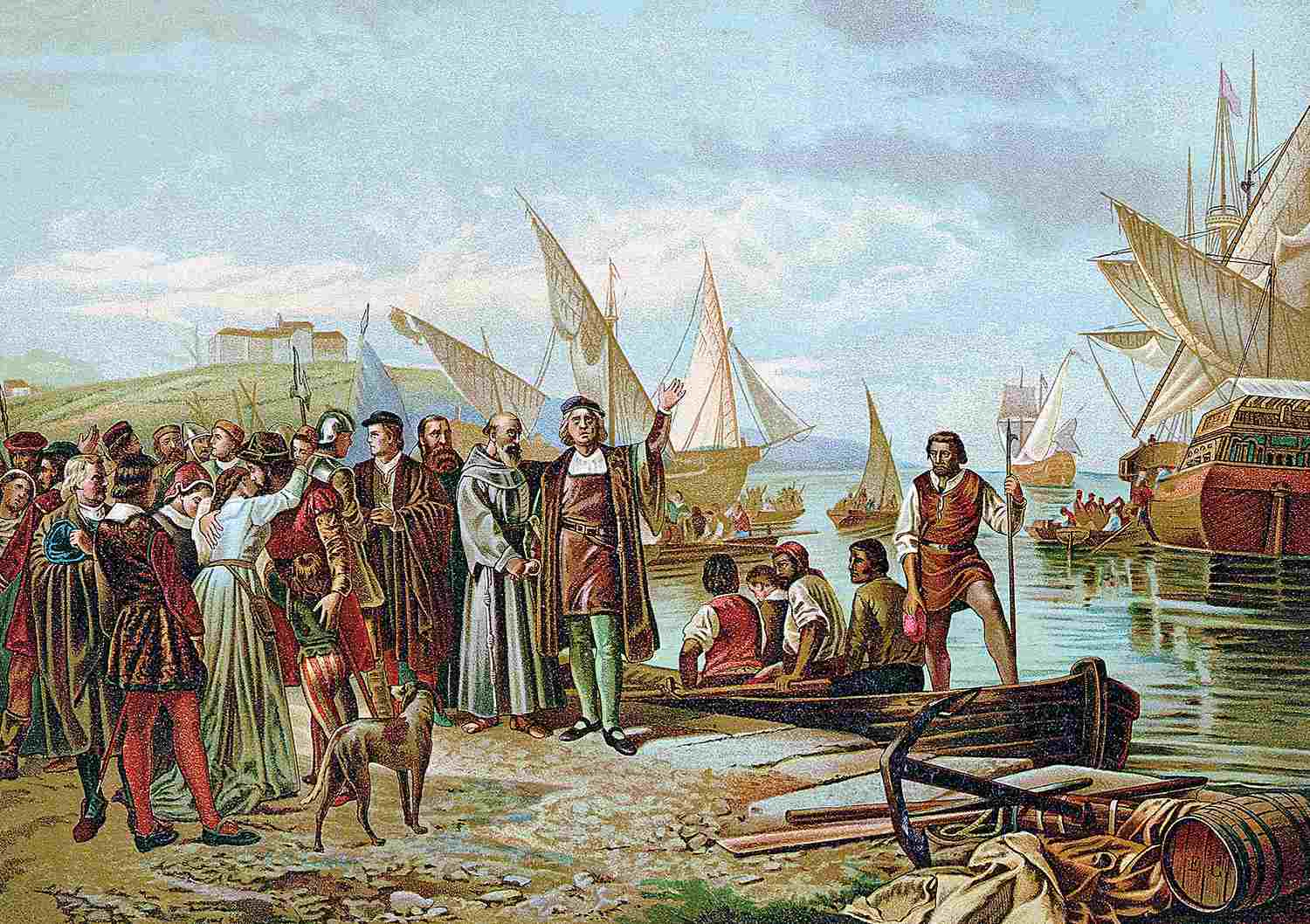


1492
Embarkation and Departure of Columbus from the Port of Palos
Illustration titled 'Embarkation and Departure of Columbus from the Port of Palos', On His First Voyage of Discovery, On The 3rd of August, 1492. Ricardo Balaca/Bettmann/Getty Images
Christopher Columbus made landfall in the Americas on October 12, 1492

1597-1599
Basket of Fruit
Caravaggio,
While still life painting had existed in some forms in earlier periods, including in ancient Egypt and Roman art, Caravaggio is widely considered one of the first to elevate still life to a prominent and independent genre in European painting, especially in Italy.
Biblioteca Ambrosiana, Milan, Italy.
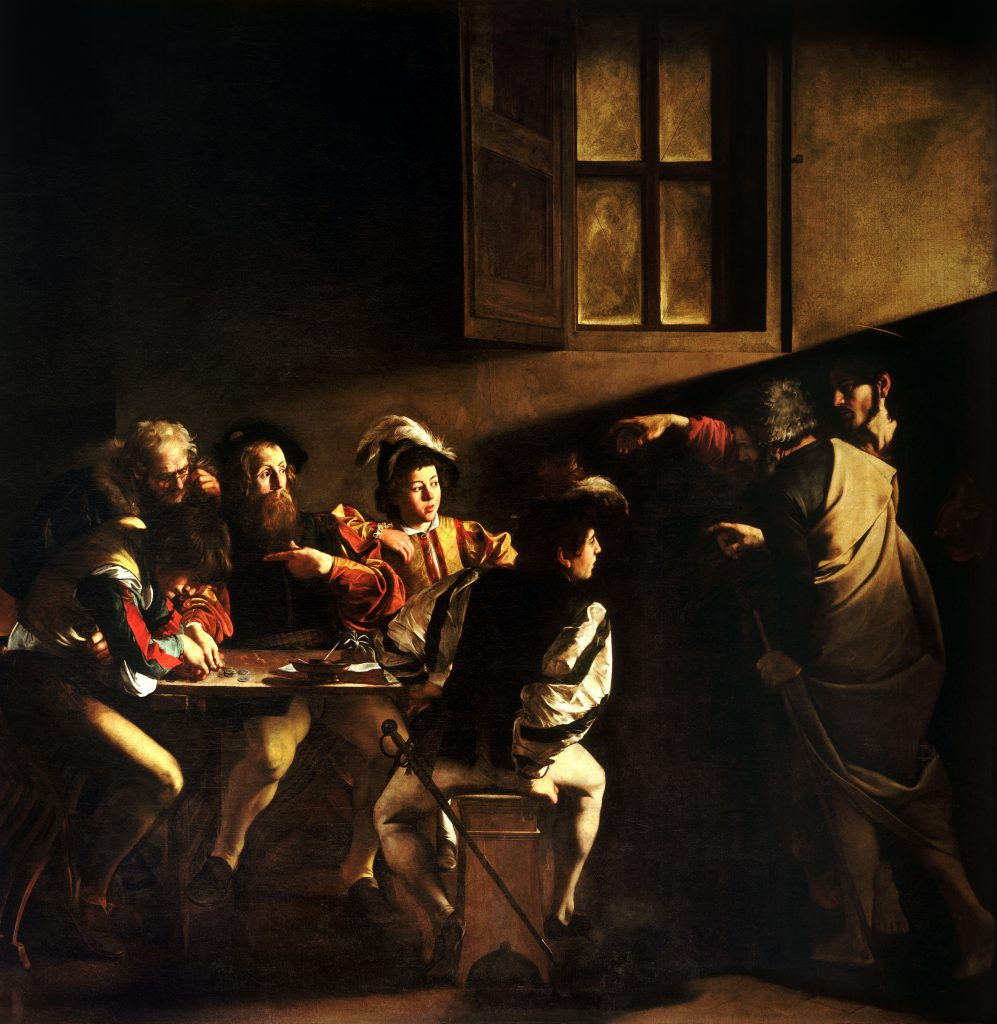

1599-
1600
The Calling of St. Matthew
Caravaggio,
San Luigi dei Francesi, Rome, Italy.
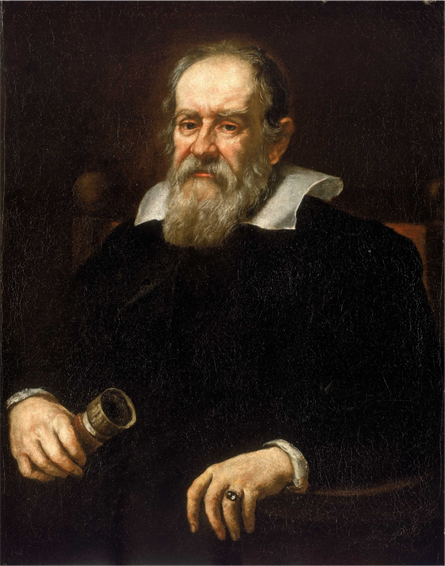
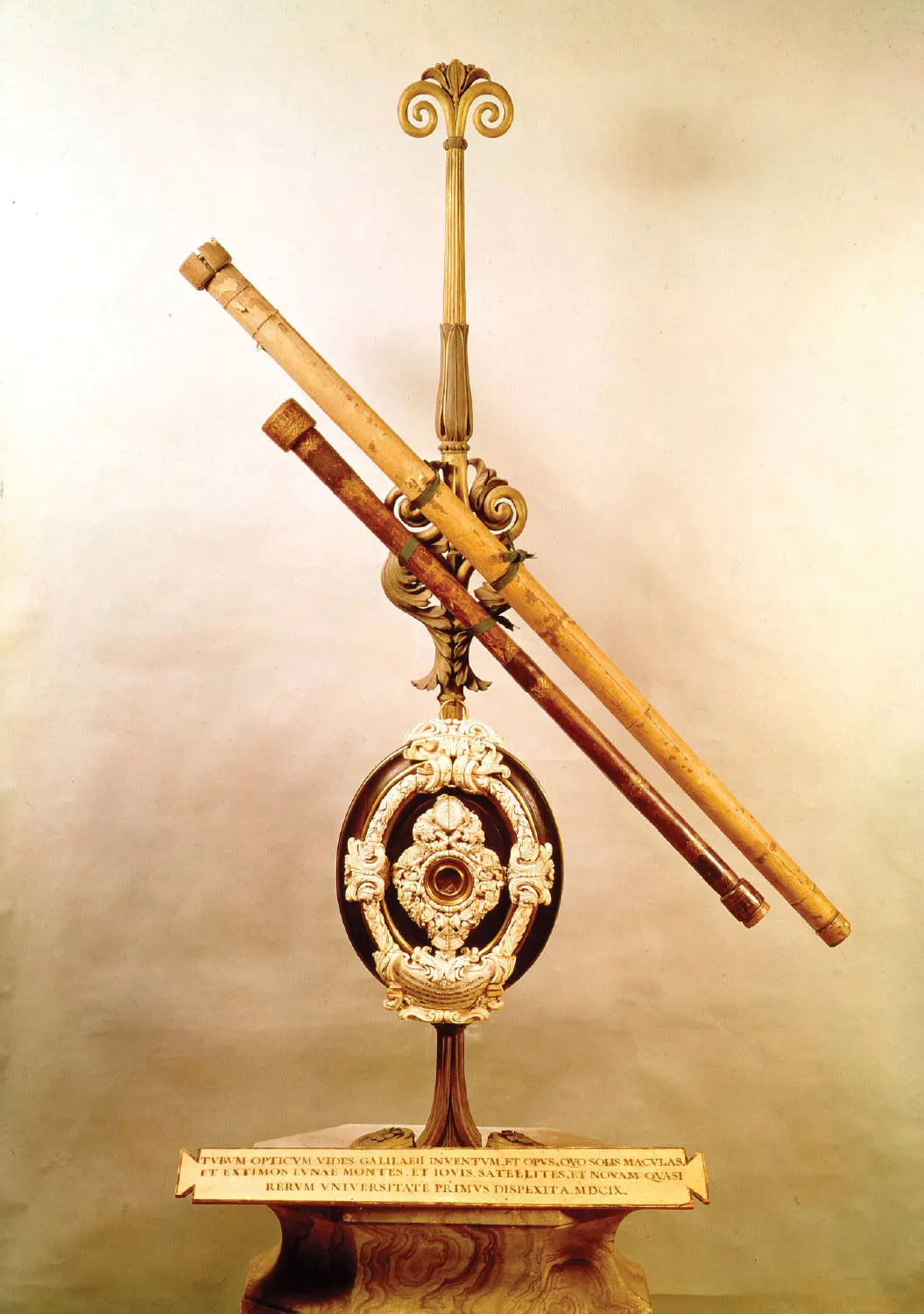


1633
sentenced by the Roman Inquisition
Galileo Galilei
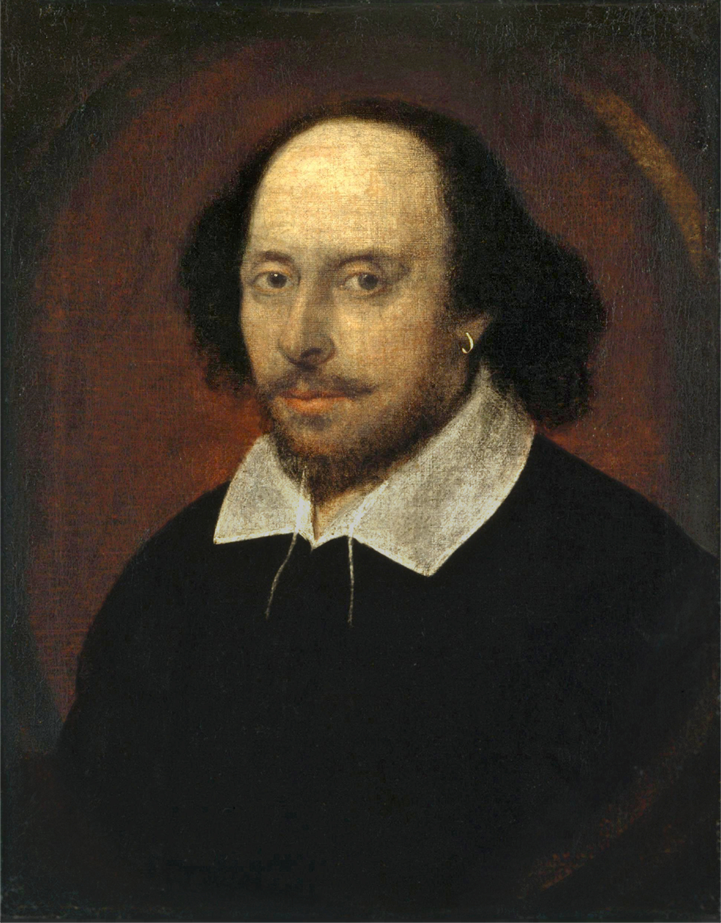

1599–1601
Hamlet
Shakespeare
1600s-1800s
Age of Discovery
대항해시대
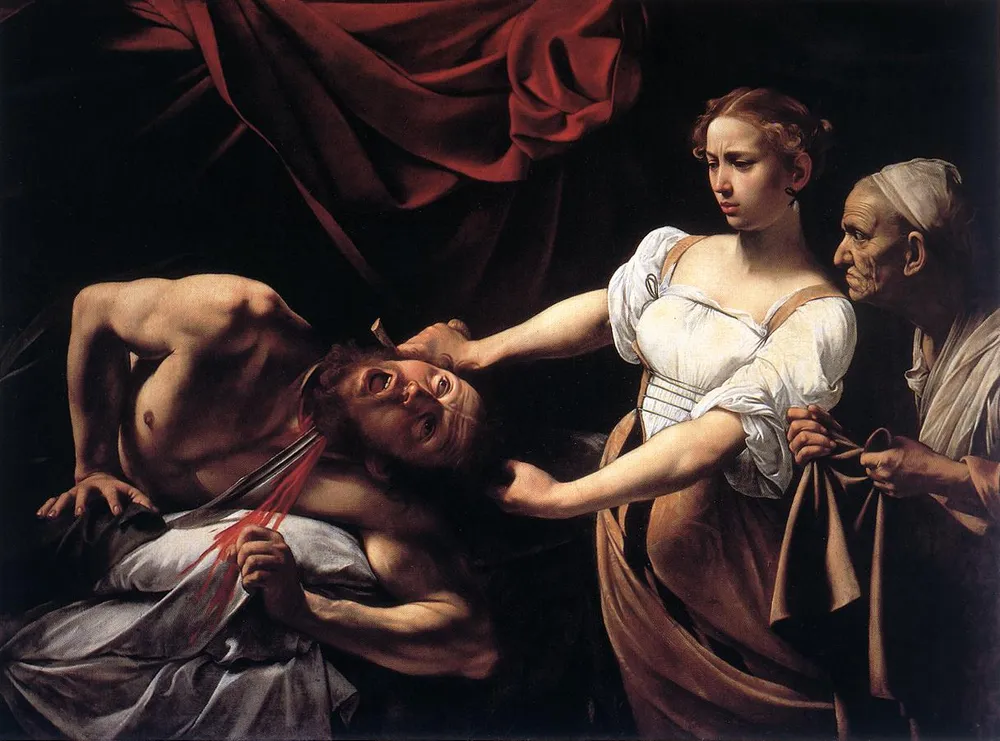

1599
Judith Beheading Holofernes
Caravaggio
"Judith Beheading Holofernes" is a famous painting by Michelangelo Merisi da Caravaggio, created around 1598-1599. It depicts the biblical story of Judith, a Jewish widow who saves her people by beheading the Assyrian general Holofernes. The painting is renowned for its dramatic realism, intense emotion, and use of chiaroscuro, a technique that employs strong contrasts between light and dark to create a dramatic effect.

1602
initial public offering (IPO)
Dutch East India Company
The modern stock market's origins trace back to 17th-century Europe, specifically Amsterdam, where the Dutch East India Company pioneered the first initial public offering (IPO) in 1602. Formal stock exchanges emerged later, with the Amsterdam Stock Exchange established in 1611. In the United States, the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) traces its roots to the Buttonwood Agreement of 1792.
rise of Capitalism
1618-1648
The Thirty Years' War
A devastating war in Europe, initially sparked by religious conflicts between Catholics and Protestants, but later involving political and dynastic factors.
one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648
1715-1775
Rococo
"Late Baroque", is an 18th-century artistic movement and style, affecting many aspects of the arts including painting, sculpture, architecture, interior design, decoration, literature, music, and theatre. It developed in the early 18th century in Paris, France as a reaction against the grandeur, symmetry, and strict regulations of the Baroque, especially of the Palace of Versailles.

1637
Discourse on the Method
René Descartes
"I think, therefore I am"
Discourse on the Method of Rightly Conducting One's Reason and of Seeking Truth in the Sciences is a philosophical and autobiographical treatise published by René Descartes in 1637. It is best known as the source of the famous quotation "Je pense, donc je suis", which occurs in Part IV of the work.
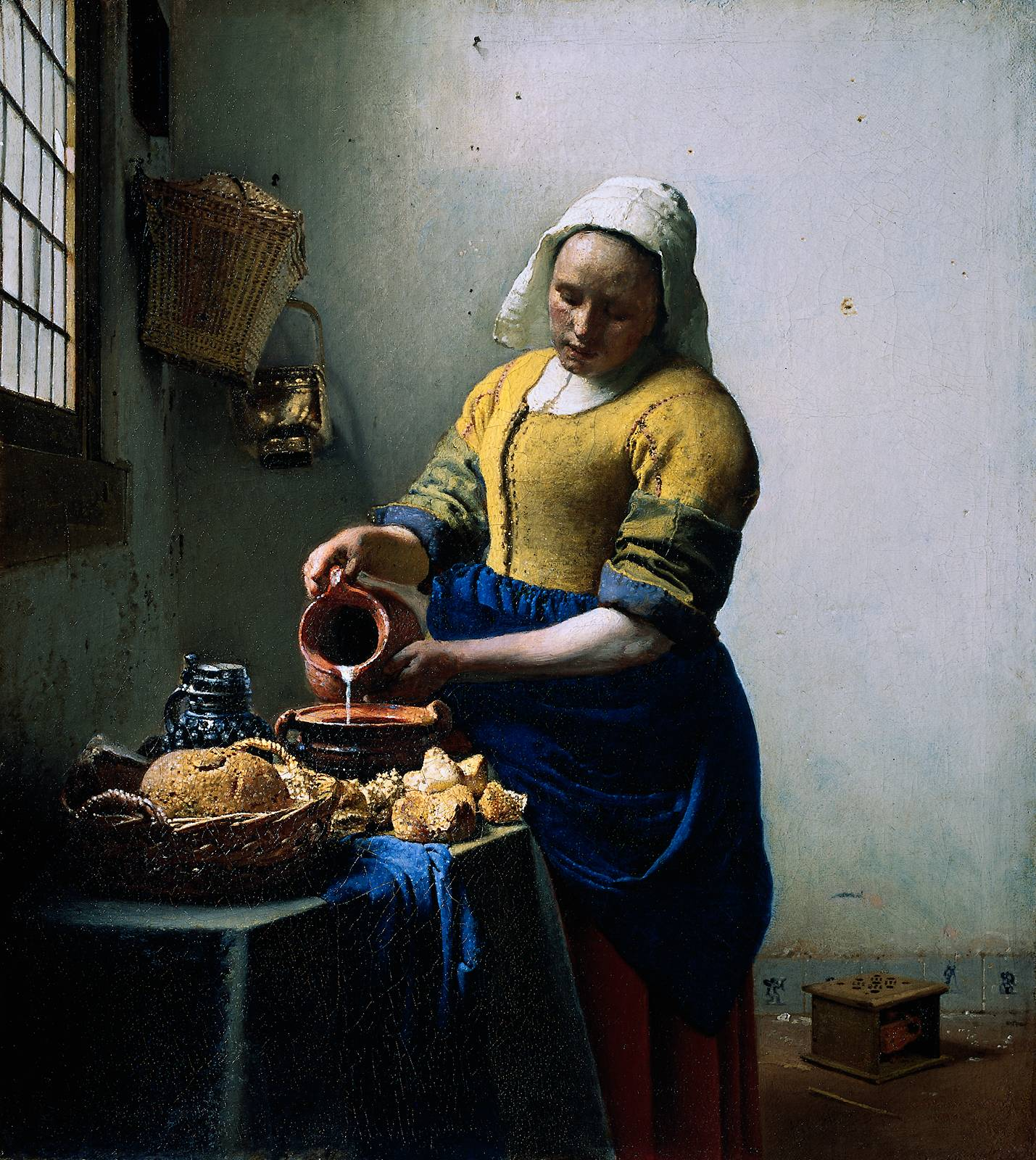

1658
Kitchen Maide
There was Protestant art during the Baroque period, but it differed significantly from Catholic Baroque art. While Catholic Baroque art often focused on religious subjects and grand, dramatic displays to reinforce the Counter-Reformation, Protestant Baroque art emphasized secular subjects like landscapes, portraits, and scenes of everyday life. This shift was largely due to the Protestant Reformation, which discouraged the use of religious imagery in churches
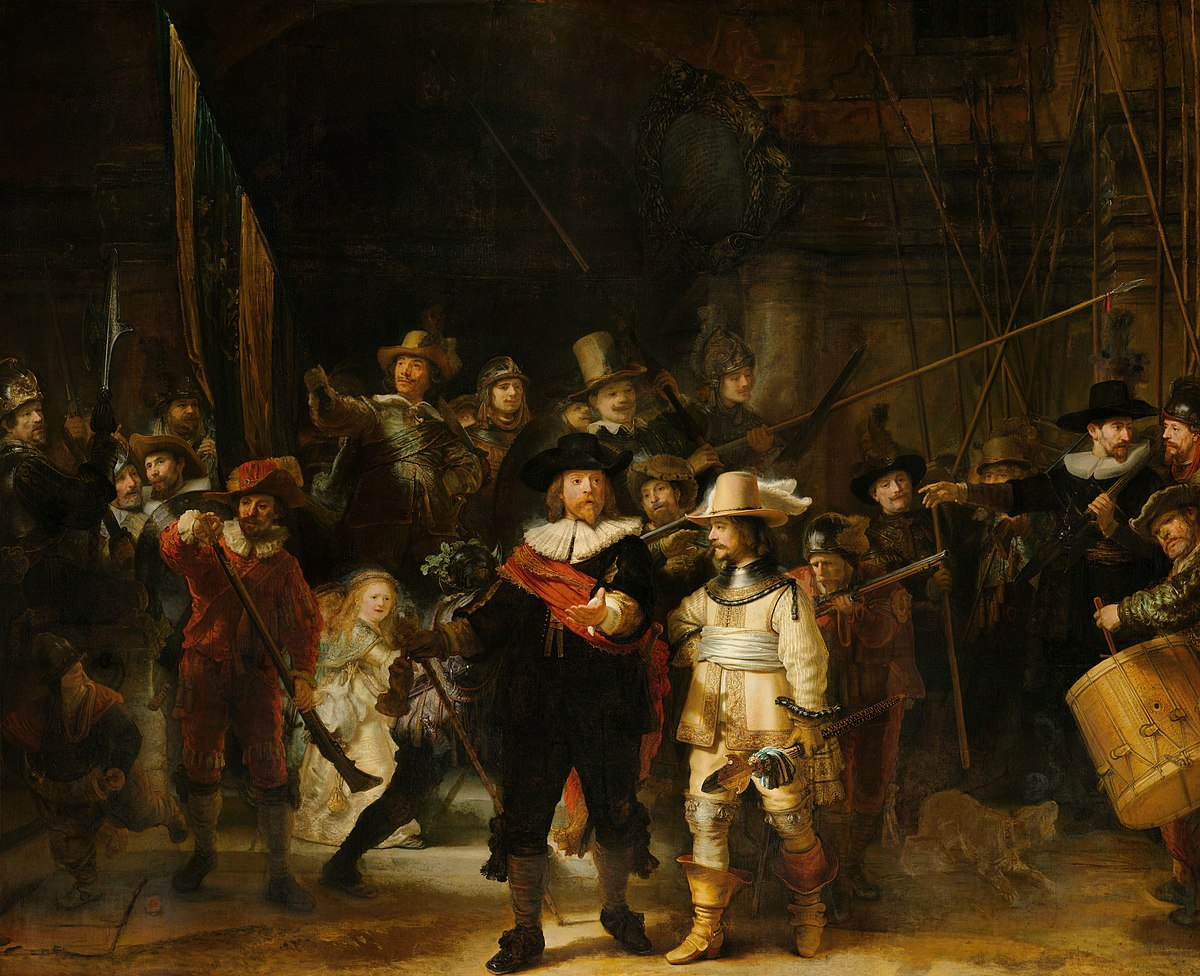

1642
The Night Watch
Rembrandt
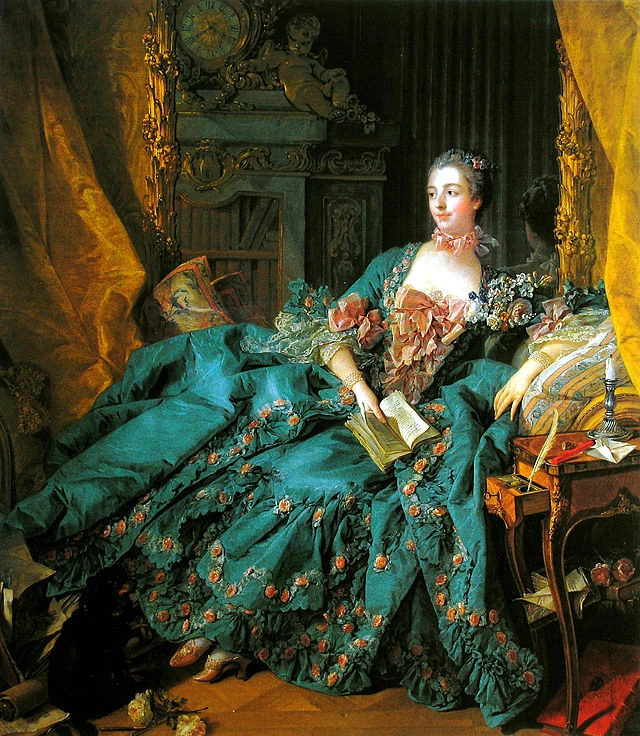

1756
Madame de Pompadour
the Overture from The Marriage of Figaro
The Overture to "The Marriage of Figaro" was composed in 1786 by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart. It was written for Mozart's opera, Le nozze di Figaro (The Marriage of Figaro), which premiered on May 1, 1786, at the Burgtheater in Vienna. The overture itself was completed very shortly before the premiere,

1711
The Spectator
Joseph Addison and Richard Steele
The earliest newspaper known as "The Spectator" was a British periodical published in London by Joseph Addison and Richard Steele. It was first published on March 1, 1711, and ran until December 6, 1712, with a revival in 1714. The Spectator was known for its essays on politics, society, and manners, often presented through the fictional character of "the Spectator".
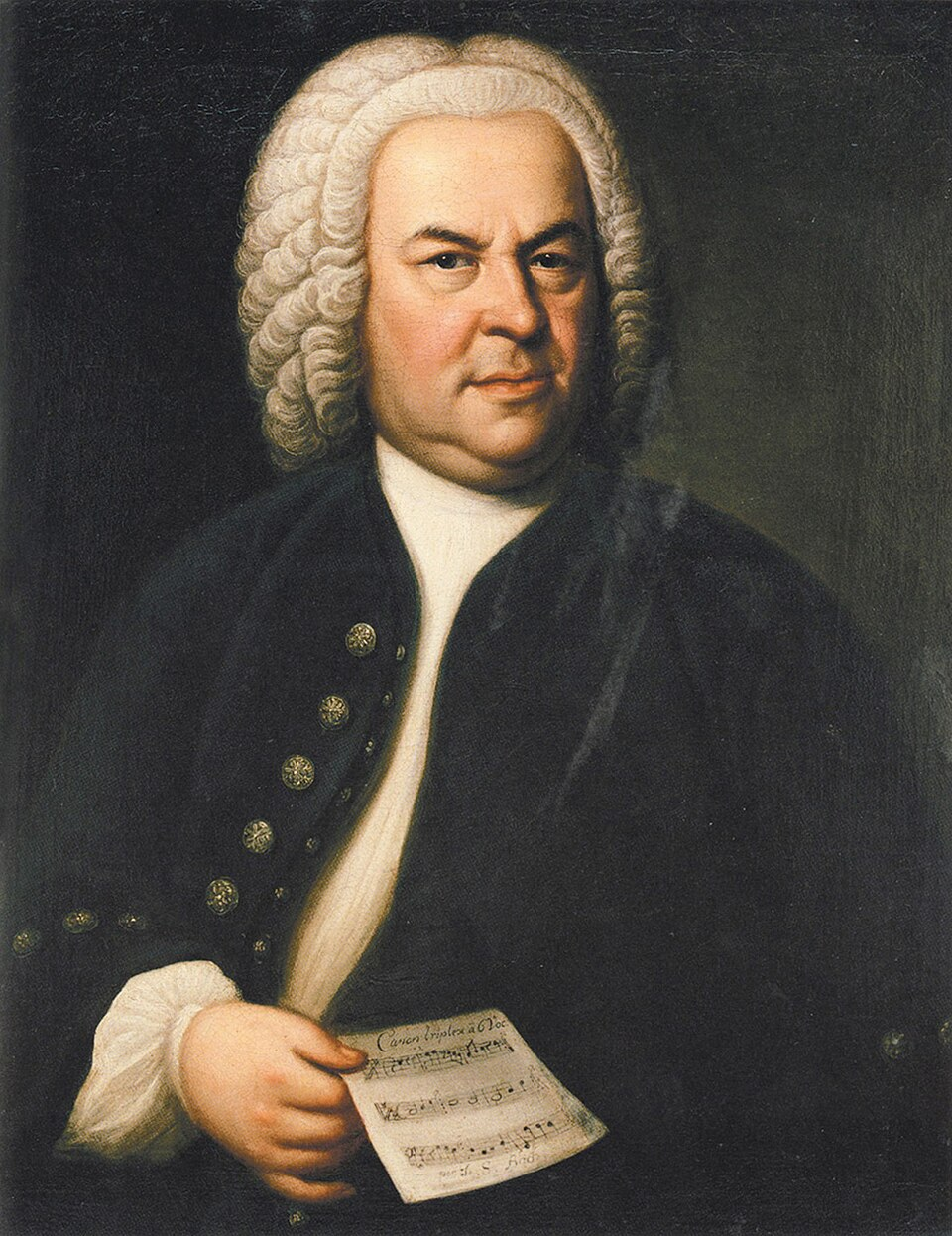

1721
The Brandenburg Concertos
Johann Sebastian Bach

1759
The Invisible Hand
Adam Smith

1759
The Theory of Moral Sentiments
Adam Smith
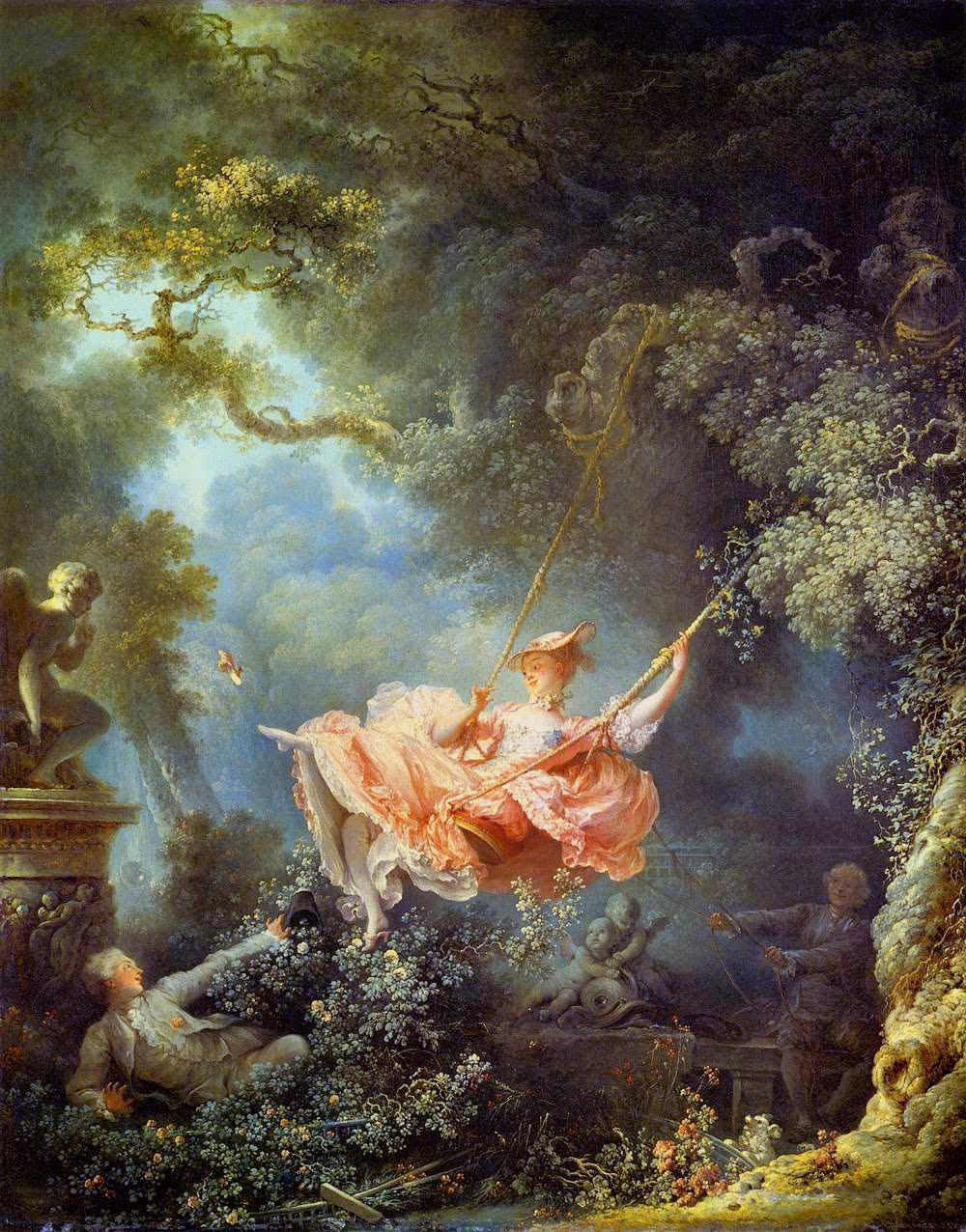

1766
The swing
Jean-Honoré Fragonard
1750-1820
classicism
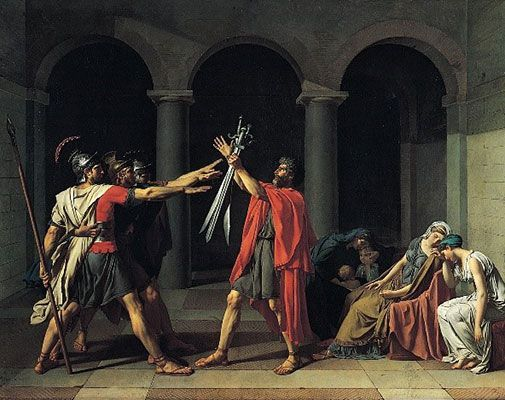

1784
Oath of the Horatii
Jacques-Louis David
Oath of the Horatii (French: Le Serment des Horaces) is a large painting by the French artist Jacques-Louis David painted in 1784 and 1785 and now on display in the Louvre in Paris.[1] The painting immediately became a huge success with critics and the public and remains one of the best-known paintings in the Neoclassical style.
vs

1787
The Death of Socrates
Jacques-Louis David
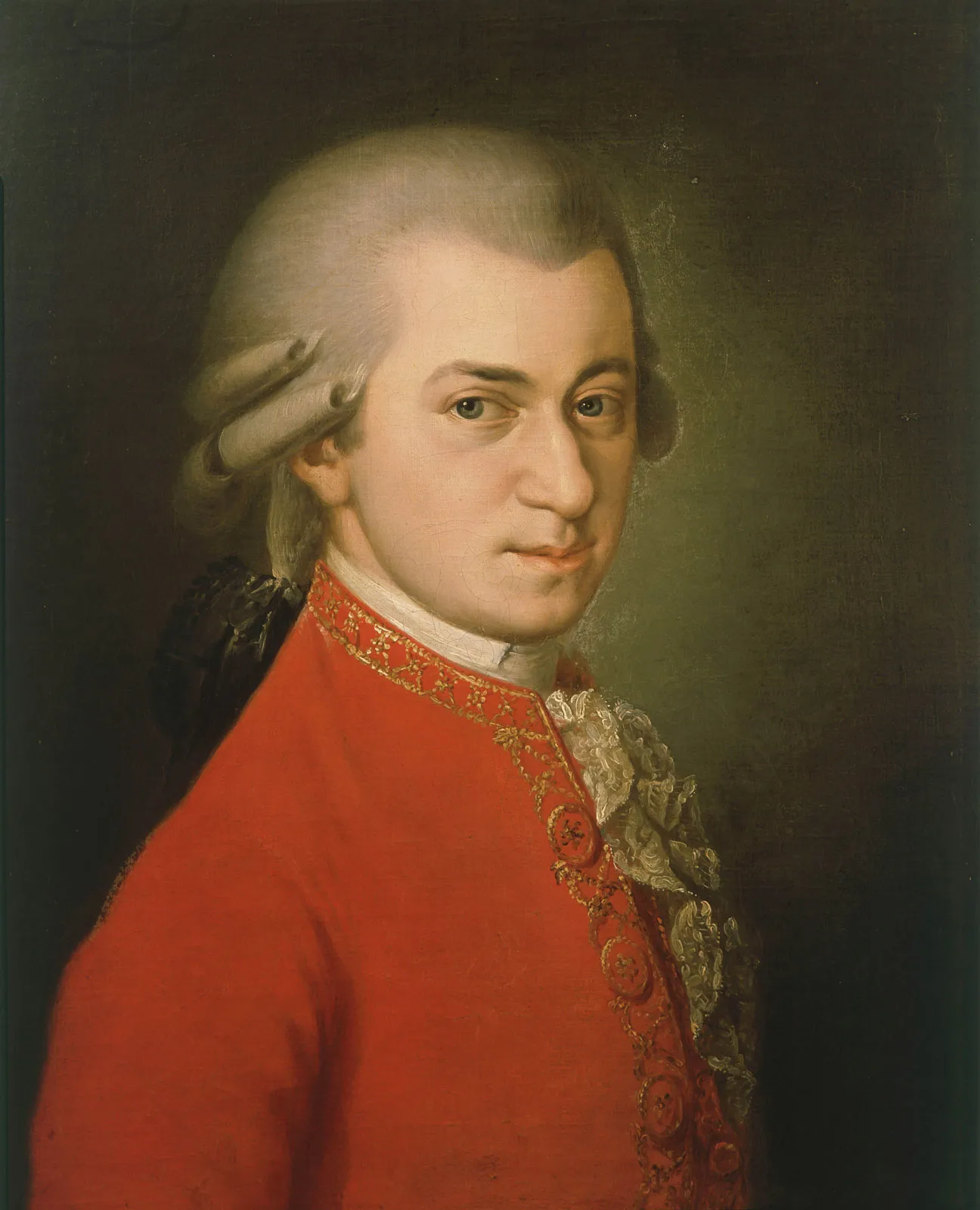

1786
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
the Overture from The Marriage of Figaro
The Overture to "The Marriage of Figaro" was composed in 1786 by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart. It was written for Mozart's opera, Le nozze di Figaro (The Marriage of Figaro), which premiered on May 1, 1786, at the Burgtheater in Vienna. The overture itself was completed very shortly before the premiere,

1762
The Social Contract
Jean-Jacques Rousseau
The

1784
Critique of Pure Reason
Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant's most famous and arguably most influential book is his Critique of Pure Reason. Published in 1781 (with a revised edition in 1787), it is considered a landmark text in modern philosophy, particularly in metaphysics and epistemology.
May 1789 – Nov 1799
French Revolution
#1 SOCIAL INEQUALITY IN FRANCE DUE TO THE ESTATES SYSTEM
#2 TAX BURDEN ON THE THIRD ESTATE
#3 THE RISE OF THE BOURGEOISIE
#4 IDEAS PUT FORWARD BY ENLIGHTENMENT PHILOSOPHERS
#5 FINANCIAL CRISIS CAUSED DUE TO COSTLY WARS
#6 DRASTIC WEATHER AND POOR HARVESTS IN THE PRECEDING YEARS
#7 THE RISE IN THE COST OF BREAD
#8 INEFFECTIVE LEADERSHIP OF LOUIS XV AND LOUIS XVI
#9 PARLEMENTS’ SUCCESSFUL OPPOSITION TO REFORMS
#10 THE EXTRAVAGANT LIFESTYLE OF THE FRENCH MONARCHY
Discovery
of
Individual

1793
The Death of Marat
Jacques-Louis David

Jan 1793
Execution of Louis XVI
During the French Revolution, the guillotine became the primary symbol of capital punishment and was used to execute thousands of people, including King Louis XVI and Marie Antoinette. The guillotine was a machine designed to swiftly and cleanly sever the head, and it was seen as a symbol of revolutionary equality because it was used on nobles and commoners alike. The execution of King Louis XVI in 1793 was a pivotal moment in the revolution, signaling the end of the monarchy and the beginning of a new era of republican ideals.

1806
The Coronation of Napoleon
Jacques-Louis David
Dec 1804
Napoleon crowned emperor
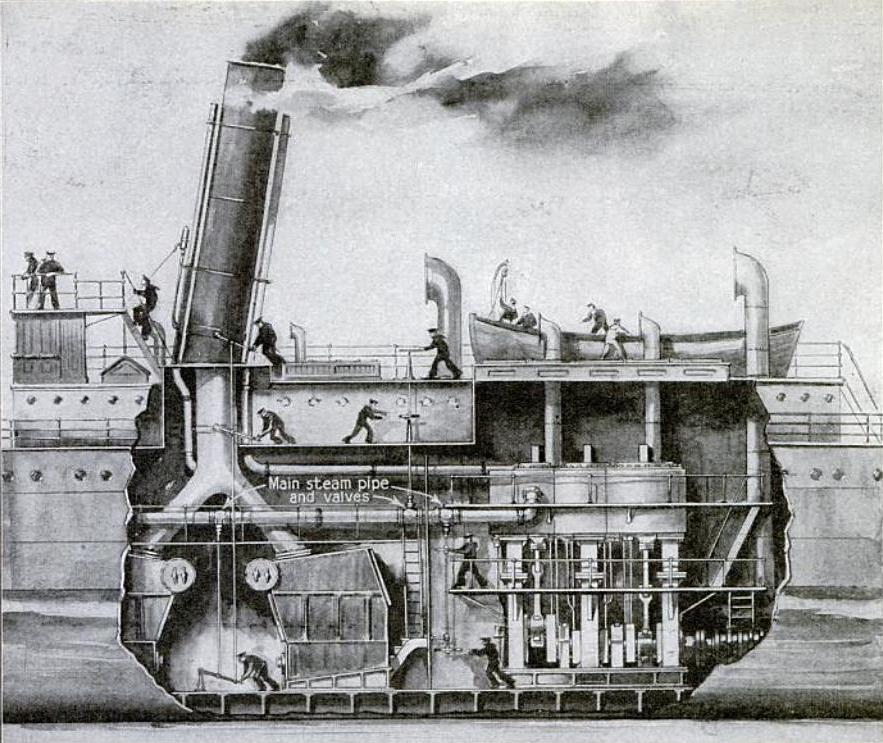
1807
invention of the steamboat
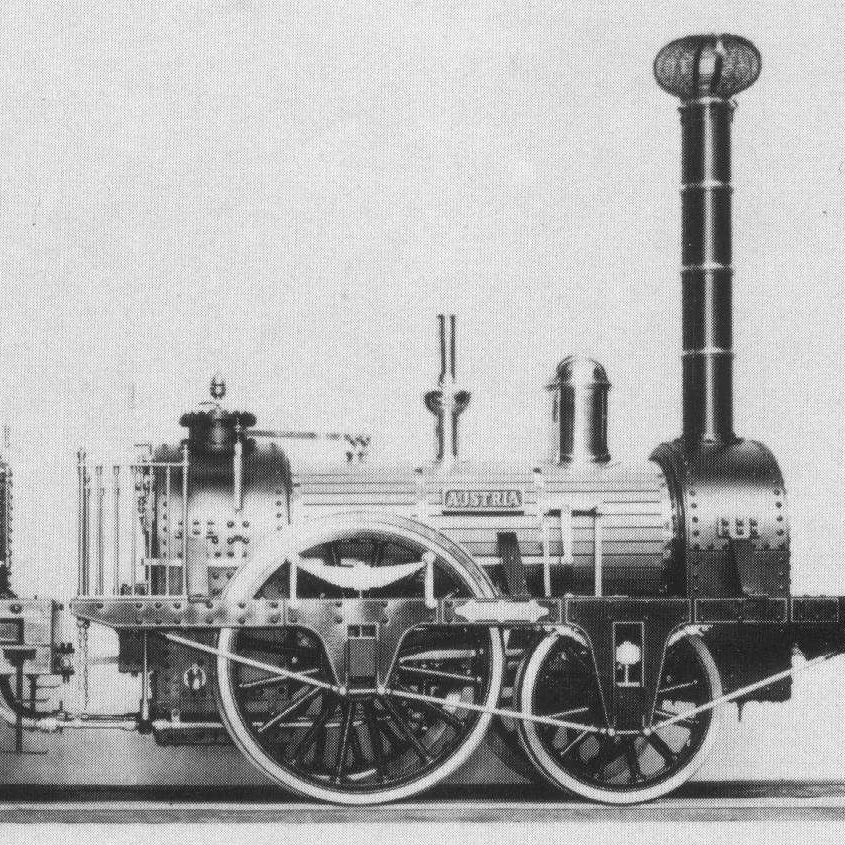
1804
Pen-y-darren
Steam
Engine

1807
The Phenomenology of Spirit
Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel
Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel's most famous and influential book is The Phenomenology of Spirit (also sometimes translated as Phenomenology of Mind), published in 1807. It is a foundational text in modern philosophy, outlining his unique approach to the relationship between consciousness and reality.
1760-1840
Industrial Revolution
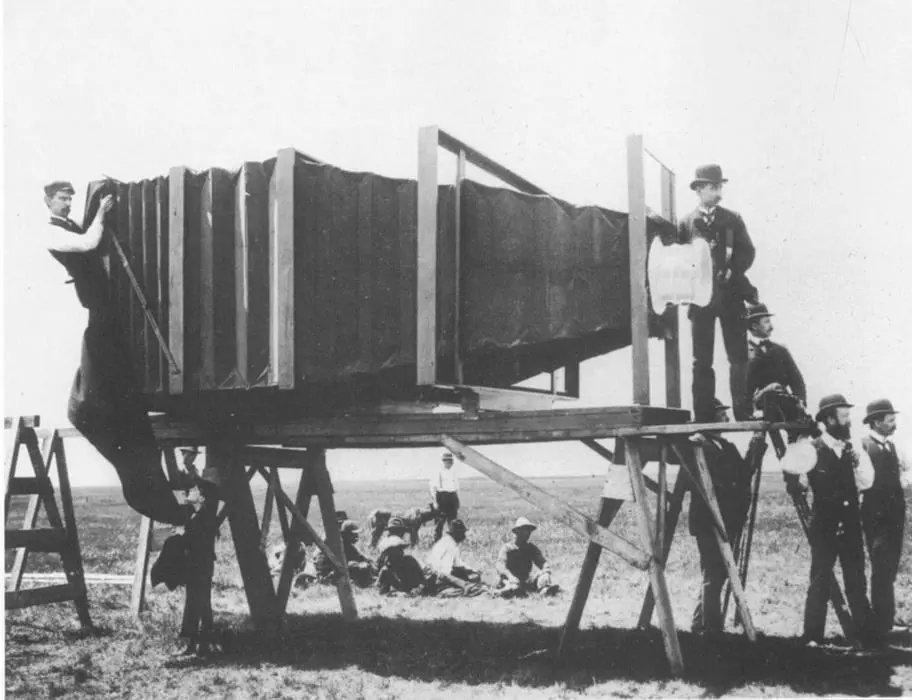
1816
first camera

1811-1816
Luddites

1814
The Third of May 1808
Francisco Goya
"The Third of May 1808" is a powerful anti-war painting by Francisco Goya, completed in 1814, that depicts the aftermath of the Dos de Mayo Uprising in Madrid. It portrays the execution of Spanish civilians by French soldiers, emphasizing the brutality and human cost of conflict. The painting is renowned for its emotional intensity, innovative composition, and its impact as one of the first modern works of art.
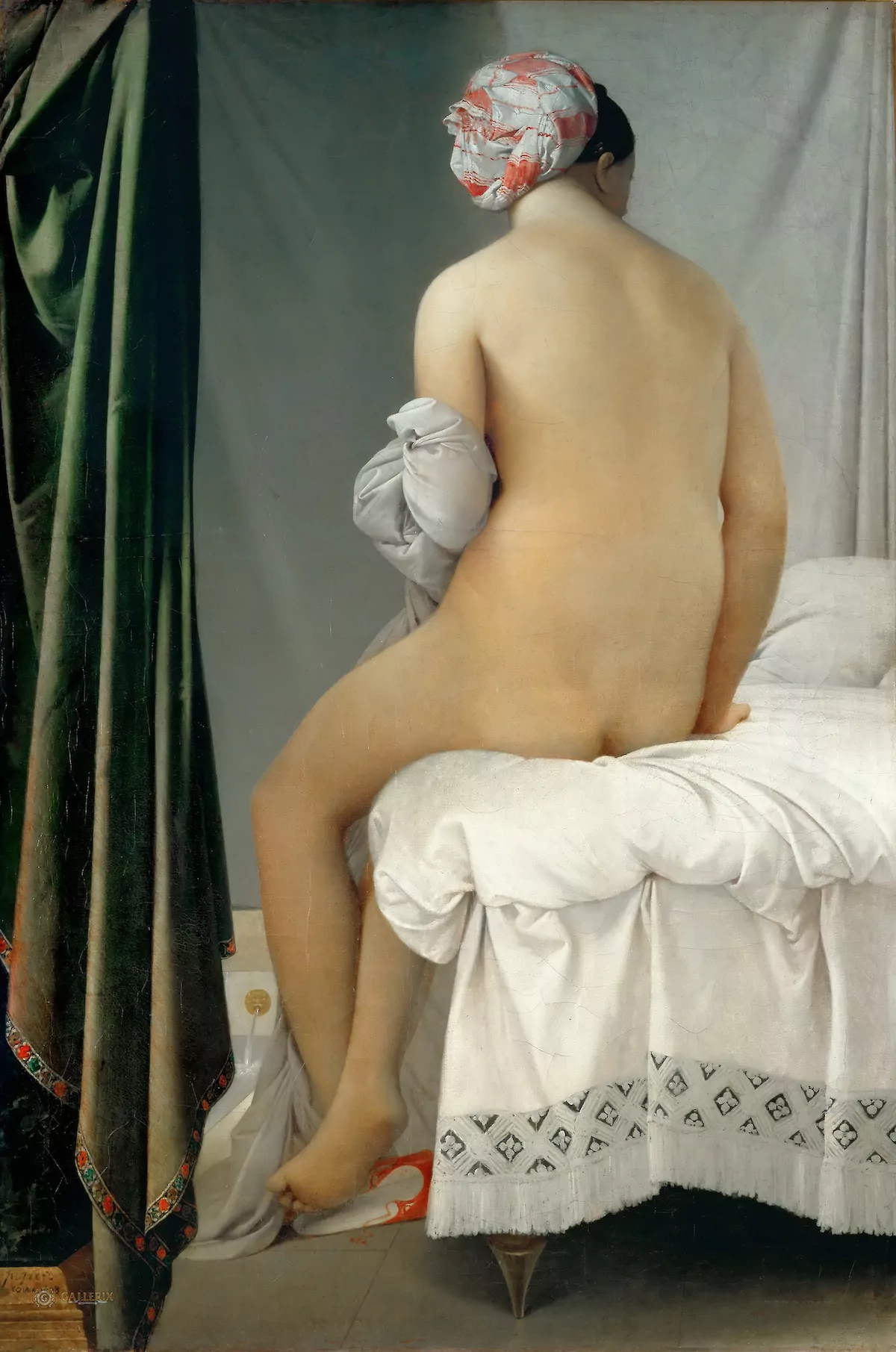

1808
Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres
1815
Napoleon Bonaparte defeated at the Battle of Waterloo,
1808
the first movement of the
Fifth Symphony
Ludwig van Beethoven
A devastating war in Europe, initially sparked by religious conflicts between Catholics and Protestants, but later involving political and dynastic factors.
one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648
Camera
Productivity

1830
Liberty Leading the People
Eugene Delacroix
"Liberty Leading the People" is a famous painting by Eugène Delacroix, completed in 1830, depicting the July Revolution in France. It symbolizes the struggle for liberty and is considered a masterpiece of French Romanticism.
1824
The National Gallery in London
Individual

1886
The Statue of Liberty
Frédéric Auguste Bartholdi,
Richard Morris Hunt

1845
A Little Match Girl
Hans Christian Andersen

Feb 1848
The Communist Manifesto
Karl Marx, Friedrich Engels
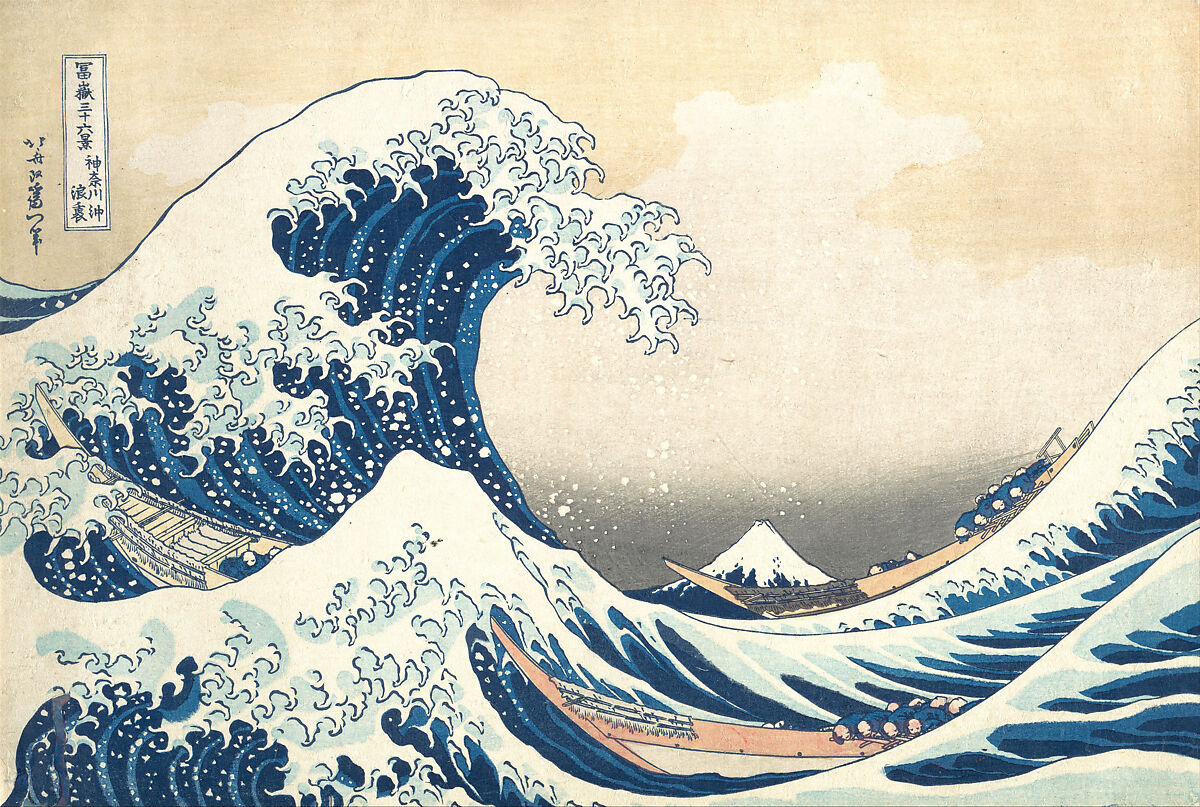

1831
The Great Wave off Kanagawa
Hokusai

1840
paint tube

1838
Oliver Twist
Charles Dickens

Victorian era
The Victorian era was the reign of Queen Victoria,
from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January
1901.
Paint
Tube
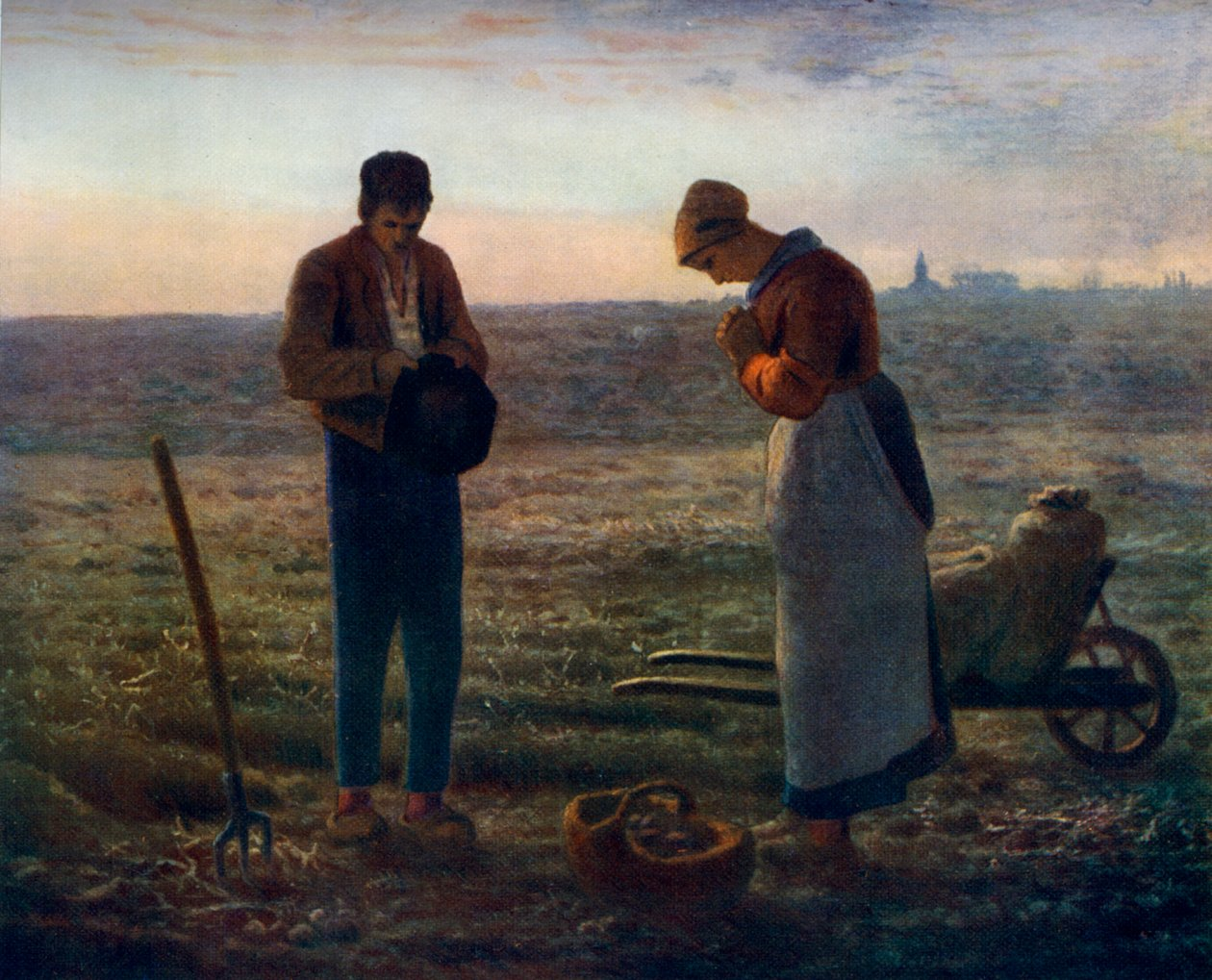

1857
The Angelus
Jean Francois Millet
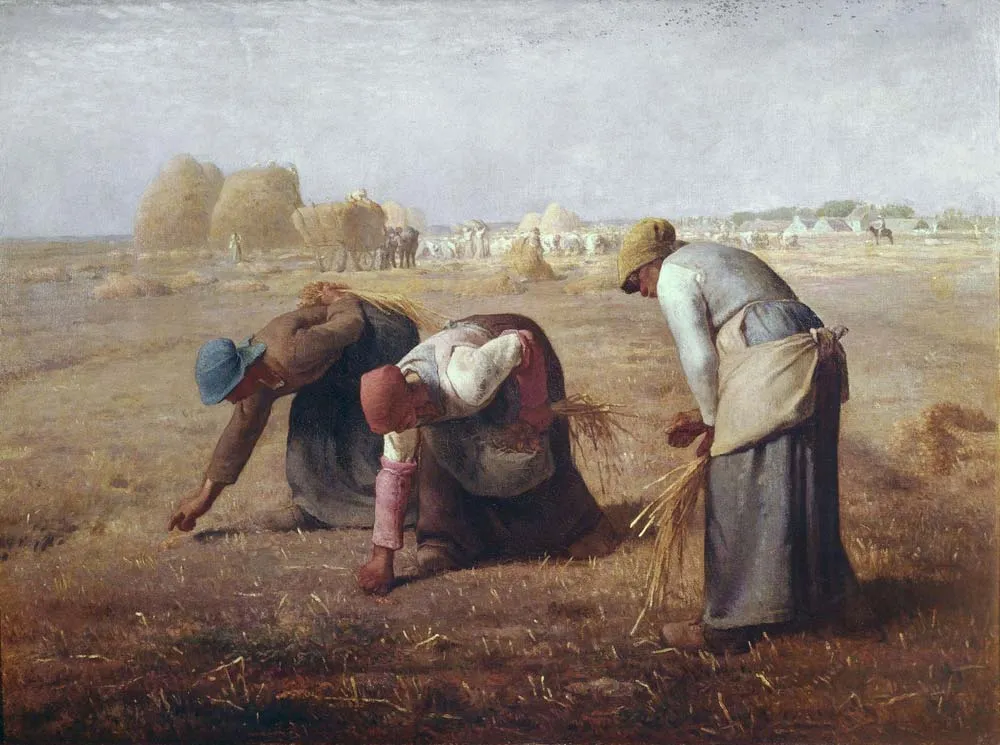

1857
The Gleaners
Jean Francois Millet

Nov 1859
Origin of
the species
Origin
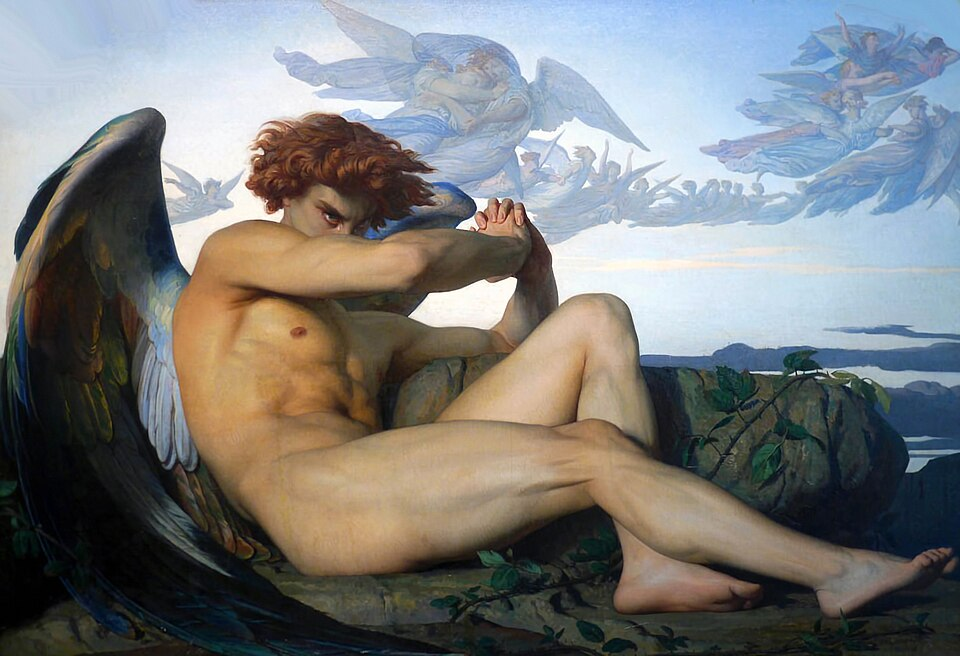

1847
The Fallen Angel
Alexandre Cabanel
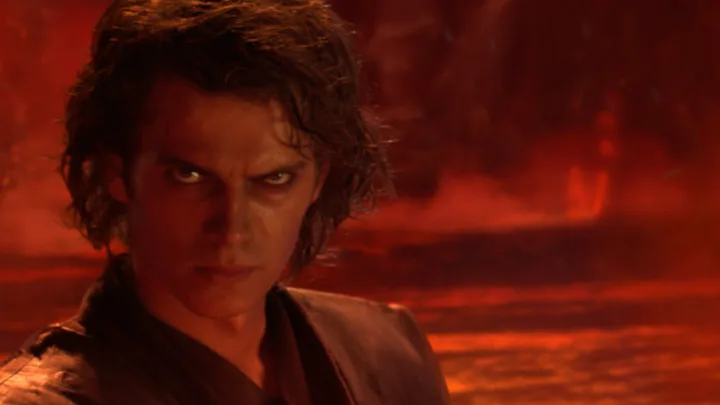

May 2005
Star Wars : E3
Revenge of the Sith
George Lucas

March 31, 1862
Les Misérables
Victor Hugo

drawing of Victor Hugo
the period of settled and comfortable life preceding World War I.
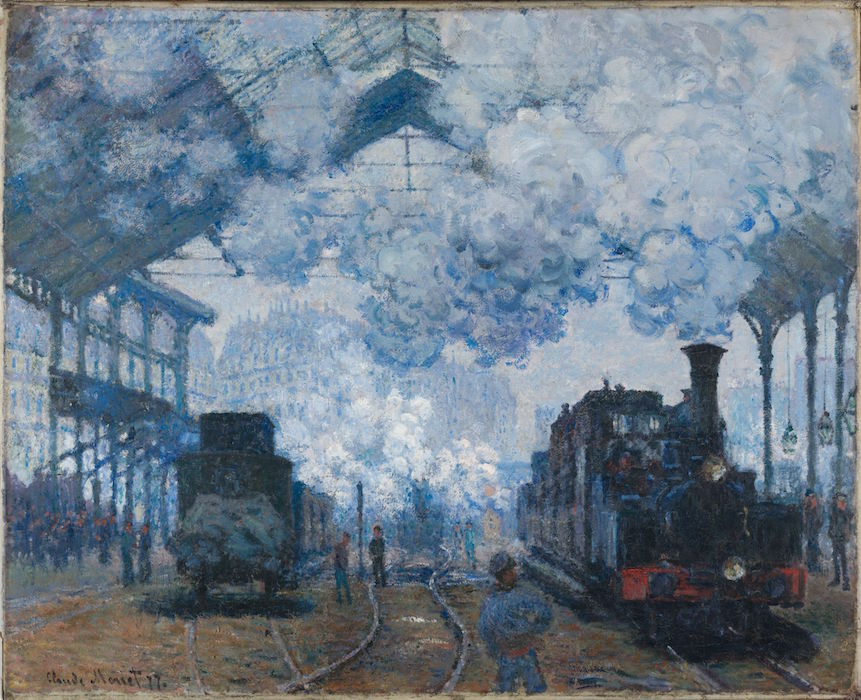

1877
The Gare Saint-Lazare: Arrival of a Train, Monet
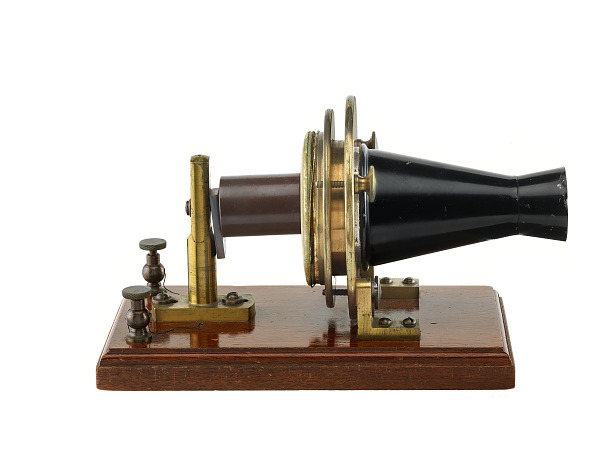

1876
Invention of Telephones
Alexander Graham Bell

1874
The First Impressionist Exhibition. Paris
1860s-1880s
Impressionism

1863
Olympia
Manet
1871-1914
Belle Époque
1867
Das Kapital
Karl Marx

1877
Paris Street; Rainy Day
Gustave Caillebotte

1876
Bal du moulin de la Galette (Dance at Le moulin de la Galette)
Pierre-Auguste Renoir
Individual
Camera
Paint Tube
Train
Productivity

1883
Thus Spoke Zarathustra
1879
Thomas Edison's development of the electric power system
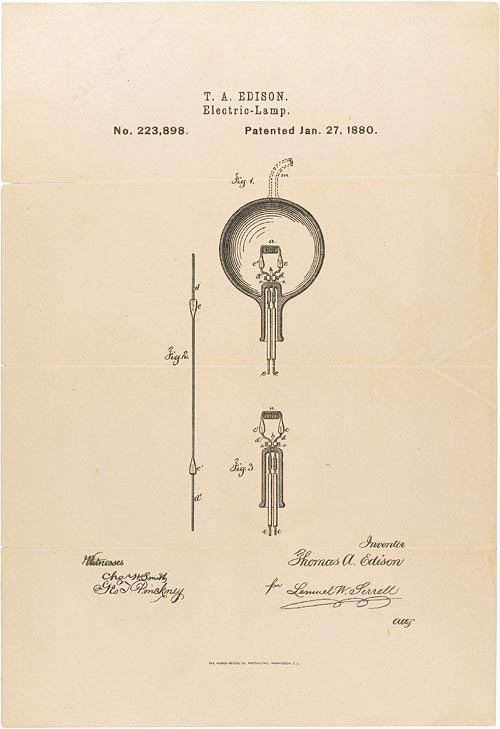

1880
Light bulb
Edison
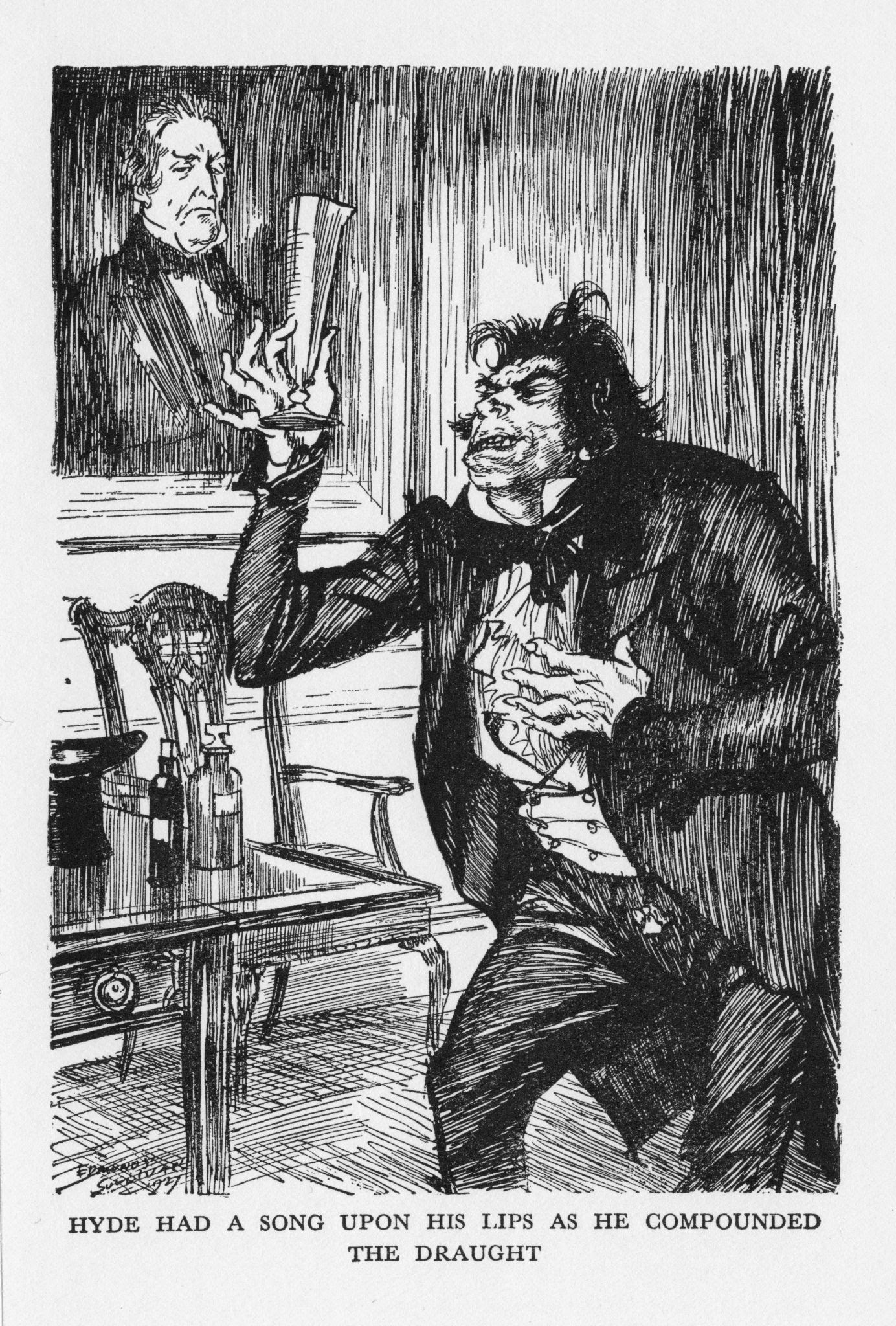

1886
Strange Case of Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde
Robert Louis Stevenson
Strange Case of Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde is an 1886 Gothic horror novella by Scottish author Robert Louis Stevenson. It follows Gabriel John Utterson, a London-based legal practitioner who investigates a series of strange occurrences between his old friend, Dr. Henry Jekyll, and a murderous criminal named Edward Hyde.
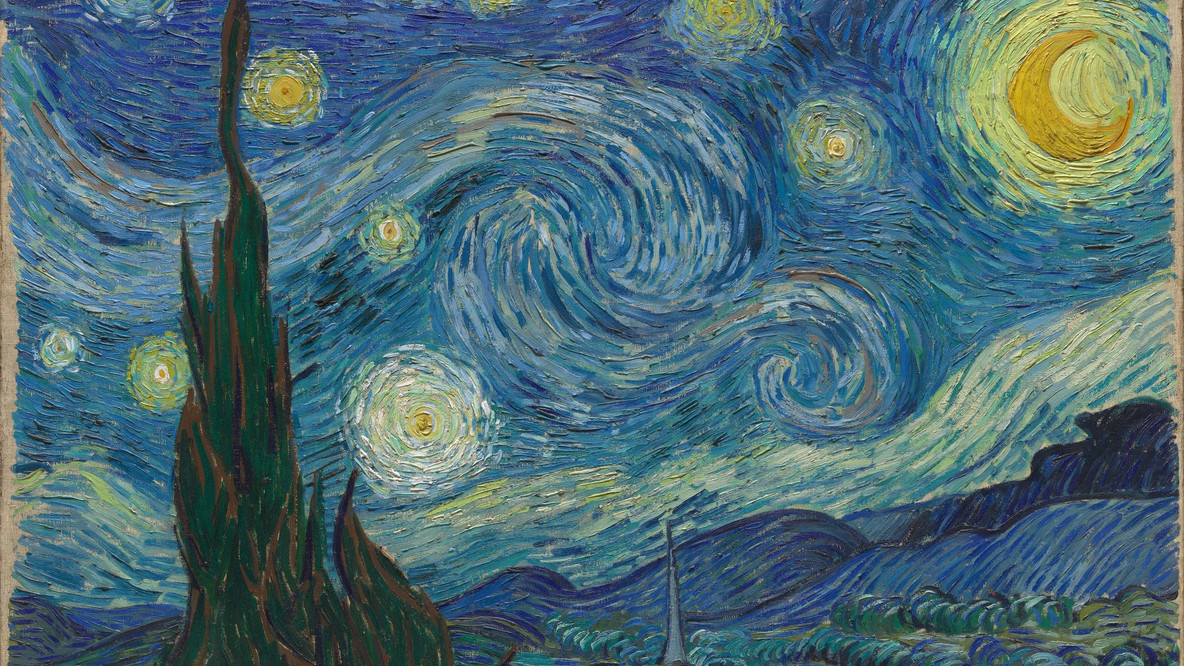

1889
The Starry Night
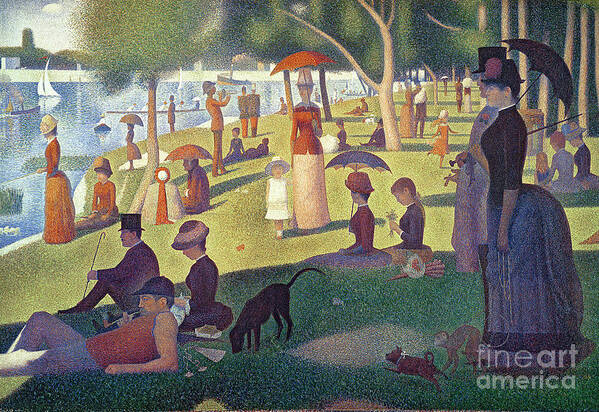
1884-1886
Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte
Georges Seurat

1888
Sunflowers
1884
Art Nouveau

1892
Le Lit,
Toulouse-Lautrec

Alfons Mucha

1889
Eiffel Tower
1889
Exposition Universelle

1886
The Statue of Liberty
Frédéric Auguste Bartholdi, Richard Morris Hunt
The Statue of Liberty was built in France, with construction completed in July 1884. It was then shipped to the United States and assembled on Liberty Island, with the dedication ceremony taking place on October 28, 1886.

1900
Sigmund Freud
The Interpretation of Dreams
Discovery of
Unconciousness

1895-1900
apples and oranges

1897
Where Do We Come From What Are We Where Are We Going
Paul Gauguin
Origin
Paint Tube
Individual
Steam Engine
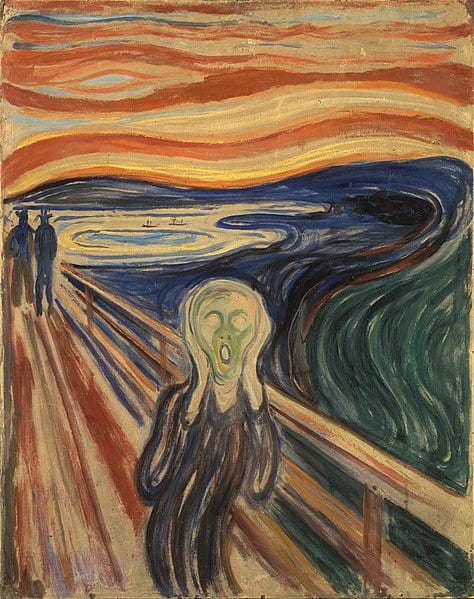

1893
The Scream
Edvard Munch
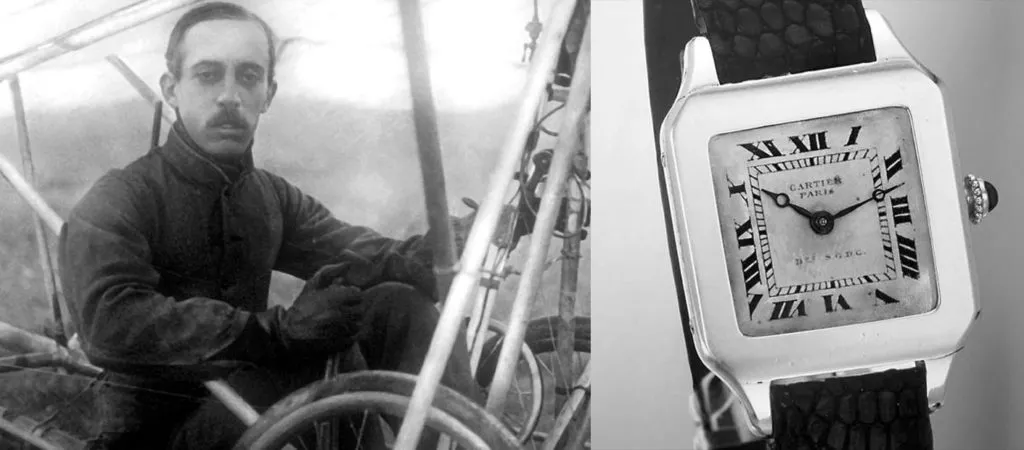

1904
Louis Cartier designed the first wrist watch
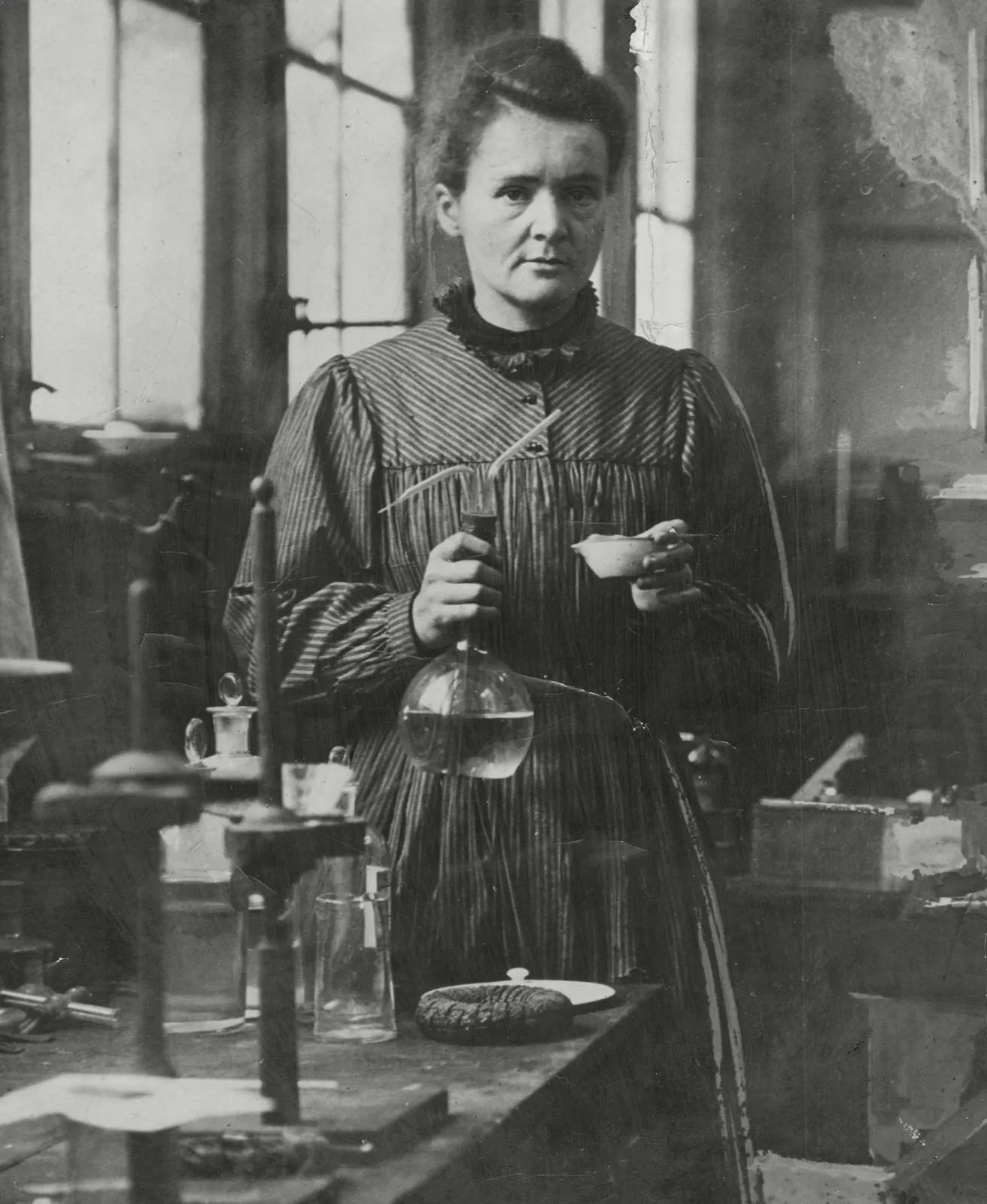

1903
awarded half of the Nobel Prize for Physics
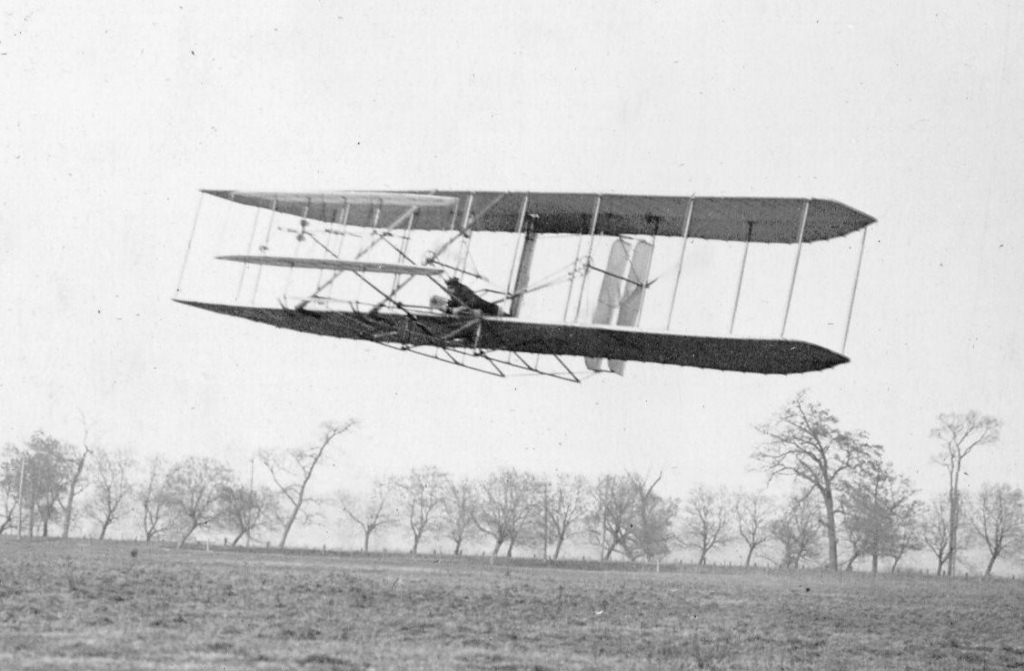
Dec 1903
Wright Flyer
Wright Brothers
1905
Clair de Lune
Debussy
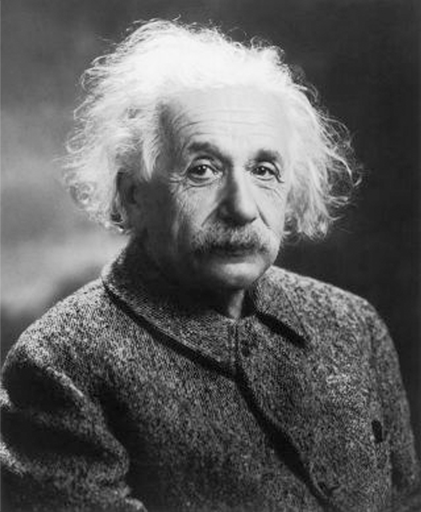
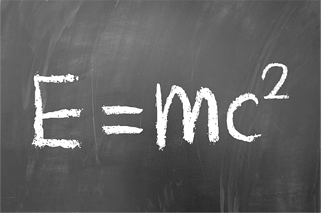

1905
Mass–energy equivalence
Albert Einstein

1907
Group IV The Ten Largest, No.7, Adulthood,
Hilma af Klint
In 1906, she started creating oil paintings showing swirling colourful forms. Although other artists, like Wassily Kandinsky and Piet Mondrian, became famous for pioneering this abstract style, it's likely Hilma was actually doing this a few years before them!
Unconciousness

1897
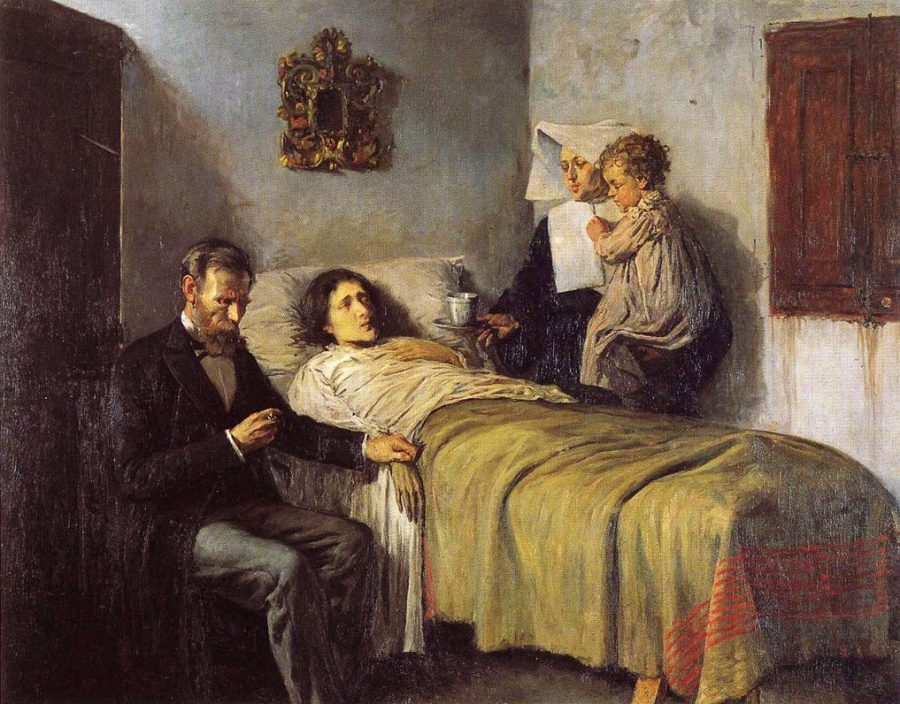
Science and Charity
Pablo Picasso
Assembly Line
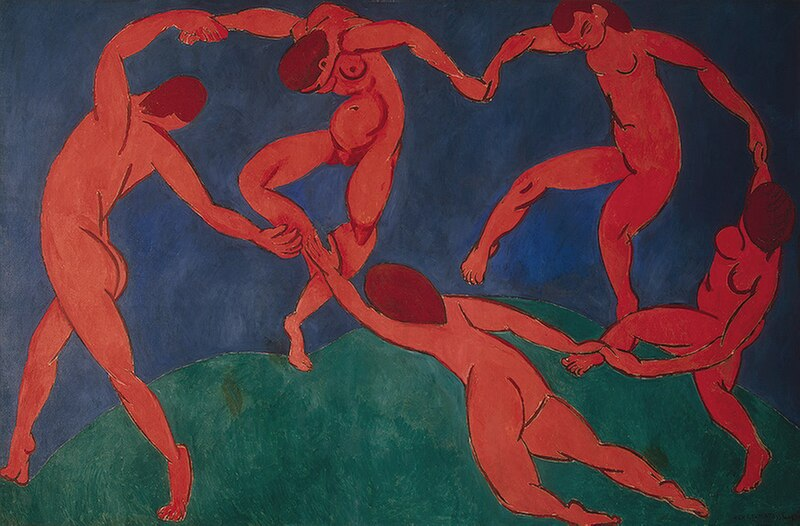
1910
The Dance, Henri Matisse
1904-1910
Fauvism
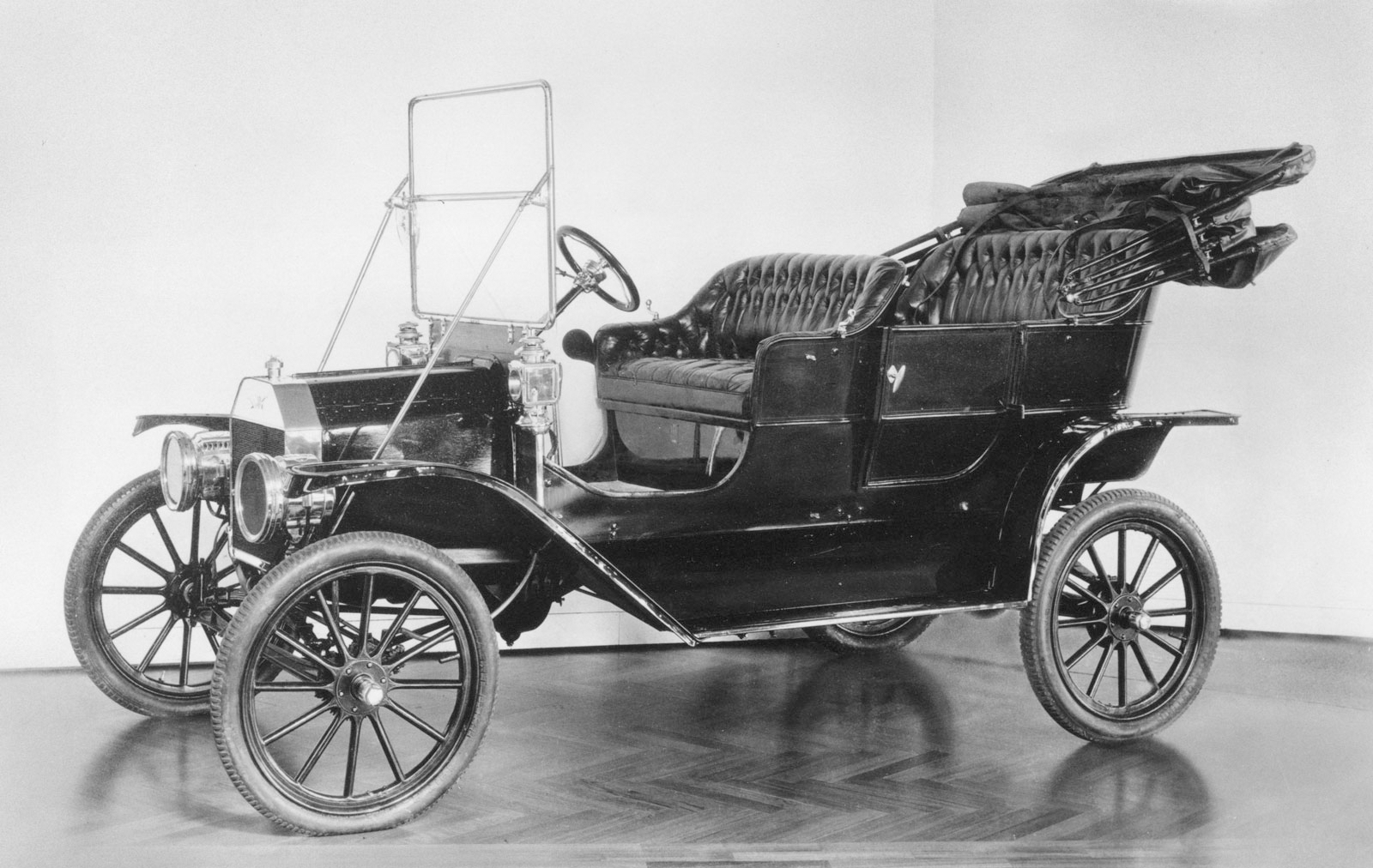

1908
Model-T, assembly line
Henry Ford,
Model - T shortened the travel time.
Gave people fresher produce, better education. also quite a bit of pollution

1910
Art Deco
Art Deco was strongly influenced by the machine age and industrialization, including the advancements in manufacturing and mass production methods like the assembly line.
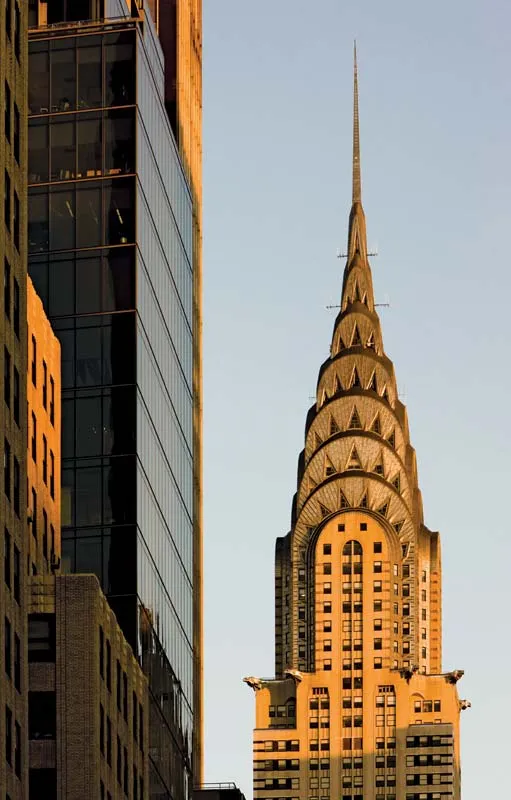

1928
Chrysler Building
Productivity

1907–1908
Gustav Klimt
15-22 million deaths





rise of Fascism
Jul 1914 – Nov 1918
WW1
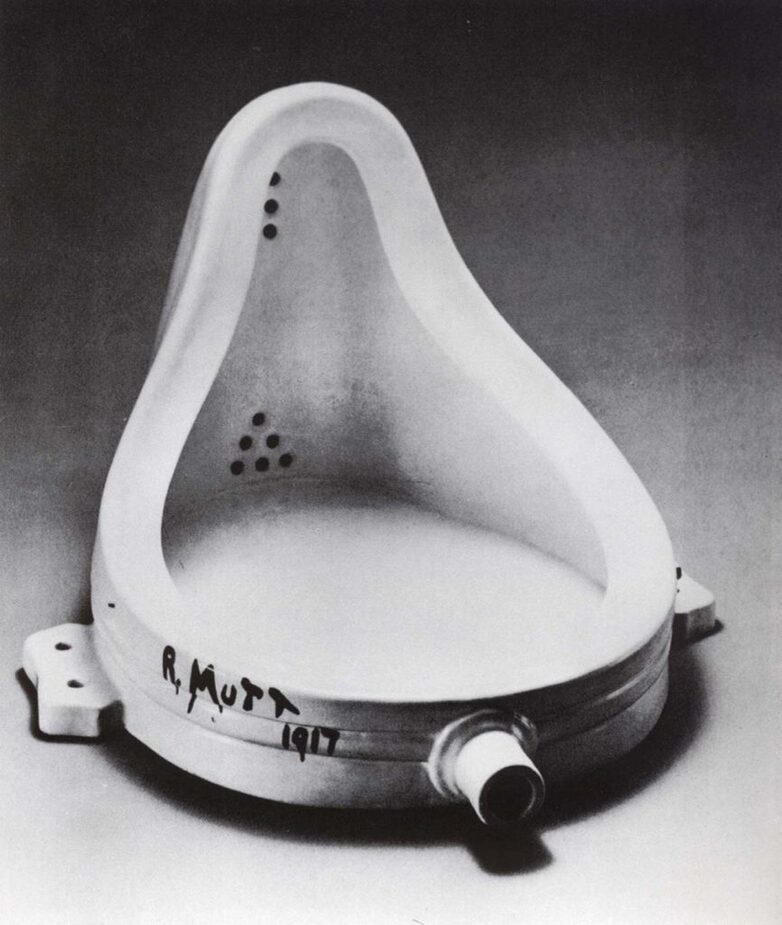


1917
Fountain
Marcel Duchamp,
DADA
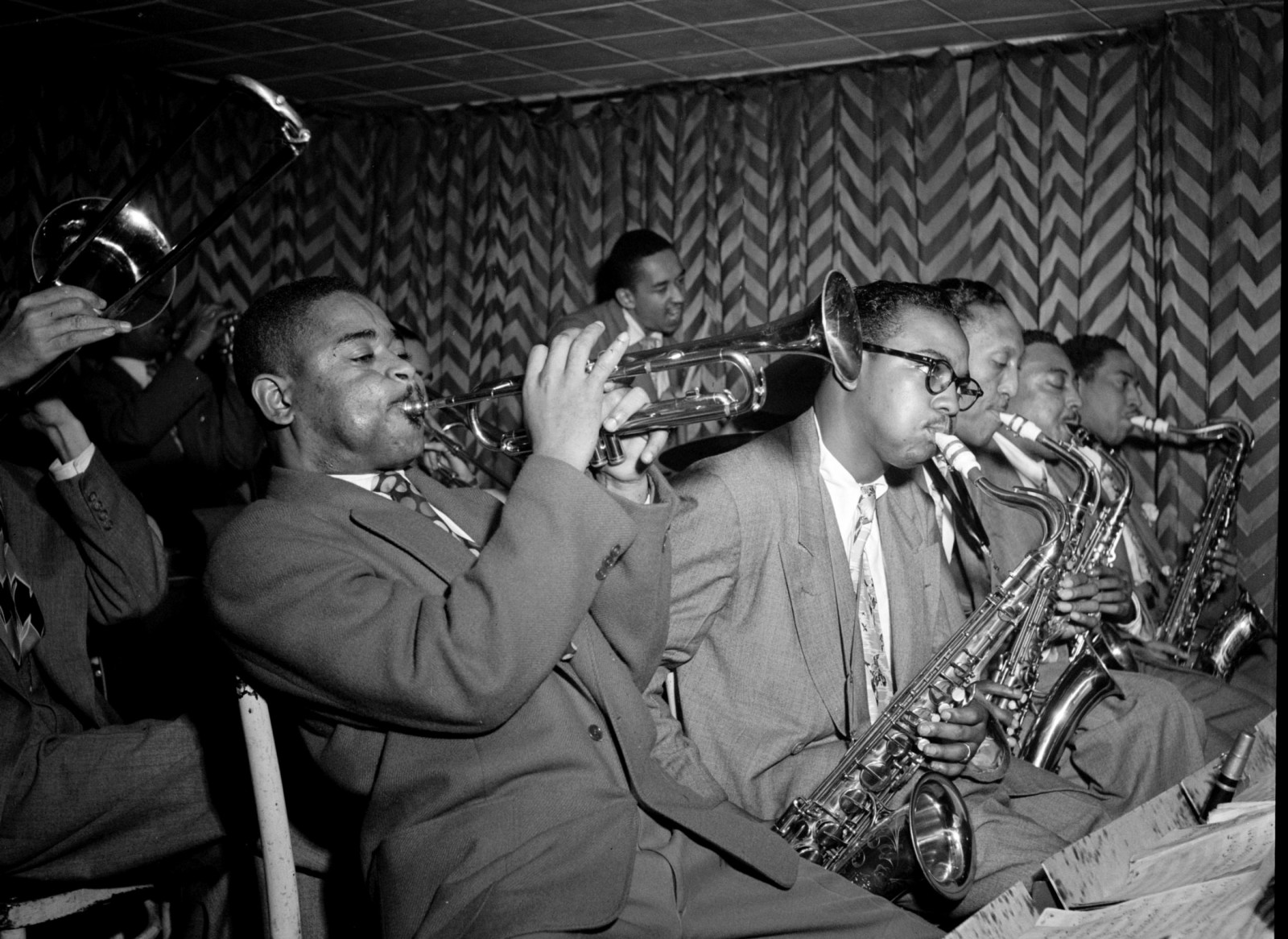

1920s-1930s
Jazz
Jazz music originated in the late 19th and early 20th centuries in New Orleans, Louisiana, within the African American community. It emerged from a blend of various musical traditions, including ragtime, blues, European harmonies, and African rhythmic elements. The confluence of these influences in the diverse cultural landscape of New Orleans created a unique and innovative musical style.
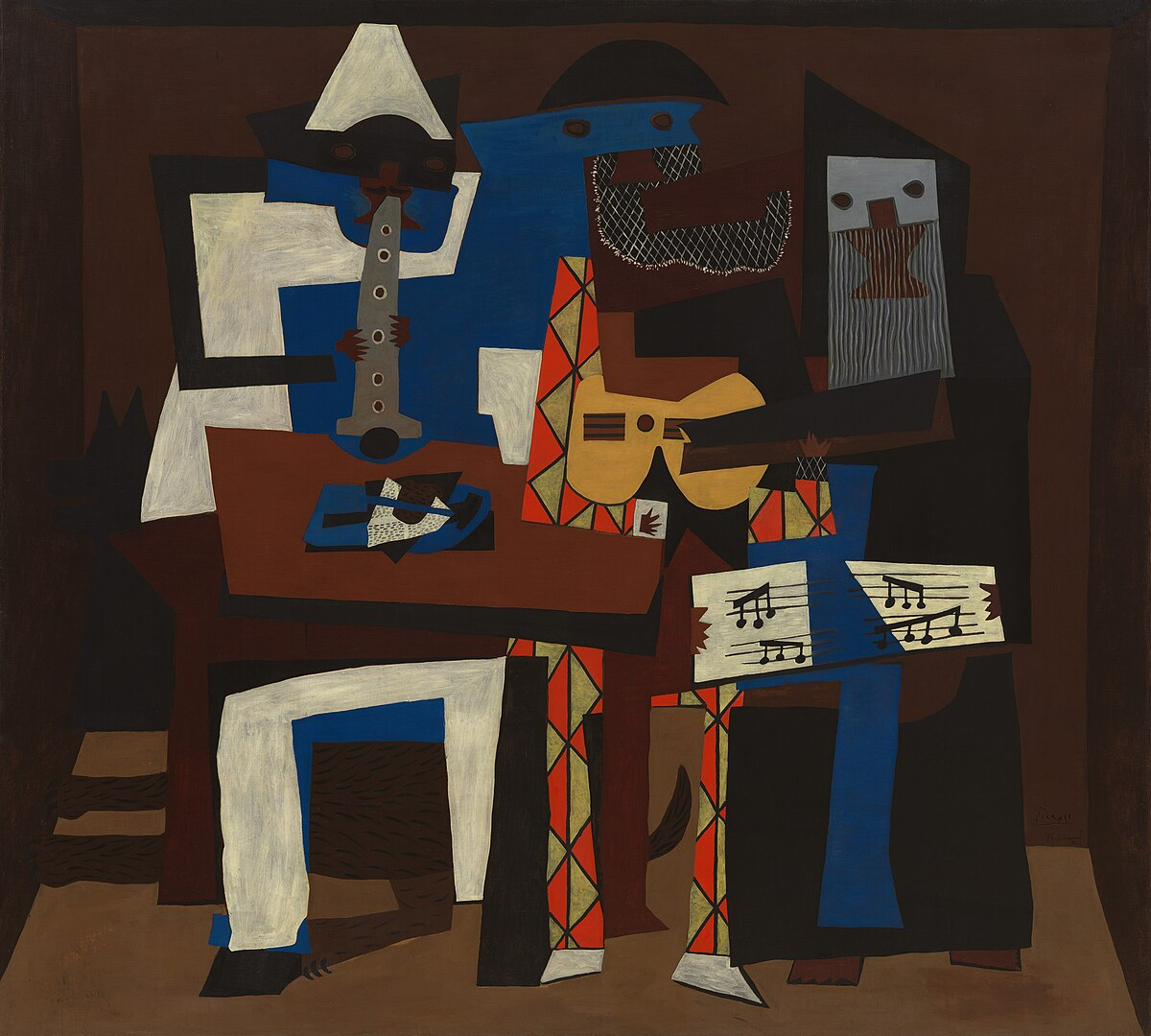

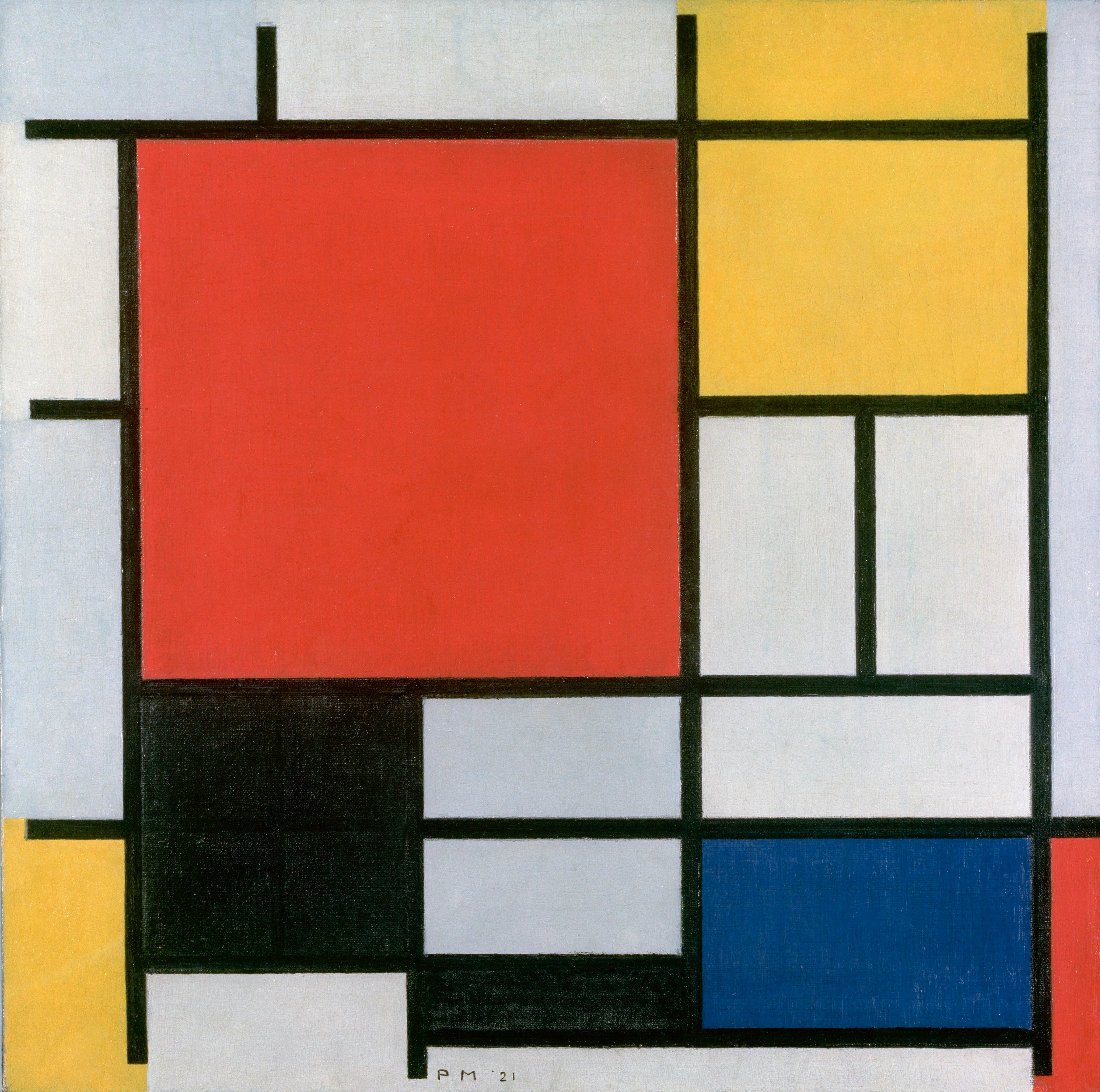
1920
Mondrian

1923
Wassily Kandinsky
1917
Russian revolution
Lenin
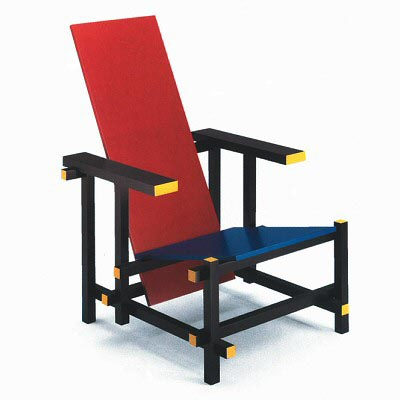

1917
Red and Blue Chair
Gerrit Rietveld
De Stijl
(The Style)

1919-1933
Bauhaus
Modern
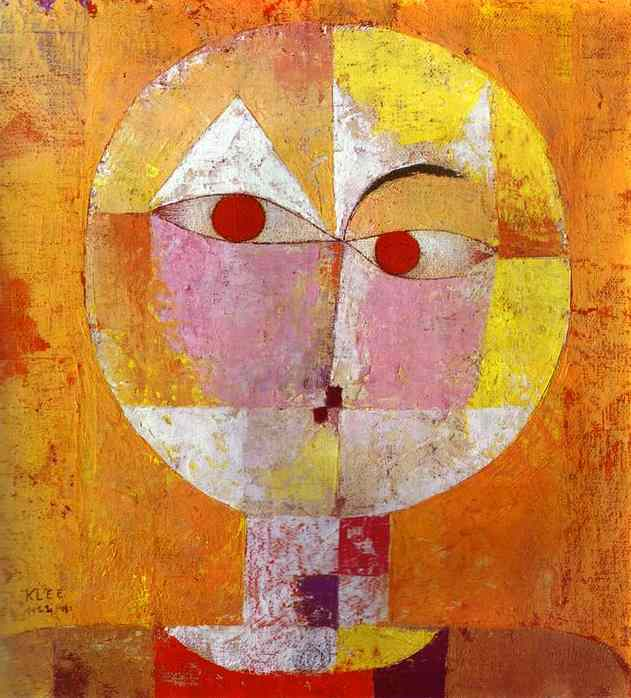

1922
Paul Klee
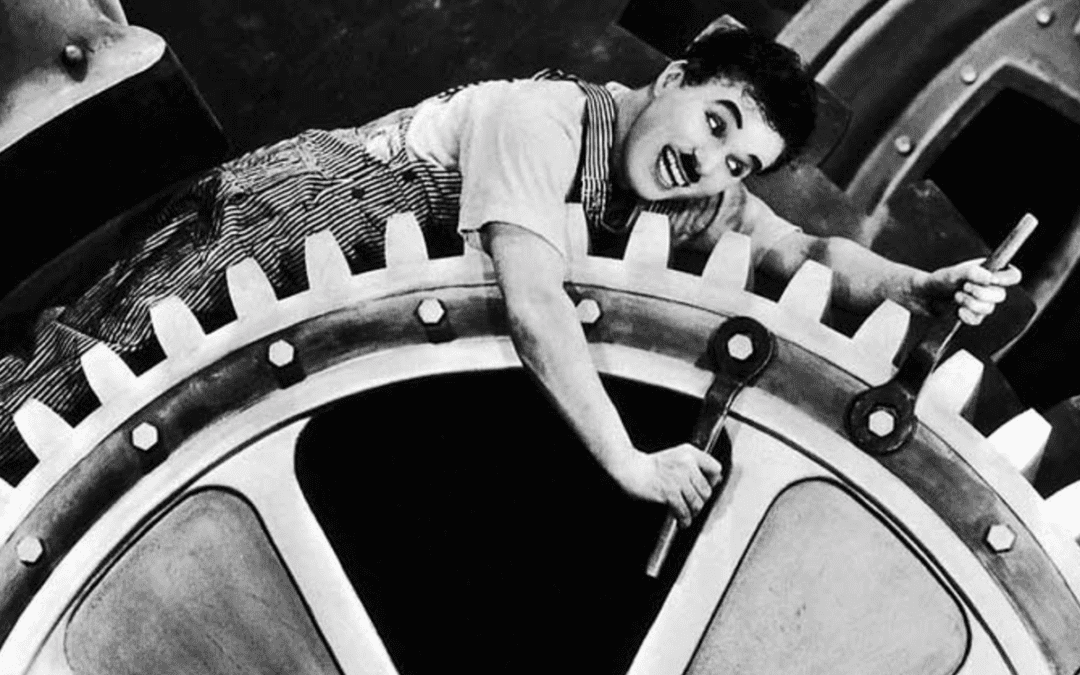

1936
Mondern Times

1937
Guernica
Pablo Picasso

Sep 1932
Lunch atop a Skyscraper
Sep 1932
The "Great Depression"
refers to the severe worldwide economic downturn that began in 1929 and lasted until the 1930s
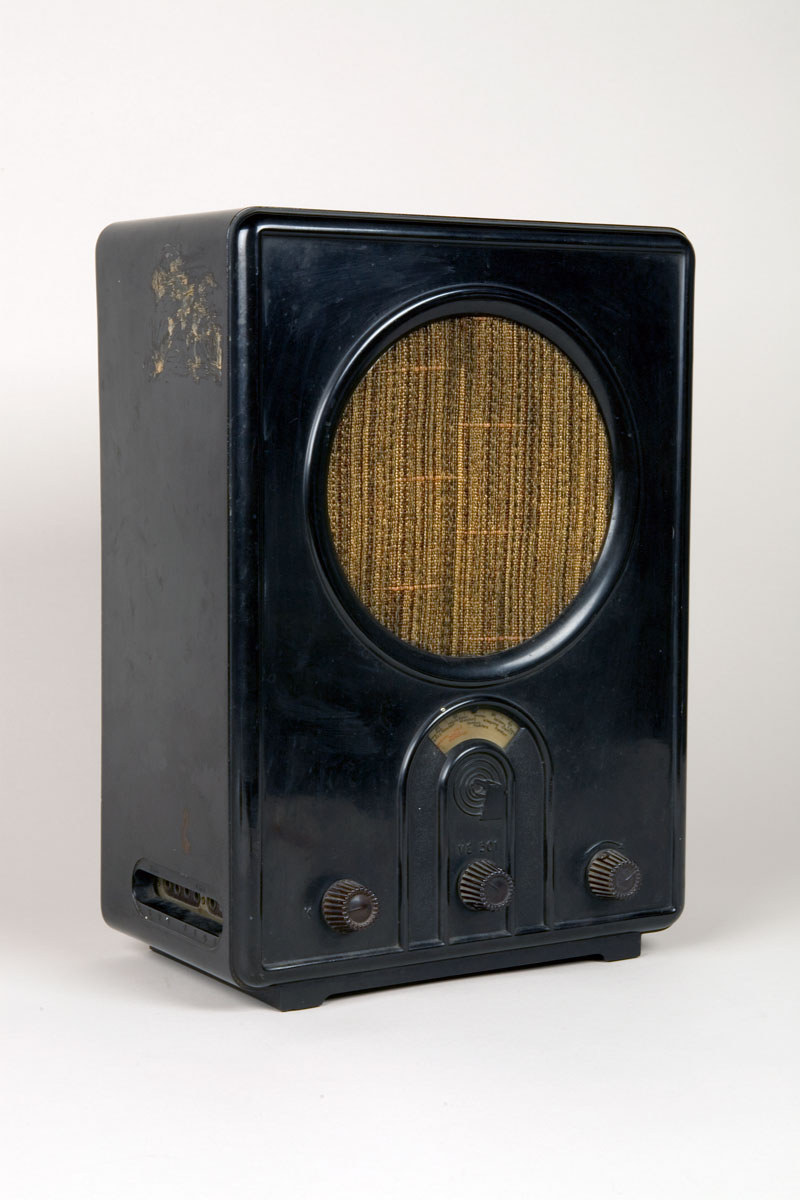

1930s
Golden Age of Radio
1930s were known as the "Golden Age of Radio"

1925
The Great Gatsby
F. Scott Fitzgerald
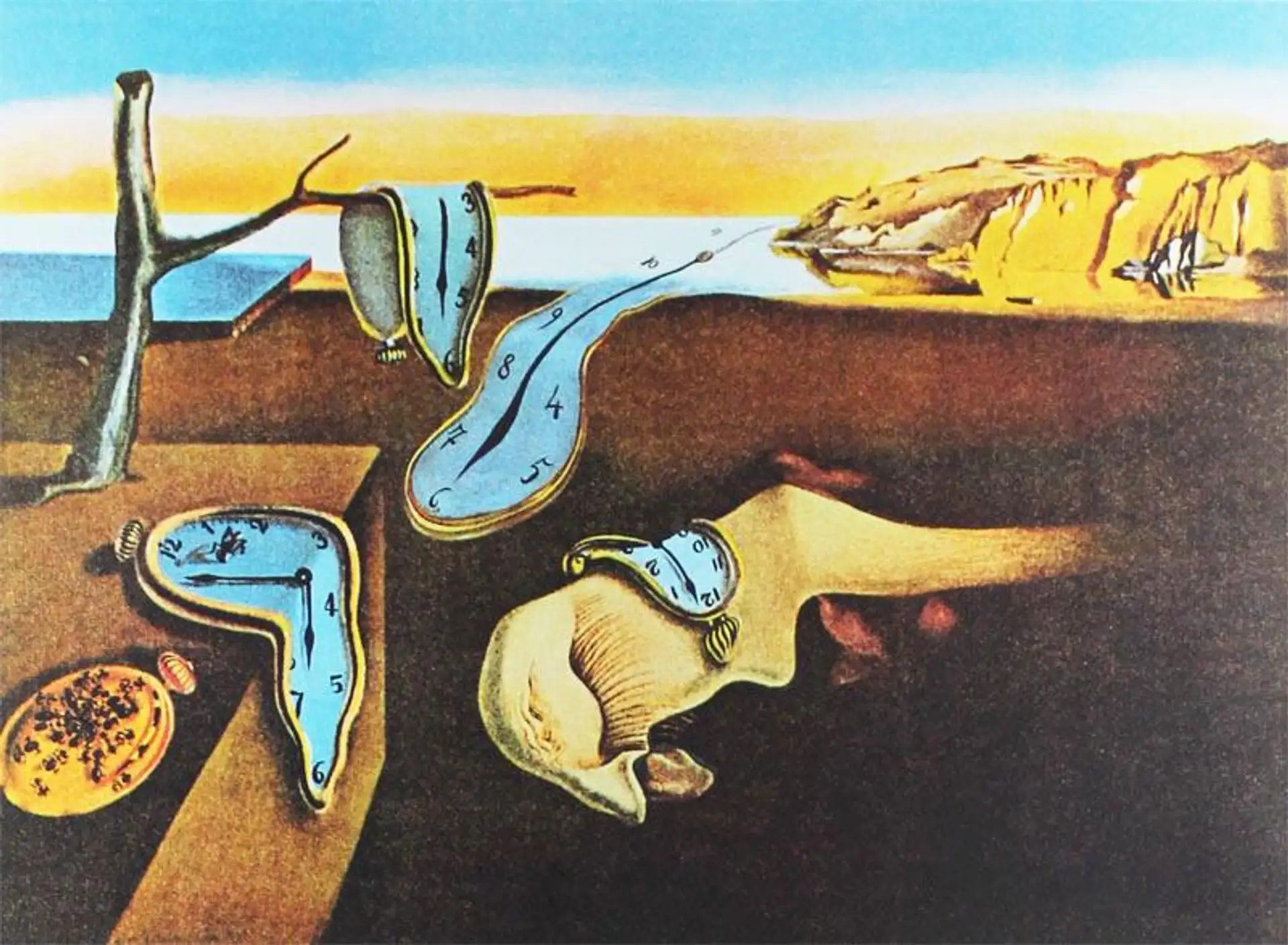
1931
The Persistence of Memory
Salvador Dalí
Unconsciousness
1939-1945
WW2
70 to 85 million deaths
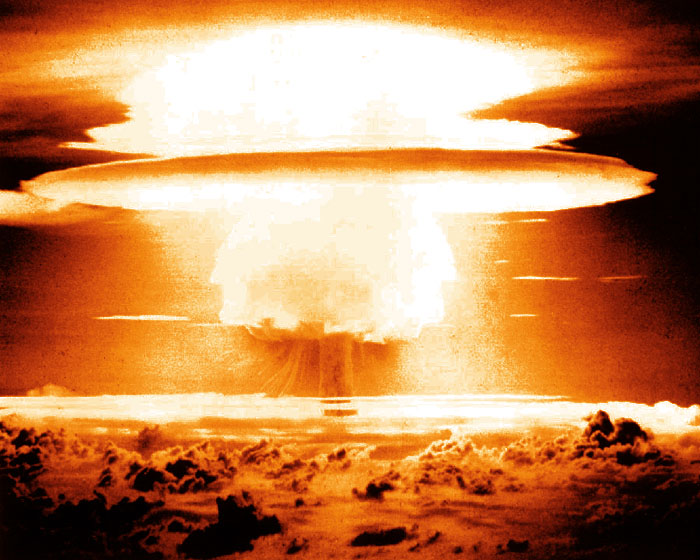

Aug 1945
nuclear bomb dropped
Harry S. Truman, J. Robert Oppenheimer
1950–54
McCarthyism
Joseph McCarthy
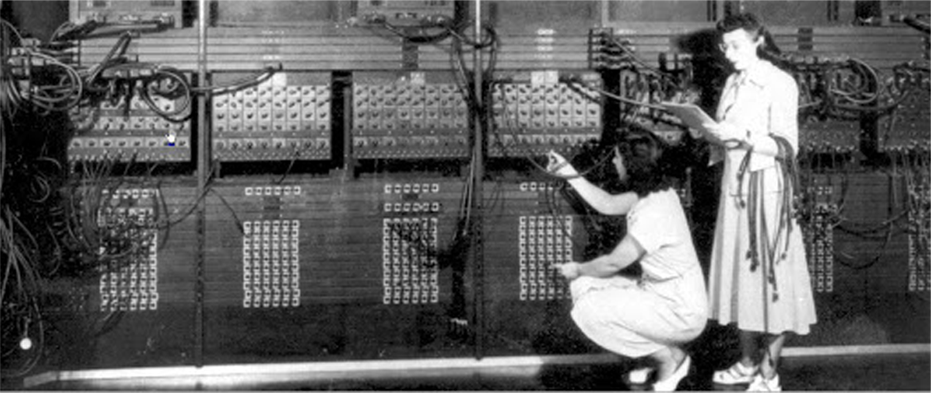
Feb 14, 1946
first computer Eniac
End of WW

1950
Jackson Pollok

1942-3
Broadway Boogie Woogie
Mondrian
1947-1991
Cold War

1950-
1960
Television
for Every households
The period of television "universalization," where it became a widespread household appliance, is generally considered to be between 1950 and 1960 in the United States. While some households had TVs before 1950, by 1960, about 90% of American homes had a television set.

1951
Massacre in Korea 한국의 학살
Pablo Picasso
고야의 “5월3일” 의 구도를 응용하여 제작하였다.
1948
4.3 Jeju Uprising
1950-1953
6.25 korean war
The Korean War, also known as the "6.25 War" in South Korea (referring to the date it began, June 25, 1950), was a conflict on the Korean Peninsula fought between North Korea (supported by China and the Soviet Union) and South Korea (supported by the United Nations, primarily the United States). It lasted from 1950 to 1953.
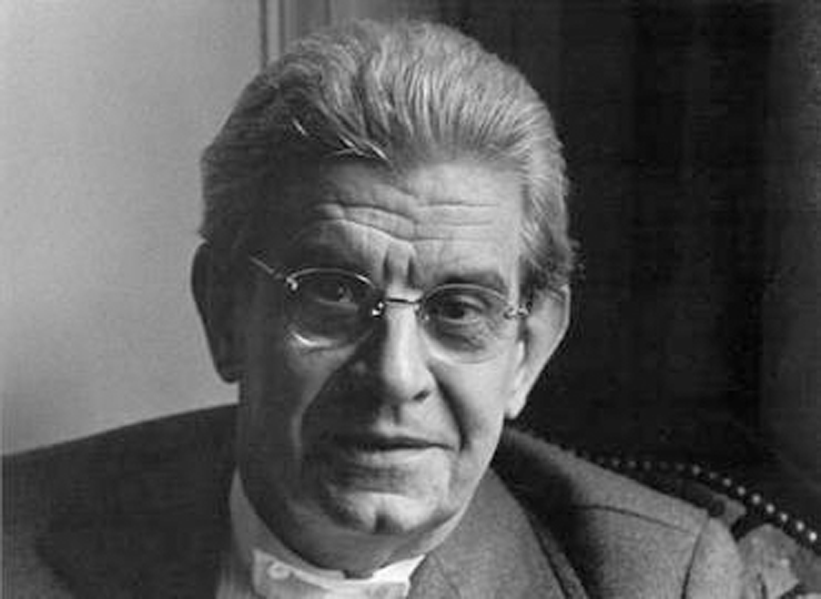

1953-1981
The Four Fundamental Concepts of Psychoanalysis
Jacques Lacan

1962
Campbell's Soup Cans
Andy Warhol

1967
Hippie
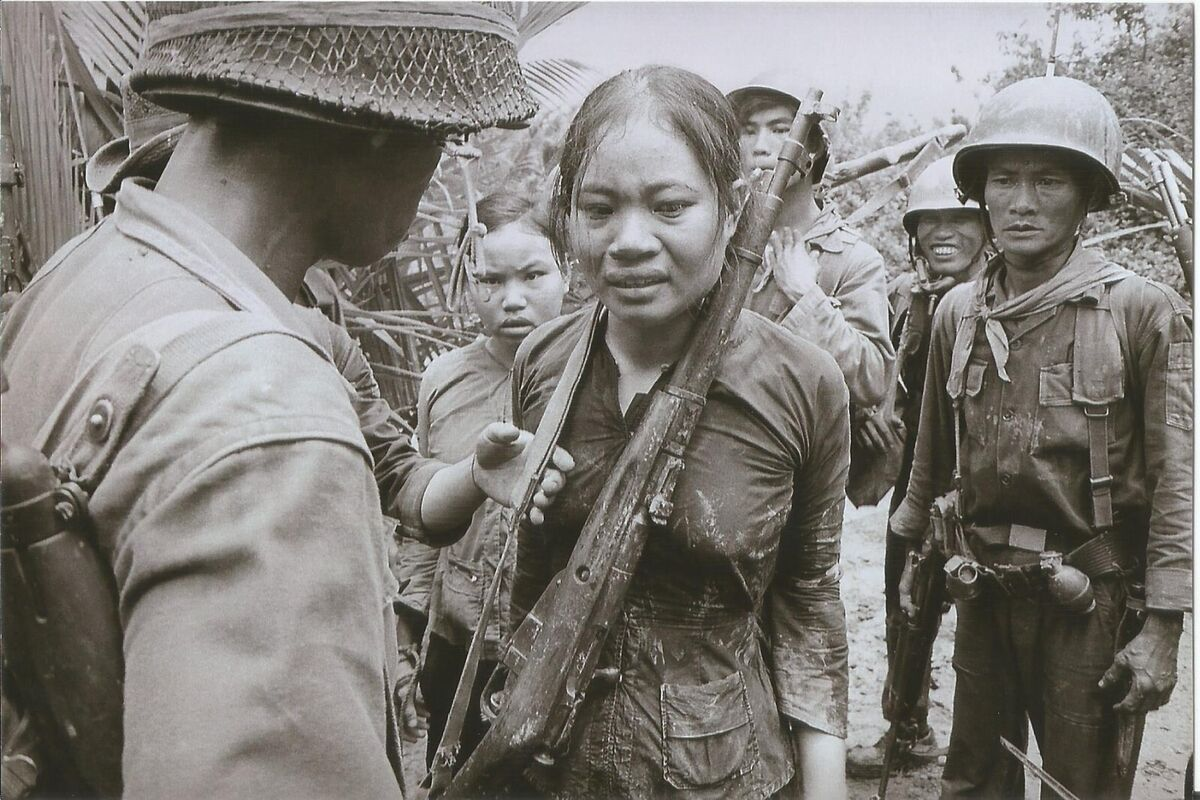

1955-
1975
Vietnam war
The Vietnam War was an armed conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia fought between North Vietnam and South Vietnam and their allies. North Vietnam was supported by the Soviet Union and China, while South Vietnam was supported by the United States and other anti-communist nations.
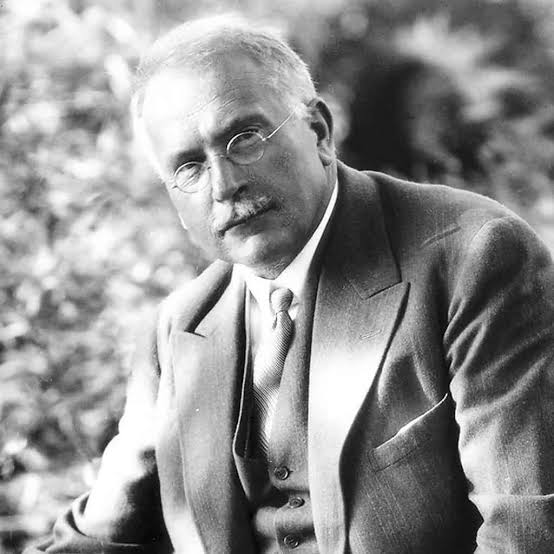

1961
Memories, Dreams, Reflections
Carl Jung

1952
Untitled
Mark Rothko
Television

1963
Whaam!
Roy Lichtenstein
Pop
Post Modern
Globalization
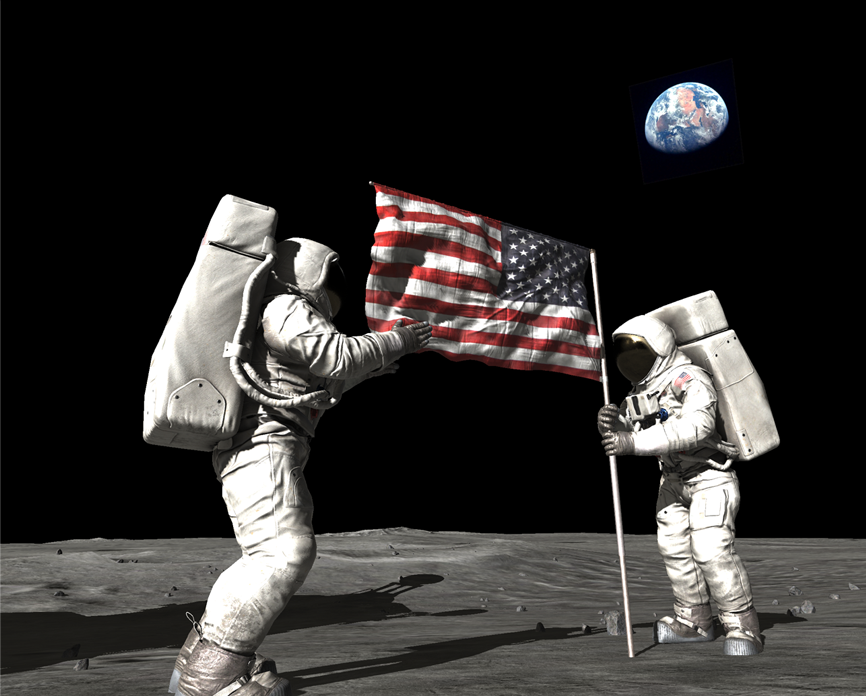
Jul 1969
First step on the moon
1983
Korean Air Lines Flight 007
1975-1979
The Killing Fields
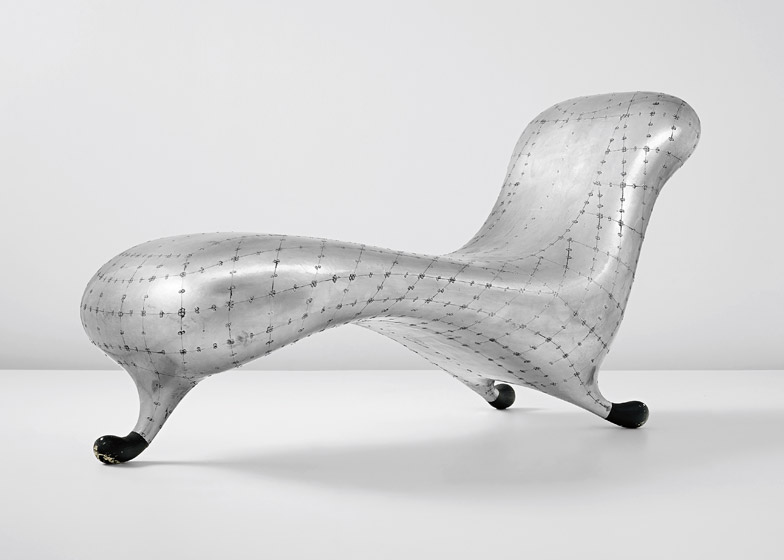

1988
Marc Newson
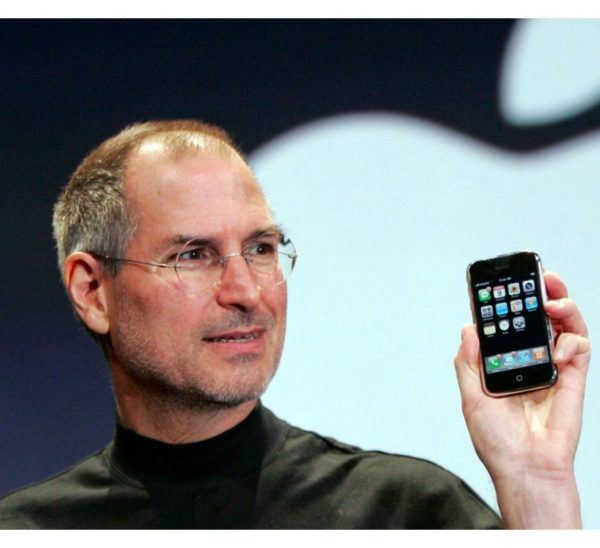

June 29, 2007
iPhone

1967
Death of Che Guevara
Ernesto "Che" Guevara was an Argentine Marxist revolutionary, physician, author, guerrilla leader, diplomat, and military theorist. A major figure of the Cuban Revolution, his stylized visage has become a ubiquitous countercultural symbol of rebellion and global insignia in popular culture.

1982
Untitled
Jean-Michel Basquiat
Untitled is a painting created by Haitian American artist Jean-Michel Basquiat in 1982. The artwork, which depicts a skull, is among the most expensive paintings ever. In May 2017, it sold for $110.5 million at Sotheby's, the highest price ever paid at auction for artwork by an American artist in a public sale. That record was surpassed by Shot Marilyns by Andy Warhol, which sold for $195 million in May 2022.
1968
Protests of 1968
The protests of 1968 comprised a worldwide escalation of social conflicts, which were predominantly characterized by the rise of left-wing politics.
1963
I Have a Dream
Martin Luther King, Jr
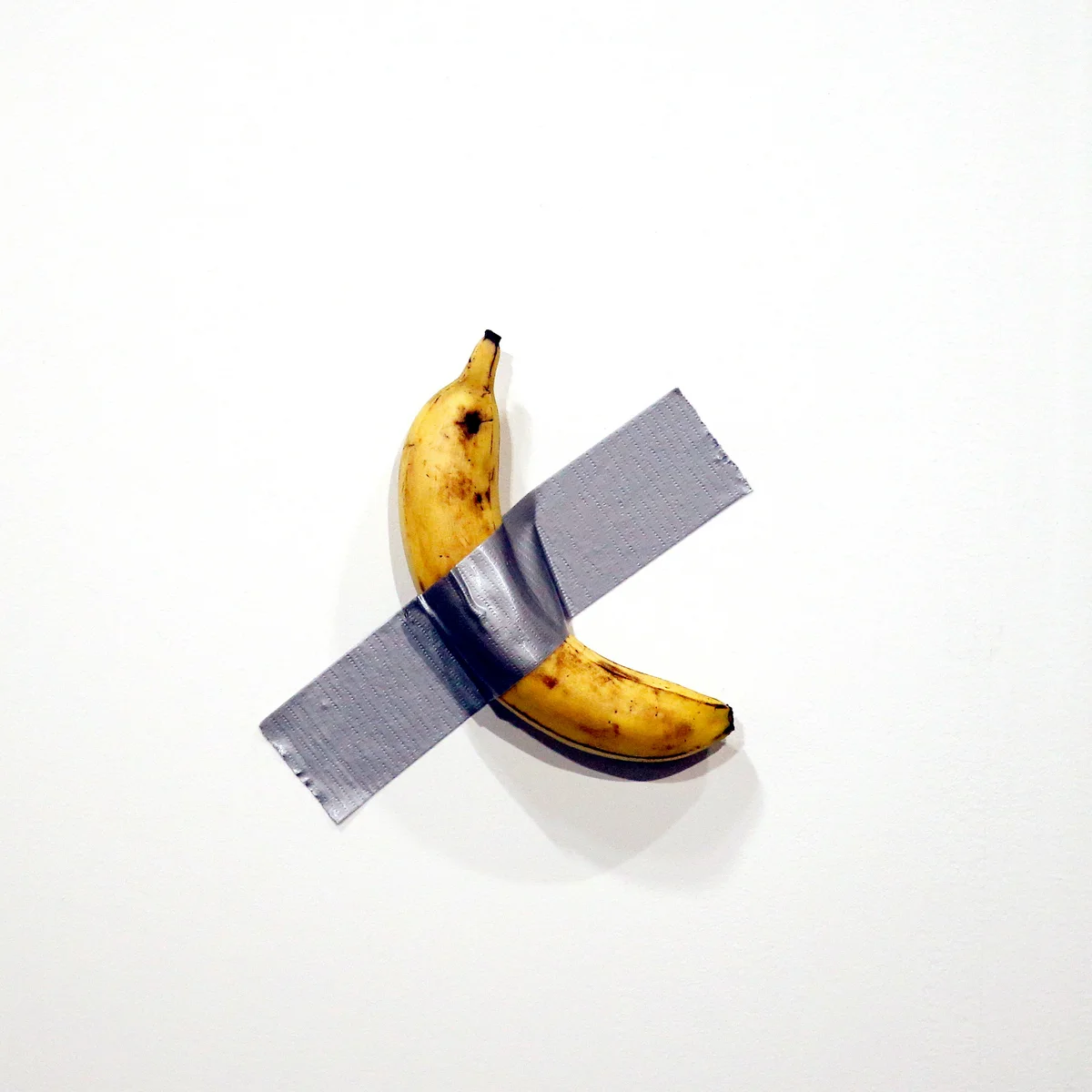

2019
Comedian
Maurizio Cattelan


1985
We Are the World
Michael Jackson and Lionel Richie
"We Are the World" is a charity single recorded by the supergroup USA for Africa in 1985. It was written by Michael Jackson and Lionel Richie and produced by Quincy Jones and Michael Omartian for the album We Are the World.

1988
88 Olympic, Hand in Hand

TECH

1993
Daft Punk

late 1990s
ADSL
ADSL was originally patented in 1988 but took over a decade to start rolling out due to its prohibitive costs. The ADSL rollout began in the late 1990s, primarily in developed countries, and this rapidly accelerated throughout the 2000s.
1991
fall of the Soviet Union in 1991

1963
Please Please Me

1989
Keith Haring

1981
MTV

1953-1981
The Four Fundamental Concepts of Psychoanalysis
Jacques Lacan

1962
Campbell's Soup Cans
Andy Warhol

1967
Hippie

1955-
1975
Vietnam war
The Vietnam War was an armed conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia fought between North Vietnam and South Vietnam and their allies. North Vietnam was supported by the Soviet Union and China, while South Vietnam was supported by the United States and other anti-communist nations.

1961
Memories, Dreams, Reflections
Carl Jung
ctrl+f to search, ctrl+ +or- to zoom
buy me a coffee
Long before recorded history, before stories were written or tools were refined, humans were already painting. Deep inside caves, surrounded by flickering torchlight, they mixed earth pigments and traced images of the world they knew—animals, hunts, and symbols whose meanings we can only guess. Some of these artworks, dating back over 45,000 years, stand as the earliest expressions of imagination ever found. In a time when our ancestors still shared the planet with Neanderthals and Ice Age creatures like giant beavers, saber-toothed cats, and enormous ground sloths.
The Lion Man made of Mammoth ivory
During the Ice Age, art was intimate—tiny figurines, carved stones, and painted walls made in the shelter of caves. These small creations fit the lives of nomadic people who carried their world on their backs. But when the Ice Age ended around 11,700 BC and the Earth grew warmer, everything began to change. People settled, villages formed, and art stepped into the open air. Suddenly, humanity was building vast stone sanctuaries like Göbekli Tepe—our first glimpse of art meant not just to be carried, but to be walked through.
As the Ice Age faded and the world grew warmer, humanity stepped out of the caves and began shaping the land itself. Settlements turned into villages, and villages into the first cities. Art evolved from personal symbols and small carvings into shared monuments that gathered people together. In places like Mesopotamia and Egypt, creativity merged with architecture, belief, and power—temples, statues, and painted walls told stories of gods, kings, and the rhythms of daily life. What began as markings in the dark of a cave became a visual language that built civilizations.
When Christianity became the state religion of Rome, art itself was reborn with a new purpose. The graceful gods and idealized bodies of Greek and Roman art faded into memory, replaced by sacred images meant to guide the soul rather than please the eye. Artists turned from celebrating human perfection to depicting divine truth. Figures grew more symbolic, light became spiritual, and every image carried meaning beyond what was seen. Temples became churches, and art became a bridge between heaven and earth — marking the dawn of the Medieval age.
Ancient Greek and Roman theme fades away until Reneissance
Ancient Greek and Roman theme returns
From the Medieval to the Renaissance
Focus on the afterlife → Focus on the present world
Spiritual values → Material values
Collective-centered → Individual-centered
The Rebirth of Still Life
In the ancient world, still life celebrated the material joys of existence — fruit, bread, glass, and light rendered with pride and pleasure. The Romans saw beauty not only in gods and heroes, but in the simple things of daily life.
During the Medieval era, that vision faded. Art turned its gaze toward heaven, and earthly objects survived only as religious symbols — a lily for purity, grapes for Christ’s blood. The physical world was seen as fleeting, its beauty secondary to the eternal.
With the Renaissance, attention returned to observation and nature. Artists once again found wonder in the tangible world — a study of light, texture, and form became an act of reverence. By the seventeenth century, still life had fully re-emerged, especially in the Netherlands, where tables of flowers and fruit celebrated abundance while quietly reminding viewers of life’s impermanence.
Historical Context — The World Gets Bigger, and Richer
After the Age of Discovery (15th–17th centuries), Europe entered a period of enormous economic expansion:
- Global trade routes connected Asia, Africa, and the Americas.
- Ships brought porcelain from China, silks from the East, sugar and tobacco from the Caribbean, and gold from the New World.
- These luxuries flooded European markets and homes, especially among the urban elite and merchant class — people newly wealthy from trade and colonial enterprise.
This influx of wealth and exotic goods reshaped taste. The aristocracy and upper middle class wanted interiors and artworks that mirrored their opulence, sophistication, and access to global treasures.
The Turning Point: From the Medieval World to the Renaissance
The late Middle Ages were an age of crisis and awakening. In the 14th century, the Black Plague swept through Europe, taking millions of lives and shattering the old order. Faith alone could not explain the suffering, and as people rebuilt, they began to look inward — toward human reason, experience, and creativity. The idea of humanism was born: that the human mind and hand could shape the world as powerfully as divine will.
During the Medieval period (roughly 5th–14th centuries), art was dominated by Christian themes.
- Ancient Greek and Roman mythology, humanist philosophy, and naturalistic representation were largely abandoned or suppressed because they were seen as “pagan.”
- Art’s goal was spiritual teaching, not worldly beauty. Figures became symbolic and stylized, not idealized or realistic.
However, classical influence never vanished entirely:
- Ancient Roman architecture survived physically — ruins, columns, arches — and influenced church building.
- Some Roman texts (especially by Aristotle and Plato) were preserved in Byzantine and Islamic libraries, then reintroduced to Europe later.
- Occasionally, Medieval manuscripts and sculptures would use classical motifs — vines, drapery, mythological figures — but in fragmented or decorative ways, not as core subjects.
So, while the ideas of Greece and Rome dimmed, they were never completely forgotten — they were waiting to be rediscovered.
Giotto and Dante were good friends
As the Middle Ages gave way to the Renaissance, the focus of art turned from heaven to earth. Artists who once painted saints and symbols for faith began to study light, anatomy, and perspective to capture the beauty of real life. Humanity itself became the new subject of wonder. This shift from the collective to the individual brought portraits, human emotion, and curiosity about nature to the center of creativity. In this era, art was no longer just a reflection of divine order—it became a celebration of human potential.
Raphael’s School of Athens (1511) — The Triumphant Return of Greece to Art
- Painted in the Vatican for Pope Julius II, it shows Plato and Aristotle surrounded by ancient philosophers, scientists, and mathematicians — a pure celebration of classical intellect.
- The architecture echoes Roman grandeur — arches, domes, symmetry — reminiscent of the Pantheon.
- Even more strikingly, the painting places philosophical inquiry on equal ground with faith. In the same building, Raphael painted Christian scenes — showing that by the High Renaissance, the Church itself had embraced the classical world as part of divine truth.
So The School of Athens isn’t just an homage — it’s a visual manifesto of the Renaissance worldview: that reason, beauty, and faith could coexist, and that human thought itself was sacred.
A century later, another world-changing event shook Europe — the fall of Constantinople in 1453. The city’s ancient walls, thought to be indestructible, crumbled under the force of Orban’s giant cannon, which required the most refined engineering skills to make at that time. Scholars fled west, bringing with them the texts and knowledge of ancient Greece and Rome. At the same time, people started to realize, engineering can bring down walls that was once considered indestructible.
Artists and thinkers embraced this spirit. Brunelleschi discovered the laws of perspective, giving art a new sense of depth and realism. Leonardo da Vinci studied anatomy, flight, and machinery, merging art and science into one pursuit of truth. And beyond Europe’s shores, advances in shipbuilding and navigation allowed explorers to cross oceans once thought impassable.
Long before silk and spices crossed continents, another stone traveled quietly through Asia—jade. As early as 6000 BC, people of the Hongshan culture carved jade into sacred forms like the coiled dragon, symbols of life, spirit, and celestial power. Jade’s cool luster and near indestructibility made it more than decoration; it was believed to hold virtue and eternity within it. Over centuries, the trade and reverence for jade connected distant regions, forming what some call the “Jade Road”—a precursor to the Silk Road. Through jade, early cultures began not only exchanging goods, but also ideas, beliefs, and artistry that would shape civilizations to come.
With the dawn of farming, people no longer wandered from place to place—they settled, stored harvests, and began shaping clay into vessels. What began as a practical need soon became an art form, with patterns and designs that reflected the rhythm of their new, rooted lives.
In the eighteenth century, after the great voyages of discovery, Europe was awash in color and luxury. Gold from the Americas, silks from China, spices and porcelain from distant seas — the world had become smaller, and its treasures closer. Out of this new wealth and pleasure grew a new style: Rococo.
Where Baroque once spoke of power and faith, Rococo whispered of leisure, beauty, and delight. Walls bloomed with curling shells and pastel swirls; paintings shimmered with silk, pearls, and laughter. Artists like Fragonard and Boucher painted a world of love and play, where the purpose of art was not to preach, but to please.
It was the art of a global age — born from trade, curiosity, and the rising tide of capitalism. But as wealth gathered in palaces and pleasure filled the salons, voices of reason and reform began to stir. By century’s end, Rococo’s golden light would fade, giving way to the clear lines and moral strength of Neoclassicism — a mirror of revolution and a new world to come.
After the French Revolution, crowns fell and with them the old order of art. No longer bound to kings or cathedrals, artists began to paint for themselves — and for the public. The idea of the individual was born: each person, and each artist, a world of their own.
Galleries replaced royal courts, and paintings moved from palaces to cafés. Art became faster, freer, and closer to life. Impressionists like Monet and Renoir captured the shimmer of the moment — sunlight on water, friends in conversation, a passing cloud — as if to say that beauty now belonged to everyone.
In this new age, art no longer served power. It served experience — the fleeting, personal, human truth of simply being alive.
The Industrial Revolution filled cities with smoke and streets with light. Machines roared, trains raced, and the world grew richer — but not for everyone. While one class built empires of steel, another toiled in the shadows: children in factories full of machines and chemicals, families in slums, lives measured by the clock.
Writers like Dickens and Andersen gave them names and stories. Thinkers like Marx and Engels gave them theory and voice. And artists like Millet gave them dignity — the bowed figures in The Gleaners, the silent prayer in The Angelus.
Out of the noise of progress rose a new kind of art — one that didn’t praise power, but asked what it meant to be human in the age of machines.
Invention of paint tube during Industrial Revolution allows artist to paint anywhere. paint tube and steam engine ship combined, artists like Gauguin can even paint on remote islands.
As cities grew denser during the late 19th century, a new problem began to surface — the crisis of the modern mind. The Victorian era brought extraordinary progress in science, technology, and urban life, but it also demanded strict moral restraint. Desire, emotion, and instinct were often suppressed beneath a façade of civility.
Stories like The Strange Case of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde captured this tension — the split between the polished “gentleman” and the repressed self hiding within. Mental illness, meanwhile, was still seen as shameful or even sinful, more often met with moral judgment than understanding.
But as urban pressures grew and cases of psychological distress became harder to ignore, society began to shift. The haunting cry in Edvard Munch’s The Scream (1893) seems to echo this awakening — a visual expression of inner turmoil finally breaking into public view.
Around the same time, Sigmund Freud and early psychoanalysts began exploring the unconscious, marking a new era where the human psyche itself became a subject worthy of study. Munch’s art, filled with fear, longing, and isolation, reflects not only his personal struggle but also the collective anxiety of a world standing at the threshold of modern psychology.
Every culture has told its own origin story — Prometheus shaping man from clay, Athena breathing life into dust. But after Darwin’s Origin of Species, those stories began to tremble. Humanity started to ask new questions about itself — not to the gods, but to nature. In Where Do We Come From? What Are We? Where Are We Going?, Paul Gauguin captures this moment of uncertainty. His painting is less an answer and more a prayer — a reflection of a world caught between myth and modernity.
Freud’s exploration of the unconscious redefined how humans understood the mind—and artists like Salvador Dalí turned those ideas into imagery. (few more scrolls down in year 1931) Drawing on Freud’s theories of dreams and repression, Dalí used his “paranoiac-critical method” to visualize the logic of the subconscious. In his surreal worlds, time melts, identities blur, and desire takes symbolic form. Dalí’s art became a kind of visual psychoanalysis—where Freud’s science of dreams transformed into the poetry of paint.
Technology had always promised progress — faster machines, brighter cities, and a better life. The early 20th century, often remembered as the Belle Époque, glowed with optimism and invention. But when war erupted in 1914, that same technology turned against humanity: machine guns, chemical gas, barbed wire — tools of efficiency became instruments of mass death. Over 15 million lives were lost, and the myth of progress collapsed.
The pursuit of “greatness” — of stronger nations, superior technologies, and dominant empires — revealed its dark underside. Twisted forms of Darwinism and industrial pride began to justify hierarchy and exclusion, devaluing those seen as “lesser.” What began as faith in civilization’s advancement had become a machinery of destruction.
Out of this disillusionment emerged Dada — an art movement that mocked the very idea of meaning, reason, and “greatness” itself. To the Dadaists, traditional culture had failed; logic had led only to slaughter. So they responded with absurdity, randomness, and provocation. Marcel Duchamp’s Fountain — a simple urinal turned into art — was not just a joke, but a mirror held up to a world gone mad. It asked a radical question: if reason and refinement could justify war, perhaps only nonsense could tell the truth.
During the early 20th century, industrialization and nationalism fueled an age that valued collective power and efficiency. These ideals, when combined with authoritarian politics, evolved into fascist regimes that glorified unity, order, and technological progress — but at the cost of individuality and freedom.
This mechanized sense of collective efficiency became the very tool of destruction in World War II, when industrial technology was turned toward mass warfare and genocide — one of the darkest chapters in human history.
In the aftermath, a profound cultural and philosophical shift occurred. The horrors of totalitarian control led many thinkers and artists to question systems that suppressed the individual. The emphasis turned inward — toward the self, personal experience, and emotion as authentic sources of meaning.
From this existential landscape emerged Abstract Expressionism, particularly in postwar America. Artists like Mark Rothko and Jackson Pollock rejected propaganda and realism alike, using abstraction as a means to express the depth and vulnerability of human emotion. Their work wasn’t about depicting the world outside but revealing the inner world within — a human response to a century that had nearly destroyed humanity itself.
Work In Progress
50,000 BC
35,000 BC
15,000 BC
10,000 BC
9,000 BC
5,000 BC
2,600 BC
1,700 BC
1,000 BC
500 BC
200 BC
150 BC
0
500
1,000
1,300
1,400
1,500
1,600
1,700
1,800
1,850
1,900
1,910
1,920
1,930
1,940
1,950
1,960
1,970
1,980
1,990
2,000